Acala Blockchain

Acala is a decentralized finance (DeFi) platform and a layer-1 blockchain built on the Polkadot network. It functions as a liquidity hub within the Polkadot ecosystem, aiming to be the financial backbone for Polkadot and its canary network, Kusama (via Karura).
Core Vision and Role
The main objective of Acala is to make decentralized money possible on Polkadot. It offers dependable, quick, and inexpensive DeFi services to deliver a safe, integrated, and user-focused blockchain ecosystem. With an emphasis on offering cutting-edge liquidity solutions and infrastructure for a range of financial applications, Acala markets itself as a strong and all-inclusive DeFi platform.
Key Offerings and Protocols
Acala’s ecosystem is powered by several interconnected protocols and features:
AUSD Stablecoin (Honzon Protocol):
- The native, decentralized, multi-collateral stablecoin of Acala, aUSD, is soft-pegged to the US dollar. Being the de facto stablecoin for the Polkadot ecosystem is its goal.
- By using DOT, ACA, and other cryptocurrency assets as collateral, users can create aUSD. The stability of the aUSD is guaranteed by the Honzon protocol, which also oversees the collateralized debt positions (CDPs).
- The market value of the cryptocurrency collateral must continuously exceed the loan’s aUSD value since the aUSD is over-collateralized.
- The protocol uses stability fees (interest on aUSD loans) and liquidation procedures to keep its peg. A CDP’s circulating supply is decreased when it is refunded because the matching aUSD is consumed.
- Note: aSEED is Acala’s upgraded asset, which was converted from aUSD and gives investors the option to sell their current holdings or participate in future aUSD treasury growth.
Liquid Staking (Homa Protocol & LDOT):
- Through the Homa Protocol, users can continue to earn staking rewards while preserving the liquidity of their staked assets.
- Using this methodology, Acala’s unique product is called Liquid DOT (LDOT). Users have the option to stake their DOT and get LDOT in exchange, which is the sum of their accumulated prizes and the staked DOT.
- This special asset offers capital efficiency, enabling users to trade LDOT on the DEX, utilize it as collateral in DeFi applications, or employ it in liquidity pools. This solves the traditional staked tokens’ illiquidity problem.
- During Acala’s crowdloan, LCDOT, a token that represented DOT, was locked, offering liquidity.
AcalaSwap (Automated Market Maker DEX):
- Users can exchange tokens directly on-chain with Acala’s integrated AMM-based Decentralized Exchange (DEX), which is comparable to Uniswap.
- It facilitates trading in Polkadot-based assets such as DOT, ACA, and aUSD.
- Users can earn trading fees and other incentives by contributing liquidity.
- In comparison to Ethereum-based DEX platforms, Polkadot’s high throughput allows for tiny gas fees, which make it more affordable.
- With the Polkadot network, it enables native cross-chain trade between cryptocurrencies.
EVM+ Compatibility:
- By supporting the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), Acala enables developers to implement smart contracts built on Solidity.
- Acala EVM+ gives developers who are accustomed to Solidity, Substrate, and Web3 a smooth, full-stack experience by offering deeper integration with Substrate’s native features.
- At the runtime level, this hybrid solution enables access to both native and cross-chain assets (such as DOT, aUSD, PolkaBTC, and XBTC).
- The option to use any token to pay petrol fees is a significant enhancement to the user experience.
Euphrates:
- Euphrates is a platform that distributes liquidity and offers a variety of financial options.
- It enables users to earn ACA and native ecosystem benefits while supporting many protocols with their wealth.
- It offers a strong distribution platform for developers, creating a financially encouraging atmosphere.
Governance:
- Through a decentralized governance paradigm, the community of Acala governs itself.
- Owners of ACA tokens have the ability to vote on and suggest modifications to network settings, enhancements, and other important choices. This guarantees community governance and a decentralized platform evolution.
How Acala Works within Polkadot
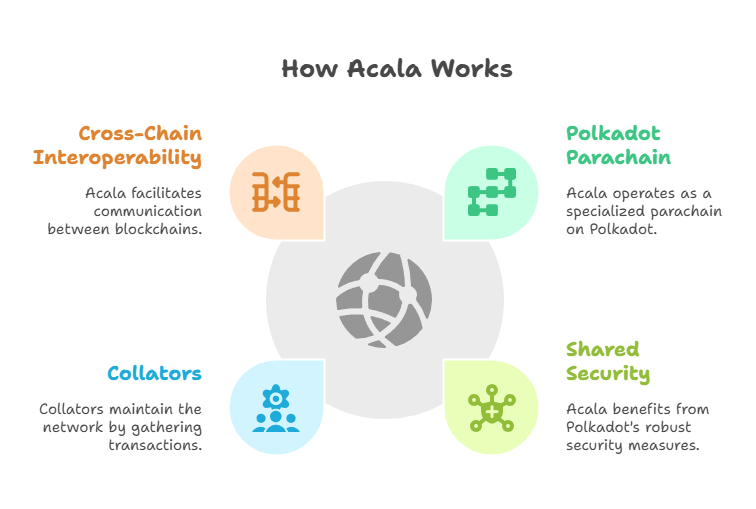
How Acala Works
Acala is deeply integrated into the Polkadot ecosystem:
- Polkadot Parachain: Acala functions on the Polkadot Relay Chain as a specialized parachain. A crowdloan secured its place, making it one of Polkadot’s initial parachains.
