Hedera Hashgraph and Blockchain
Hedera Hashgraph is a cutting-edge distributed ledger technology (DLT) network that bills itself as a next-generation or substitute for blockchain consensus systems. Its mainnet was formally launched in August 2018 after it was created in 2019. The Hedera Hashgraph system’s native coin is called HBAR.
Here’s a detailed explanation:
Fundamental Architecture and How it Works
- Hedera employs a directed acyclic graph (DAG) structure, in which information is exchanged via “events,” as opposed to blockchains, which document transactions in sequential blocks. By doing away with the requirement for conventional mining and blocks, this graph-like structure enables the creation and confirmation of transactions in parallel, leading to a high transaction throughput. A DAG requires confirmation of at least two prior transactions before a new transaction may be submitted; hence, the more transactions submitted, the faster the chain expands.
- Consensus Model: ABFT(ashgraph): Hashgraph is the consensus algorithm and central data structure of Hedera. An asynchronous Byzantine Fault Tolerant (ABFT) algorithm, which is regarded as the most secure, is used in it. This makes sure that trustworthy nodes stay up and running even if a third of the network behaves erratically or maliciously. Because it enables asynchronous agreement-making between nodes, it is robust and scalable. Unlike Proof of Work (PoW) systems, which need synchronous circumstances to be active, Hashgraph can continue to function even in the event that an attacker delays communications. Using the ideas of “gossip,” “gossip about gossip,” and virtual voting, the consensus is formed.
- Information about data is gossip. One node passes data to another during a transaction, effectively “gossiping” about what is happening throughout the network. A transaction’s data structure consists of an encrypted signature, two hashes from parent containers, further transactions or zeros, and a timestamp. Nodes are constantly synchronising and producing events.
- Gossip About Gossip: This refers to details on transaction data. The hashgraph network synchronises information via a “gossip sync,” a shared history of “gossip events” throughout the network. This ensures unanimity and prevents data manipulation. Information can be transmitted swiftly throughout the network using the gossip-about-gossip protocol.
- Virtual Voting: Nodes evaluate the shared history they receive from gossip to establish a consensus timestamp for every transaction without the need for explicit voting rounds or extra communication. A node assigns a timestamp to a transaction as it is received, and the vote result is the median of all timestamps received by the transaction as it spreads. A more equitable system is produced when the network, not a single node, makes the decisions. Malicious actors are likewise kept from affecting the consensus-building process by virtual voting.
History and Development
Inventor and Founders: Hashgraph was invented in the mid-2010s by American computer scientist Leemon Baird. He is the co-founder and chief technical officer of Swirlds, the company that originally held patents covering the hashgraph algorithm. Hedera was founded by Leemon Baird, Mance Harmon, and Andrew Masanto.
Open-Source Transition: In September 2024, Hedera provided the Linux Foundation complete access to the Hedera Hashgraph’s source code, allowing Hiero to be vendor-neutral and open-source. This includes all key services, tools, libraries, and the hashgraph consensus technique to promote international cooperation and interoperability. The Hashgraph algorithm was made open source under the Apache License after the Hedera Governing Council voted in 2022 to buy the method’s patent rights.
Key Features and Benefits (Compared to Blockchain)
- High Performance and Speed: Hedera can process over 10,000 bitcoin transactions per second (TPS), finalising the ledger in three to five seconds. This outperforms Ethereum (12-15 TPS) and Bitcoin (6-8 TPS). Blockchain consensus takes minutes, but hashing certifies transactions in seconds.
- Energy Efficiency: Unlike energy-intensive Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) methods, Hedera’s protocols use few computational resources, making it environmentally friendly. No energy is wasted on unaccepted blocks, as all information is retained.
- Scalability: As usage grows, the DAG architecture’s capacity to handle transactions simultaneously offers scalability without sacrificing efficiency. Massive volumes of data and transactions can be handled by Hedera.
- Fixed and Predictable Fees: The transaction fees charged by Hedera are consistently modest, at about $0.001. The Governing Council regulates them, and they facilitate application development by being set in fiat USD but paid in HBAR.
- Security: In addition to ABFT, Hedera’s consensus method guards against malevolent individuals affecting the process. For safe transaction recording and authentication, it combines consensus and cryptography methods.
- Fairness: The network is made equitable and all nodes are given equal influence via the gossip protocol, which guarantees that each node has an equal opportunity to provide information. Hashgraph consensus also eliminates the impact of a single node or group of nodes on transactions by using timestamping and network-wide communication.
- No-Fork Guarantee: It offers a stable environment for creating decentralized applications (DApps) with an assurance of no-fork.
