Oracle Blockchain Chainlink (LINK)

In essence, Chainlink is not a stand-alone blockchain but rather a decentralized “oracle” network. Serving as a blockchain abstraction layer or middleware, it safely links Smart Contracts running on different blockchains to external, real-world data, or off-chain data. With its native currency, LINK, being an ERC-20 token, the Chainlink network is compatible with Ethereum’s protocols and runs on the Ethereum platform. It also employs a Proof Of Stake operational model. It’s important to note that Chainlink can operate on many blockchains at once and is compatible with any blockchain that supports smart contracts.
Purpose and History
Addressing the “Oracle Problem”: “Blockchain oracle problem” was the reason behind the creation of Chainlink. Blockchains cannot directly access external data since they are closed. Self-executing blockchain-based smart contracts require real-world data like asset prices, weather, and events. Using a single, centralized oracle for this data presents a single point of failure, compromising blockchain security. Decentralizing the process of transferring data on and off blockchains is how Chainlink addresses this issue.
Founders and Launch: Sergey Nazarov and Steve Ellis, who co-authored a white paper with Ari Juels in 2017, developed Chainlink. The project began in 2019 after being suggested in 2017. It was created by Smart Contract, a 2014 startup company specializing on blockchain technology. Including an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) in September 2017, Chainlink Labs raised over $32 million in two investment rounds.
How Oracle Blockchain Chainlink Works
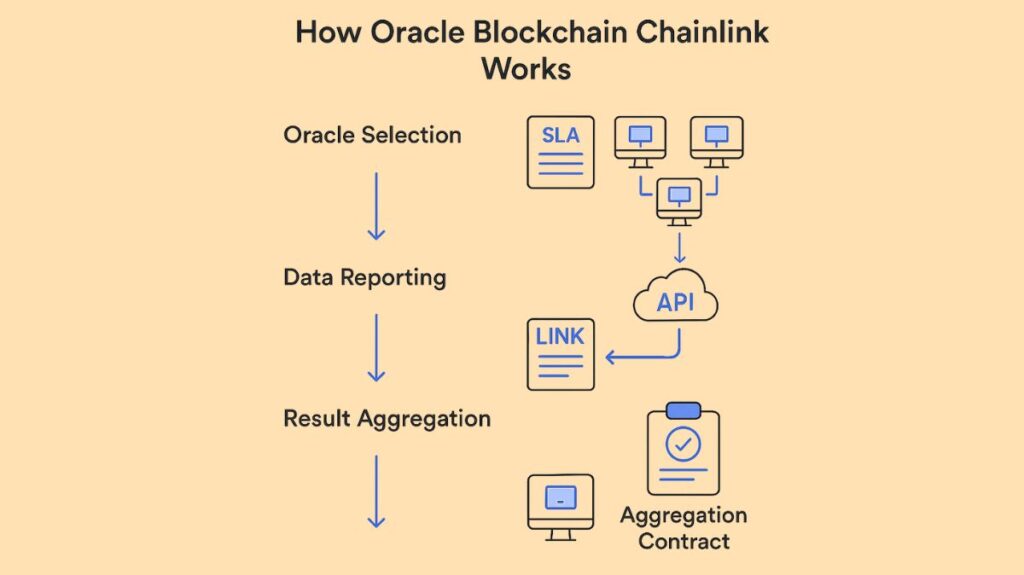
“Hybrid smart contracts” that integrate off-chain data infrastructure and on-chain code are made possible by Chainlink, which serves as a “bridge” between smart contracts and external data sources. An inventive three-step system is used in the process.
Oracle Selection
- To outline their data needs, a Chainlink user creates a Service Level Agreement (SLA).
- To match the user with the right oracles, the Chainlink software leverages this SLA.
- In an Order-Matching Contract that takes Oracle bids, the user deposits LINK tokens and submits the SLA.
- LINK tokens staked, average response time, and the total number of completed requests are some of the criteria that the Reputation Contract uses to assess and eliminate untrustworthy nodes.
Data Reporting
- Certain oracles establish connections with external data sources, such as APIs, in order to acquire the desired real-world data.
