Virtual firms have experienced exponential growth in the last ten years. Even as the virtual business landscape has made worldwide delivery easier, businesses confront ongoing cybersecurity threats and data loss. Physical disaster recovery is becoming obsolete as firms transition to cloud-based solutions for cost, scalability, and flexibility. However, cloud backup can aid disaster recovery, and data protection is essential.
In this blog we discuss how cloud backup works, the types of cloud backup solutions, and why it’s essential for data security and disaster recovery.
What is the cloud computing?
A broad term used to describe hosted resources and services that are provided online is “cloud computing“. In contrast to conventional web hosting, cloud services are elastically delivered, meaning that the user can utilize as much or as little of the service as needed, and are fully managed by the service provider. A cloud can also be either public or private. A private cloud provides hosted services to a restricted number of users within the company, whereas a public cloud sells services to anybody with an internet connection, as is the case with AWS.
What Is Cloud Backup?
Cloud backup, an off-site virtual data storage technique, is mostly concerned with safeguarding confidential company information. Online or cloud backup has grown more common as a replacement for physical backup.
Third-party service providers offer cloud-based solutions with a pay-as-you-go basis. Customers can prevent data loss by turning on on-demand cloud backup. The backed-up data can be shared with multiple cloud users and accessed from multiple access points.
How Does Cloud Backup works?
Data is copied and moved from a physical location to a virtual storage system that is easily accessible for disaster recovery as part of the cloud backup procedure. The following actions must be taken by enterprises in order to start a cloud data backup process:
- Purchase data storage space from a company that offers cloud backup solutions.
- Install software in the IT ecosystem of the company.
- Select the cloud backup apps, files, and folders.
Backups are continuous and automatic once set up, requiring little to no human involvement. Users of major cloud backup services can add new data, manage bandwidth, deal with stored files, and schedule backups.
How Do You Restore Data?
A software program provided by the cloud backup service provider is used to perform backups. The software program allows for automated backups that happen on a timetable determined by the needs of the user and the services they have acquired. For instance, the software program records, compresses, encrypts, and moves your data to the service provider’s cloud servers on a 24-hour cycle if you choose daily backups. After a full initial backup, the cloud backup service could offer incremental backups to cut down on bandwidth usage.
Users can restore data from cloud backups using the same software program. They have the option to restore all of the backup or only particular files and folders. A cloud backup’s primary benefit is that it makes restores easier from any location on any device. For instance, a company can directly restore data at the disaster recovery (DR) site, which is located in a remote area, in the event that its data centre is unavailable.
Why Use of Cloud Backup?
Cloud backup offers more than just an affordable way to store and recover data. The following are some strong arguments in favor of cloud backup for IT teams:
Disaster Recovery Strategy Is Strengthened by Cloud Backup
On-site servers that store data backups are susceptible to natural calamities like fires and floods. Businesses can automatically move their data to a more organized and safe location for convenient access in the case of a disaster by utilising the cloud.
Quick Data Restoration
Customer confidence, productivity, and income are all negatively impacted by the loss of vital data, which can have disastrous results. Cloud backup provides immediate data restoration, guaranteeing uninterrupted operations even during cyberattacks or natural disasters.
Cloud Backup Reduces Unavailable Time
The environment in which today’s organizations work is intricate and interwoven. Through the assurance of data availability, cloud backup solutions minimize downtime risks and expenses while facilitating seamless corporate operations.
Lessens the Stress on IT Teams
The IT staff is relieved of the burden of laborious and time-consuming manual backups since cloud backup automates the data storage and restoration process. The IT staff may concentrate on problems that increase output and profitability due to automated data backup and restoration.
Cloud backup makes use of the service provider’s resources and knowledge
An organisation gains complete access to the newest technology and infrastructure available when it implements backup solutions from a service provider. Furthermore, cloud backup service providers may handle legal needs particular to a given country, ensuring strict compliance and data protection.
Types of Cloud backup
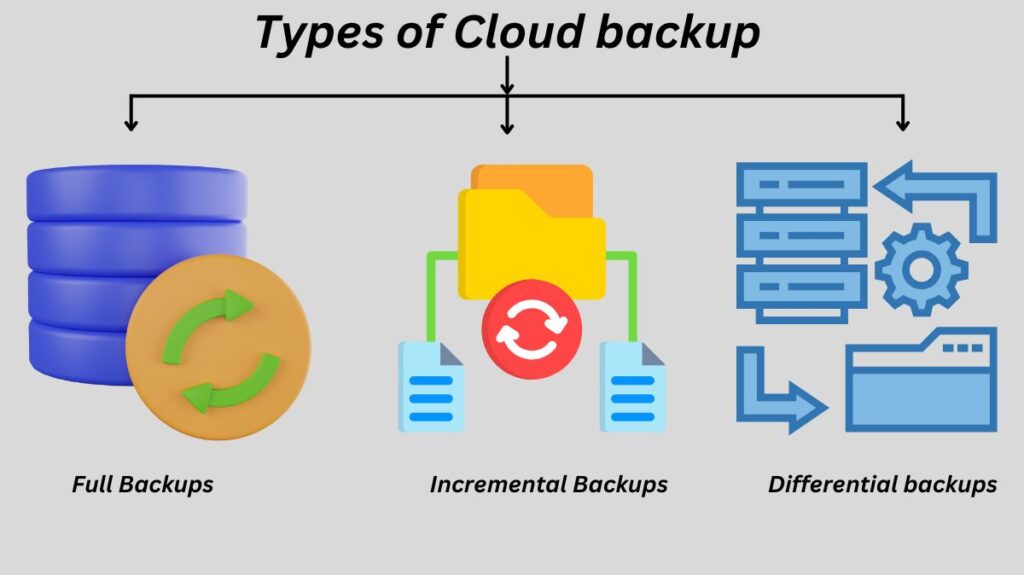
There are other backup techniques to take into account in addition to the different approaches to cloud backup. It’s crucial to comprehend the distinctions between the three primary types of backup, even though cloud backup companies allow users to select the one that best suits their requirements and applications.
- Full Backups: Every time a full backup is started, the complete data set is copied. They therefore offer the best degree of security. However, because full backups can be time-consuming and need a lot of data storage space, most organizations are unable to execute them on a regular basis.
- Incremental Backups: Instead of backing up the entire backup, incremental backups only back up the data that has changed or been updated since the last backup increment. Although this approach saves time and storage space, it may make a full restore more challenging because it will not be feasible to do a full restore if any backup increment is lost or destroyed. Since incremental backup typically uses fewer resources, it is a popular type of cloud backup.
- Differential backups: Since differential backups only include modified data, they are comparable to incremental backups. Differential backups, on the other hand, do not generally backup the most recent backup; instead, they backup data that has changed since the last complete backup. The issue of challenging restores that may occur with incremental backups is resolved by this technique.
