Learn about the Advantages Of Centrifuge, disadvantages, how it works and history.
What is Centrifuge
A decentralized finance (DeFi) system called Centrifuge serves as the framework for funding blockchain-based real-world assets (RWAs). Its main goal is to unleash liquidity for illiquid RWAs in order to bridge the gap between traditional financing (TradFi) and DeFi. For companies looking for funding and investors looking for steady, uncorrelated payouts, it offers a creative option.
Core Problem Centrifuge Solves
Long loan applications, exorbitant fees, and illiquid assets like invoices are some of the ways that traditional financing frequently hurts small businesses. This is addressed by Centrifuge, which enables companies to fund RWAs directly on-chain without going via conventional banks. At the same time, it provides DeFi investors with steady, yield-producing options that are less correlated with the erratic cryptocurrency markets.
How a Centrifuge Works: Key Components
In order to optimize accessibility and efficiency, Centrifuge uses a particular architecture that combines smart contracts implemented on other chains, most notably Ethereum, with its own proprietary blockchain.
Centrifuge Chain: A Layer 1 blockchain with a specific blockspace and reduced expenses that was created especially for RWA funding. It overcomes the drawbacks of general-purpose blockchains by guaranteeing crucial transaction sequencing and scalability. With the advantages of cross-chain interoperability and common security, it operates as a Polkadot parachain.
Real-World Asset (RWA) Tokenization: Real-world assets are tokenized as NFTs using Centrifuge, producing verified on-chain representations. These NFTs guarantee ownership and validity by connecting to off-chain data and legal records. It supports a wide range of asset types, including real estate, music royalties, and invoices.
Tinlake (The Lending Protocol): The main dApp for Centrifuge is Tinlake, an open marketplace that links investors and asset originators. Tokenised RWA NFTs are used as collateral by businesses to construct “asset pools” into which investors contribute liquidity. Investors receive a return on their capital when they use stablecoins like DAI.
- DROP Tokens (Senior Tranche): These are the senior tranche, which provides investors with more consistent, predictable returns at a lower risk. DROP holders are shielded from “first loss” in the event that any of the asset pool’s borrowers default. Within the protocol, this structure offers a safe investment choice.
- TIN Tokens (Junior Tranche): These are the junior tranche, which carries a higher inherent risk but offers greater potential profits. As a risk buffer for DROP holders, TIN holders take on the “first loss” in the event that there are any pool defaults. Within DeFi, this tiered structure produces a conventional capital stack.
Evolution to Centrifuge V3 and EVM Compatibility: Centrifuge is working to broaden its EVM compatibility by extending its fundamental features. On Ethereum, the CFG token already functions as an ERC-20. Users will be able to invest without bridging assets if liquidity pools are directly deployed on well-known EVM chains, greatly increasing accessibility.
On-chain Fund Management: For the purpose of onboarding credit funds onto public blockchains, Centrifuge offers a fund management platform. With real-time on-chain data, performance tracking, and sophisticated reporting, this simplifies institutional fund operations. For institutional capital, it improves operational excellence, security, and transparency.
The CFG Token
Centrifuge Token, or CFG, is the Centrifuge protocol’s native utility and governance token, which is crucial to its decentralized functioning and expansion.
Governance: By casting votes on proposals, CFG holders take an active part in on-chain governance. This gives them the ability to oversee the Centrifuge Protocol’s progress firsthand. It guarantees really decentralized authority over its development and strategic choices.
Transaction Fees: For all transaction fees paid on the Centrifuge Chain, CFG is the accepted currency. This gives the token a basic purpose and guarantees the network’s long-term viability.
Rewards and Incentives: Early participation is encouraged and the protocol’s continued development is financed using CFG tokens. In order to promote network health, rewards are given to organisations that carry out essential network tasks including chain security and transaction validation.
Staking: To support network security and gain benefits, CFG can be staked. Stakers assign CFG to validators that handle transactions and uphold the network’s integrity in order to accomplish this through a Nominated Proof-of-Stake (NPoS) consensus method.
Bridging: As an ERC-20 token, CFG may be easily integrated into the Ethereum network. The Centrifuge Chain and the larger Ethereum ecosystem can communicate and transfer assets with ease with this capacity.
Security: The Centrifuge Chain itself is inherently secured by CFG. By guarding against malicious behaviour and preserving a trustworthy environment, spiked CFG collateral guarantees the network’s dependability and integrity.
