History and Evolution of Blockchain Technology
Cryptography and distributed systems research have supported blockchain technology for decades. Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta pioneered digital document timestamping with a cryptographic chain of blocks in 1991. Merkle trees were invented in 1992 to properly manage large amounts of data. Additionally, digital money notions like Szabo’s 1998 bit gold proposal emerged. Bitcoin and blockchain use e-cash and distributed technology.
Satoshi Nakamoto’s 2008 book “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System” popularized the idea. The paper portrayed the structure as a chain of hashed timestamps that integrated each other in their hash, instead of “blockchain”. Bitcoin’s initial block, Block 0, was created by Satoshi Nakamoto in 2009. The first block mentioned the January 3, 2009 Times headline.
Satoshi Nakamoto worked on Bitcoin until his 2011 disappearance. “Blockchain” supplanted “chain of blocks” as the popular term.
Many generations have been identified in the evolution of blockchain technology:
You can also read Cloud Computing Tutorial
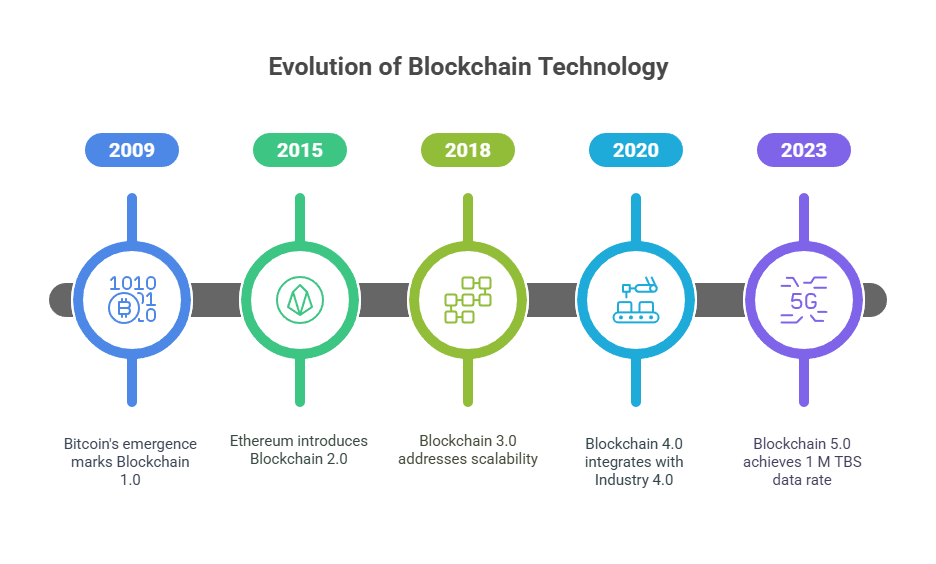
Blockchain 1.0: Most people think of Bitcoin as belonging to this generation. Financial applications including transaction verification and peer-to-peer digital currency transfers were its main focus. Its consensus procedure was complicated and energy-intensive.
Blockchain 2.0: Vitalik Buterin’s 2013 project, Ethereum, premiered in 2015. Ethereum created a programmable blockchain network that ran programs. Decentralized apps (DApps) that went beyond simple value transfer were made feasible by the massive adoption of smart contracts, which are written in languages like Solidity. When transaction processing surpassed Bitcoin, Blockchain 2.0 platforms like Ethereum faced challenges with scalability, energy consumption with its initial Proof of Work algorithm (Ethash), and efficiency (transactions per second).
Blockchain 3.0: The objective of this generation was to address the issues of 2.0, particularly those related to scalability and the challenge of implementing smart contracts. During that time, tools like DApps gained prominence. It was seen to not fully embrace new technologies for broader industrial application, and it still had issues with consensus processes related to smart contracts. Blockchain 3.0 may enable platforms to achieve data rates of hundreds of TBS.
Blockchain 4.0: In order to better align blockchain with Industry 4.0, this generation focused on connecting blockchain with advanced technologies like AI and HCI. It was a significant step forward to support interoperable blockchains, or cross-chain transactions, which allow communication across many platforms. The advantages were increased scalability and better transaction rates.
Blockchain 5.0: The latest technology is designed to benefit government, healthcare, and finance. Innovations boost security, efficiency, and dependability. A 1 M TBS data rate, energy efficiency, and cross-chain capability distinguish this iteration from prior generations.
These generations show blockchain technology’s ongoing endeavour to expand its application, scalability, and flexibility beyond cryptocurrencies.
Also follow blockchain using Gartner’s Hype Cycle. Technological innovation, productivity, enlightenment, disillusionment, and overblown expectations are common. Many believe blockchain technology can solve transactional difficulties like supply chain monitoring and payment processing. The way it moves through the hype cycle shows that early, excessively optimistic expectations give way to a more realistic assessment phase, which ultimately leads to productive, widely accepted, and helpful outcomes.
Like the decades it took for the internet’s core technology, TCP/IP, to completely develop and become integrated into organizations and daily life, it might take a while forime to go from the Innovation Trigger to the Plateau of Productivity.
Click here to know about Machine learning