- Following processing by the oracles, the data is transmitted back to the smart contracts through the use of Chainlink Core software, which translates between off-chain and on-chain programming types. Almost any third-party API endpoint can have node connections extended by external adapters.
Result Aggregation
- After gathering data from the selected oracles and validating it, the Aggregation Contract returns a weighted score or averaged result to the user’s smart contract. This approach enhances accuracy and prevents assaults by deleting false responses and checking data from several sources.
Components of Oracle Blockchain Chainlink Architecture
There are both on-chain and off-chain components in Chainlink’s architecture:
- On-chain Components: Oracle contracts that track and handle data requests are built on the Ethereum blockchain. These consist of:
- Reputation Contract: Tracks the track record of Oracle service providers and records their performance indicators.
- Aggregating Contract: Combines answers from several oracles to produce a precise final response.
- Order-Matching Contract: Collects bids from oracles, logs user proposals, and chooses reliable oracle service providers.
- Off-chain Components: The supporting software and off-chain oracle nodes are among them:
- Chainlink Node Operators: Data is retrieved, processed, and delivered by independent operators. They convert requests and data using Chainlink Core software.
- External Adapters: Node connections can be extended to almost any third-party API endpoint, allowing for interaction with practical applications.
The LINK Token
The native ERC-20 coin of the Chainlink network is called LINK. It does a number of vital tasks:
Compensation for Node Operators: Chainlink Node operators provide services like data retrieval, formatting, off-chain computations, and uptime assurances, and they are paid with LINK tokens. The demand for the data node operators supply and the state of the market determine their own rates.
Staking and Incentivisation: LINK in the network is also staked by node operators. Nodes show that they are dedicated to providing excellent service by depositing LINK. The Chainlink Reputation Contract matches nodes with data requests based on a number of factors, including the size of the node’s stake. Nodes with a larger stake are more likely to be selected to fill requests and receive LINK tokens. LINK tokens staked by dishonest or flawed nodes may be “taxed” or deleted as a form of punishment.
Tokenomics: One billion LINK tokens are the most that Chainlink can produce. More than 650 million has been distributed as of May 2025. At the 2017 initial coin offering (ICO), 35% of the supply was sold; the remaining portion was either transferred to network nodes or given to the developers for further development. There is no mechanism that expands the amount of LINK in circulation, in contrast to many other cryptocurrency assets.
Unique Features of Oracle Blockchain Chainlink
Chainlink provides various special features:
Decentralization: Chainlink aggregates and verifies data utilizing several separate oracle nodes, decentralizing the oracle process. This ensures highly available and tamper-proof data for smart contracts by removing single points of failure.
Hybrid Smart Contracts: Hybrid smart contracts can integrate off-chain data infrastructure and on-chain code with Chainlink. This increases smart contracts’ usefulness for intricate applications like Decentralized Finance DeFi and insurance by enabling them to respond to actual occurrences (such as weather or pricing changes).
Cross-chain Interoperability: The safe transfer of messages, currencies, and actions between other blockchain networks is made possible via Chainlink’s CCIP. This allows for dependable token transfers and sophisticated multi-chain dApps by bridging disparate blockchains.
Verifiable Random Function (VRF): For uses such as gaming and NFTs, Chainlink VRF offers verifiable and cryptographically safe randomization. Verifiable on-chain, this ensures provably fair results for lotteries, NFT minting, and loot drops.
Proof of Reserve (PoR): Off-chain collateral assets that support on-chain tokens (like Stablecoins) may be audited automatically and in real time with Chainlink PoR. This lowers risk for DeFi investors and improves transparency.
Data Signing: Oracles certify their data with cryptography to reassure smart contracts and consumers that it comes from reliable nodes and hasn’t been altered.
High-Quality Data: Chainlink offers access to high-quality, reliable data. This guarantees that data for smart contract applications is accurate, dependable, and resistant to manipulation.
Blockchain-Agnostic Nature: Any blockchain network that supports smart contracts can use Chainlink natively. Because of its universal interoperability, developers from a wide range of ecosystems can use its oracle services, increasing its adoption reach.