Advantages of Centrifuge
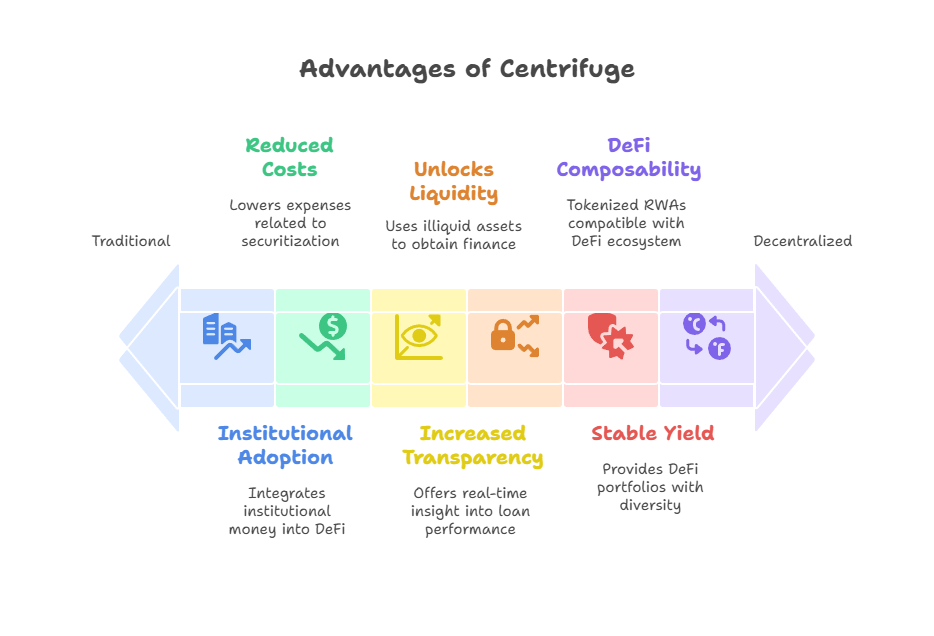
Unlocks Liquidity for RWAs: With Centrifuge, companies may use their illiquid real-world assets to obtain finance in an innovative way. It avoids the difficulties and exorbitant expenses that are typically connected to banking intermediation. This makes capital more accessible to all.
Stable Yield for DeFi: DeFi investors have access to alluring yields that are less affected by the erratic swings in the cryptocurrency market. Since their returns are based on actual, observable economic activity, they provide DeFi portfolios with an essential diversity element.
Increased Transparency: RWA tokenization on a public blockchain offers previously unheard-of asset transparency. Compared to TradFi, investors benefit from real-time insight into loan performance and collateral details, which increases trust and lessens information asymmetry.
Institutional Adoption: In order to integrate institutional money into DeFi, Centrifuge is actively developing compliance infrastructure. Notable alliances include those with companies like Janus Henderson and BlockTower, as well as the tokenization of the S&P 500 Index through the S&P Dow Jones Indices.
DeFi Composability: The purpose of tokenized RWAs is to be compatible with the larger DeFi ecosystem. They can be used in new financial primitives, sold on decentralized exchanges (DEXs), or used as collateral in other lending protocols.
Reduced Securitization Costs: Centrifuge drastically lowers the expenses related to securitization procedures. For instance, BlockTower demonstrated notable efficiency gains by tokenizing a $220 million credit fund directly on Centrifuge, resulting in a remarkable 97% reduction in securitization expenses.
Centrifuge Challenges
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating intricate and dynamic legal and territorial regulatory hurdles is necessary when tokenizing a variety of real-world assets. For the protocol, maintaining complete compliance across many international contexts is a constant issue.
Trust: Building and sustaining investor trust that the tokenised assets accurately reflect legitimate, legally enforceable claims is a basic difficulty. Strong due diligence and clear legal frameworks for off-chain assets are necessary for this.
Competition: Centrifuge works in the RWA DeFi industry, which is becoming more and more competitive. Real-world assets are also the focus of other protocols like Maple Finance (an institutional lender) and MakerDAO (which employs RWA as collateral).
Centrifuge History and Partnerships
Project Evolution: In 2017, Martin Quensel and Lucas Vogelsang founded Centrifuge. Centrifuge OS for supply chain finance was the first idea in 2018, and it was later expanded to Real World Asset (RWA) DeFi. From TradFi to DeFi, the idea of business papers as NFTs remained central.
Chain Migration & Token Rebranding: The Centrifuge Chain itself switched from being a Proof of Authority Ethereum sidechain to operating as a Nominated Proof-of-Stake consensus Polkadot parachain. In 2020, the native token’s name changed from RAD to CFG to reflect these advancements.
Key Partnerships
Centrifuge has formed important alliances to achieve its goals:
- MakerDAO: Permits Tinlake assets to serve as collateral, adding non-crypto assets to DAI’s support for greater stability.
- Ave: Perspectives The efforts of Centrifuge in promoting RWAs as an essential component for growing the RWA industry and DeFi accessibility.
- S&P Dow Jones Indices (S&P DJI): Worked together to enable the first tokenised S&P 500 Index Fund (Janus Henderson Anemoy S&P 500 Index Fund) by launching on-chain proof-of-index infrastructure.
- BlockTower Capital: Supports Centrifuge’s initiatives to create efficiencies and democratise access in the securitisation sector, as demonstrated by their 97% cost reduction.
- Janus Henderson: Partnered with Centrifuge to integrate institutional collateral pools into the DeFi ecosystem and provide a $1 billion AAA CLO strategy to the blockchain.
Centrifuge’s overall goal is to bridge the gap between the traditional and decentralized financial sectors by bringing the massive structured credit market on-chain, so creating a more transparent, inexpensive, and infinite financial system.
Summary Table
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | DeFi protocol for real-world assets |
| Built on | Polkadot (parachain), also bridges to Ethereum |
| Main Product | Tinlake lending platform |
| Native Token | CFG |
| Launch | Parachain slot won in 2021 |
| Use Cases | Financing invoices, real estate, royalties, and more |
| Key Innovation | Tokenizing RWAs as NFTs & using them as collateral |
