Identity and Access Management Risks Or IAM Risks
Too Many Permissions
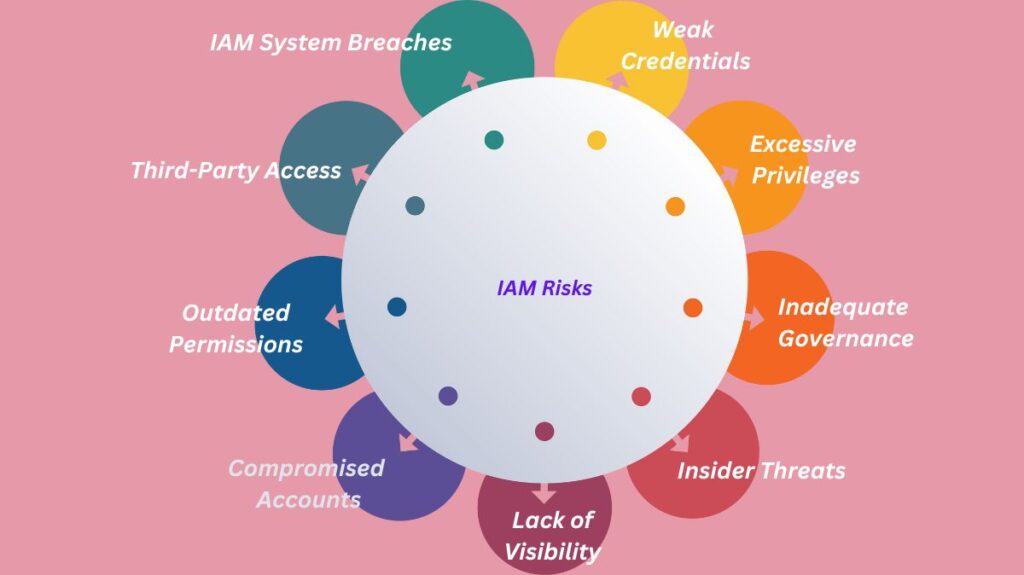
Any rights granted to an identity that are not strictly required to carry out their stated job function are referred to as excessive permissions. This may happen accidentally, or it may be because the person who granted the privilege gave a broad stroke of privilege because they were unsure of how they would use the identity in the future. By adhering to Least Privilege policies, giving identities more precise and targeted permissions, and distributing permissions among several roles, excessive permissions can be prevented.
Inaccurate setups
Identity misconfigurations might include letting unauthorized users or IP addresses log in, leaving datastores or APIs available to the public, not using multi-factor authentication (MFA), not routinely changing access keys, or not controlling data access. One of the main reasons for environmental breaches is misconfiguration. The best way to find and fix any setup errors that put environments at risk is to use Cloud Security Posture Management tools. They operate by keeping an eye on audit activities and logs and comparing them to a safe baseline.
Challenges with Compliance and Audits
Many businesses must comply with industry rules that demand specific security levels, such as HIPAA, PCI DSS, and NIST-800 53. A lot of it is related to privacy and data access. Businesses want a method to guarantee the security of their client and company information. IAM tools aid in controlling this access, stopping nefarious access, and identifying security breaches.
Escalation of Privilege
Attackers may begin with low-level identities and increase their privilege to take on more authority if privilege control isn’t in place. Self-assigning privileges with new IAM policies is one example. Access to an identity with the authorisation iam:CreatePolicyVersion is all that is required for a malicious actor to carry out this exploit. After that, they may simply grant themselves the access credentials they require to carry out their plan by creating a new version of an IAM policy. The only way to prevent this is to have a thorough understanding of each identity’s actual capabilities, or “effective permissions,” and to use a cloud security solution that can identify this risk.
Risks of Multicloud
Multicloud environments are where the majority of large businesses operate. It’s challenging enough to manage and secure identities in a single cloud; adding other environments to the mix only makes matters more complicated. Accounts and even clouds may be affected by identities and their access, which is not always detectable. Having a sufficiently sophisticated IAM mechanism designed for the cloud is essential to preventing breaches since an attack vector to sensitive data may go from Azure into AWS.
Insider Threats and Abuse of Privilege
Attackers value highly privileged identities much and frequently look for them during recon. It’s critical to stop both deliberate and inadvertent abuse of privilege. A person who poses a risk from within your surroundings is referred to as an insider threat. They can take many different forms, such as an employee acting carelessly, forgetting, or maliciously. Although you can’t always stop insider threats, you may try your best to lessen the harm they cause and restrict their capabilities. Refined privilege is crucial in this situation to restrict lateral movement and make decisions like assigning rights to roles with extremely fine-tuned privilege rather than employing root user accounts or admin accounts for routine tasks.