- Shared Security: Acala has access to Polkadot’s strong security procedures for block validation and finalization since it is a parachain. All parachains gain from the security of the central Relay Chain to Polkadot’s shared security.
- Collators: These individuals gather user-submitted parachain transactions, compile them into block candidates, and generate state transition proofs for Polkadot validators in order to sustain the network. In contrast to validators, collators are essential to maintaining the parachain but are not in charge of the network’s security, which is handled by the Polkadot Relay Chain itself.
- Cross-Chain Interoperability (XCM): Acala uses Polkadot’s Cross-Consensus Message Format (XCM) to facilitate easy, secure asset transfers and communication between various blockchains that are interconnected inside the Polkadot ecosystem. This improves user engagement across chains and asset utility.
ACA Token (Acala Token)
ACA is the Acala network’s native utility and governance token.
Primary Uses:
- Payment for transaction fees on the Acala network is made using this method. Other tokens can be used to pay fees; these are then burnt after being converted to ACA.
- Governance: Gives token owners the ability to cast votes for changes to the network, modifications to risk, and other development suggestions.
- Liquidity providers, DApp users, and developers enhancing the Acala ecosystem are all encouraged by these incentives.
- For aUSD loans, stability fees and penalties are utilised, as are penalty costs in the event of liquidations.
- Network Security/Stability: In the event of significant “shortfall events” in native Acala protocols, some staked ACA can be used as a contingency asset (e.g., severe collateral drops for aUSD loans). The stability of the aUSD can be guaranteed by automatically diluting and selling ACA to recapitalize the system.
Tokenomics:
- There is a 1.6 billion token limit on the entire ACA supply.
- Acala Network intends to release 100 million ACA a year for a maximum of six years, of which half will be used for staking and the other half for yield farming, DApps, and other projects that increase liquidity.
- In addition to burning 20% of the total amount of network fees, the network routinely uses 1% of any unused emissions each month. By increasing its scarcity and value proposition, these measures may eventually make ACA deflationary.
You can also read What Is A Relay Chain In Blockchain And How It Works
Sister Network: Karura
The sister network of Acala, Karura (KAR), acts as the DeFi hub for Polkadot’s canary network, Kusama. Karura is an EVM-compatible, scalable network that is tailored for DeFi. It offers a platform for testing features and new financial innovations in a real-world economic setting before they are taken into consideration for Acala on Polkadot.
Acala 2.0 (Exodus Upgrade)
For the protocol, Acala 2.0, sometimes referred to as the Exodus Upgrade, is a critical step towards long-term growth and self-sustainability. This upgrade’s salient features include:
- Launch of aUSD Seed (aSEED) for exiting existing positions or securing future growth.
- Introduction of the Universal Asset Hub (UAH) with DApps and liquidity partners focused on LSD.
- Yield farming ACA, LSD project tokens, and DApp tokens to DApp users, liquidity providers, and ACA holders who are engaged in governance and staking.
- Using farming rewards to increase ACA utility, encourage uptake, and increase participation.
History and Foundation
Acala started development in 2019 with funding from the Web3 Foundation. Additionally, it raised more than $8 million by August 2020, to backing from cryptocurrency investment firms including Pantera Capital and Polychain Capital. Officially, the network debuted in 2021. The Acala Foundation was established through a partnership between Polkawallet and Laminar, two Polkadot development organizations.
Significance for Polkadot and DeFi
Acala is vital to Polkadot’s mission since it offers the financial framework that a healthy environment requires. It acts as a centre for liquidity by providing aUSD and LDOT, which other DApps and parachains can use. It allows for inter-chain DeFi methods that transcend single-chain constraints and operate across various blockchains under Polkadot. Features like EVM+ compatibility and gas prices payable in any token reduce the entry barrier for users and developers. Its strong stablecoin, aUSD, is an essential component of any complex DeFi ecosystem.
Advantages and Challenges
Advantages: functions as a Polkadot parachain, carrying over Polkadot’s cross-chain and security capabilities; integrates several DeFi products into a single platform; has decentralized governance; provides minimal fees and high throughput; and is compatible with EVM. It adds EVM as a link between Polkadot and Ethereum, resolving compatibility and interoperability difficulties.
Challenges include the fact that it is still in its infancy when compared to Ethereum-based DeFi, that adoption is contingent upon the expansion of the Polkadot ecosystem, that it is up against competition from other parachains and DeFi platforms, and that stability may be impacted by the price volatility of collateral assets and ACA.
Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Layer-1 blockchain & DeFi platform |
| Built on | Polkadot (as a parachain) |
| Native token | ACA |
| Stablecoin | aUSD |
| Launch | Won a Polkadot parachain slot in 2021 |
| Key products | aUSD, Liquid Staking, DEX, EVM support |
| Governance | Decentralized, token-holder voting |
You can also read What Is Astar Network, Advantages And Disadvantages