Reputation System: Users can choose oracles using Chainlink’s reputation system, which is based on historical performance indicators. This encourages node operators to be truthful and provide high-quality service, resulting in a competitive and dependable network.
Oracle Blockchain Chainlink Use Cases
Chainlink’s widespread use can be attributed to its capacity to link blockchains to external data sources. Among the important uses are
Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Applications based on Decentralized Finance (DeFi) use Chainlink. Real-time asset prices are used to set acceptable collateralization rates for lending and borrowing methods. For many financial instruments, it retrieves current interest rates and cryptocurrency market prices. Chainlink Oracles can automate sophisticated yield farming and regularly verify DeFi platform collateralization, ensuring stability and security.
Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): Boosting Non-Fungible Tokens’ functionality and fairness, Chainlink is vital. Verifiable randomisation with Chainlink VRF ensures buyer fairness in NFT distribution during minting events or trait generation. After construction, Chainlink’s interoperability solutions enable secure cross-chain NFT transfers, allowing users to exchange digital assets between blockchain networks without losing integrity.
Gaming: Chainlink is used extensively in blockchain games for unpredictability and real-world data. Chainlink VRF (Verifiable Random Function) improves player trust and engagement by ensuring fairness and unpredictability of in-game events, outcomes, wagers, and raffles. Also generates random treasure drops, character traits, and matchmaking results. For betting dApps, Chainlink can bring off-chain data like sports results or gamify personal assets based on real-world financial success.
Stablecoins: Chainlink protects stablecoins. It provides real-time decentralised pricing feeds for stablecoin reserve ratios and pegs. This means fiat-backed stablecoins like USDT and USDC are appropriately collateralised by their underlying assets, giving users confidence. Chainlink’s accurate data helps stablecoins peg against established currencies.
On-chain Reserve Monitoring: WBTC, Wrapped Ethereum on other chains, and other tokenized assets can be fully collateralized with Chainlink’s active reserve monitoring. The digital representation of an asset on one blockchain is backed 1:1 by the actual item on another chain or in an off-chain vault by this approach. Chainlink maintains confidence and liquidity across blockchain ecosystems by repeatedly validating reserves, preventing under-collateralization.
Supply Chain: Chainlink expands supply chain transparency and traceability. IT connects logistics APIs, IoT sensors tracking products in transit, and ERP systems with smart contracts. An immutable blockchain ledger automatically records real-world events and item movement, confirming origin, condition, and delivery, eliminating fraud and enhancing efficiency.
Chainlink’s Role in the Ecosystem and Future Prospects
Chainlink has emerged as a key component of the blockchain and DeFi ecosystem, enabling safe connectivity between off-chain data sources and initiatives. By September 2024, Chainlink had a 46.6% market share among oracle providers and was assisting in the acquisition of $20 billion worth of value across 404 chains. Chainlink wants to keep growing by supporting more blockchain ecosystems and enabling new hybrid smart contract use cases. Since blockchains do not yet house large data and record stores, Chainlink has a plethora of chances to link blockchain networks with off-chain data. As technology advances and its use continues, it maintains its position at the top of the oracle chain.
Comparison to Other Oracle Networks
Despite being the industry leader, there are other oracle networks:
Band Protocol: Comparable to Chainlink, this decentralized network is “not as feature-rich” but offers cross-chain interoperability and a staking mechanism through validators that provide secure data for smart contracts.
API3: An additional decentralized oracle network that employs an API network with adjustable timing and data input, as well as a governance architecture in which tokenholders cast votes for network developments.
Chainlink continues to dominate the market because of its extensive feature set, robust security, and widespread use.
Buying LINK Tokens
LINK tokens are sold on reputable cryptocurrency exchanges like Kraken, Coinbase, and Kriptomat. The most common means to deposit money are bank transfer, credit/debit card, or cryptocurrency. It is possible to withdraw LINK to a self-custody cryptocurrency wallet like Trezor, Ledger, or MetaMask after making their purchase. LINK can also be exchanged for other cryptocurrencies on certain platforms.