Inadequate Policies and Practices for Access Management
Unless a central IAM solution is in place, teams must manually create security protocols and functionality when new applications are launched. There are several obstacles to these manual efforts. Time and money are frequently limited, so there is little motivation to address data security early and proactively. In the absence of a well-defined procedure, developers might allow more access than is advised. Your identification program and any required remediations can be operationalised with the aid of automation and intelligent workflows.
Risks of Data Access
Any enterprise’s top concern should be safeguarding data and vital applications. A data breach can result in financial penalties, customer backlash, and business disruption or destruction. Data security is directly impacted by inadequate identity and access management.
Offboarding Workers and Orphaned Persons
An important component of any identity governance systems is properly offboarding personnel. Identity permits must be deprovisioned in order to remove actions and abilities, just as they are provisioned during their tenures. This lessens an attack surface and helps stop insider threats in the future. Visibility into cloud-native identities that is, any identities that were developed as offshoots, like roles and role-assignments is one of the major challenges in the cloud. ensuring that you terminate not just the worker but also any personas they developed.
IAM use cases
IAM projects can support a number of use cases in corporate operations, cybersecurity, and other areas.
Digital Transformation
As multi-cloud environments, artificial intelligence, automation, and remote work become more common, businesses must enable safe access to a wider range of resources in more places for a greater number of people.
All of these users and resources, including nonhuman and nonemployee users, can have their access management centralised by IAM systems. Organisations may now manage access for both internal and external users from the same system thanks to the increasing number of IAM platforms that integrate or contain CIAM technologies.
Workplace identity and access management
The typical corporate network consists of a combination of more recent cloud-based apps and services and legacy on-premises systems, and businesses nowadays maintain remote and hybrid workforces. In these intricate settings, access management can be simplified with IAM solutions.
While safeguarding important assets, features like SSO and adaptive access enable users to authenticate with little difficulty. From a single, central IAM solution, organisations can manage digital identities and access control policies for every system. A single source of truth, administration, and enforcement is established for the entire IT environment by comprehensive IAM solutions, as opposed to implementing distinct identity tools for various assets.
Network administration and IT management
Instead of creating separate accounts for each service, IAM systems especially those that support SSO allow users to access numerous services with a single identity. The number of user accounts that IT teams have to handle is greatly decreased as a result. IT management may become easier with the rise of bring your own identity (BYOI) solutions, which let users control and transfer their identities between systems.
RBAC techniques, which automatically allocate user access based on role and responsibilities, can help IAM systems expedite the user permissions assignment process. IT and security teams may define and enforce access controls for all users on a single platform with the help of IAM technologies.
Regulatory compliance
Strict guidelines about who can access data and for what purposes are mandated by standards like as GDPR, PCI-DSS, and SOX. Businesses can establish and implement formal access control policies that adhere to those standards with the help of IAM solutions. In order to demonstrate compliance during an audit, businesses can also monitor user activities.
Data and network security
The Cost of a Data Breach report from IBM lists credential theft as a major cause of data breaches. Overprovisioned accounts with more rights than necessary are frequently the target of hackers. These accounts provide hackers access to large portions of the system, although they are typically less secure than admin accounts.
By introducing additional authentication layers, IAM can help prevent credential-based attacks by requiring more than just a password for hackers to access sensitive data. IAM systems aid in preventing lateral movement, even in the event that a hacker gains access. Users are only granted the permissions they require. While criminal actors and insider threats have restricted capabilities, legitimate users have on-demand access to all the resources they require.
Identity and Access Management vendors
The following is a brief summary of the leading Identity and Access Management (IAM) providers along with their salient features:
- Microsoft Azure AD: Provides SSO, MFA, and Conditional Access; ideal for businesses with Microsoft ecosystems.
- Okta: Perfect for a variety of IT contexts, this vendor-neutral platform has robust third-party interaction.
- Ping Identity: An excellent choice for large-scale operations, this enterprise-grade IAM offers CIAM and API security.
- IBM Security Verify: insights powered by AI for identity governance and compliance.
- ForgeRock: Open-source IAM solutions that are scalable and highly configurable.
- Google Workspace: For companies that prioritise the cloud, Google Cloud Identity offers close connectivity with Google Workspace.
- CyberArk Identity: Pay attention to Zero Trust models and safeguard privileged access.
- SailPoint: sophisticated tools for compliance and lifecycle management.
- Duo Security (Cisco): Zero Trust security and easy-to-use MFA.
- Developer-focused platform with unique IAM features is Auth0 (Okta).
- AWS IAM: AWS infrastructure with smooth role-based access.
- OneLogin: An affordable option for medium-sized companies.
- Strong in intricate identity governance and workflows is NetIQ Identity Manager.