- Enterprise-Ready: Hedera is made to perform well enough for applications at the enterprise level. IBM, Boeing, and Deutsche Telekom have supported it, boosting its reputation and usage.
Hedera Governing Council
- Composition and Function: A Hedera Governing Council, which consists of up to 39 internationally renowned corporations, oversees the Hedera network. Prominent companies like Google, IBM, Dell, Deutsche Telekom, FIS Global, Tata Communications, Avery Dennison, Boeing, and LG Electronics are among the members.
- Governance: Every Council member has an equal say in matters such as network pricing, treasury management, and software updates. They have a set tenure and get no pay from Hedera. Proposals for Hedera Improvement (HIPs) are put to a vote by the Council.
- Impact on Fees: The Council also plays a role in regulating transaction fees, contributing to their stability.
- HBAR: The Native Cryptocurrency
- Dual Role: HBAR is designed to serve a dual role: as fuel to pay for network services (transaction fees, smart contract execution, file storage) and to incentivise node participation.
- Security: By participating in transaction validation and consensus, nodes that stake HBAR maintain the integrity of the network and collect rewards.
- Supply: A 50 billion HBAR total supply was available when the network was launched. This cannot be changed without the members of the Hedera Governing Council agreeing unanimously. To ensure market-driven value and avoid accumulation by any one company, a planned release that is slow and managed is in place.
You can also read ByzCoin: Scalable & Consistent Blockchain Consensus Protocol
Services Provided by Hedera
Hedera broadly offers three types of services:
- Hedera Consensus Service (HCS): Offers distributed applications transparent, safe, and impenetrable data logging. Timestamped event ordering is supported, which is essential for sectors like banking, supply chain management, and healthcare.
- With features like personalised token configurations, account-level controls, and minimal costs, Hedera Token Service (HTS) makes it easier to create, manage, and move digital tokens (fungible and NFTs) on the Hedera network. It facilitates the effective tokenization of assets, including commodities and real estate, while providing compliance features like AML checks, account freezing, KYC verification, token supply management, and transfer limitations.
- Because of Hedera’s fast network, developers may create DApps that interact with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) and are performed efficiently and affordably with Hedera Smart-Contract Services (HSCS). DeFi, gaming, and enterprise automation are examples of use cases.
Use Cases and Applications
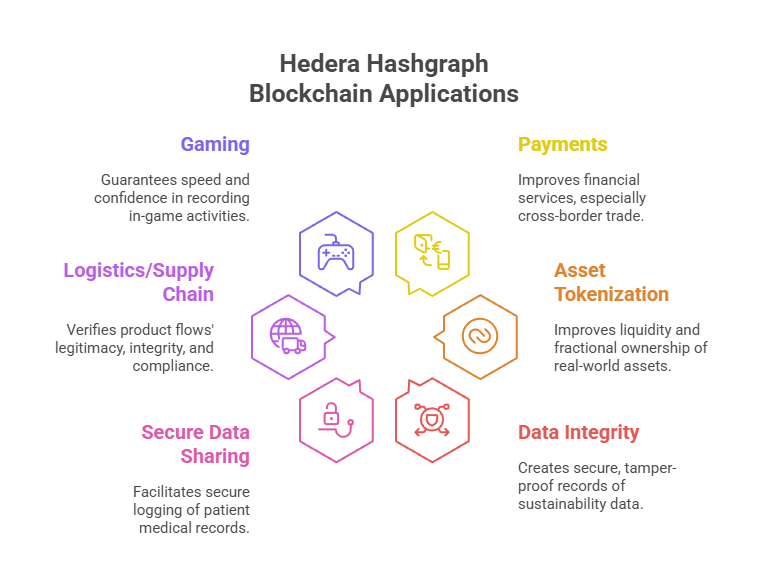
Hedera Hashgraph Blockchain Applications
Hedera’s features make it suitable for diverse industries:
- Fast, cheap, and transparent payments improve financial services, especially cross-border trade.
- Asset tokenization allows the construction, administration, and trade of digital representations of real-world assets (RWAs) like commodities, real estate, and artwork, improving liquidity and fractional ownership.
- Data Integrity: HCS helps create secure, tamper-proof records of sustainability data, fostering trust and preventing manipulation.
- Secure Data Sharing: Facilitates secure and immutable logging of patient medical records and trial data in healthcare while preserving privacy and compliance.
- Logistics/Supply Chain: Verifies product flows’ legitimacy, integrity, and compliance without tracking every transaction.
- By guaranteeing speed and confidence in the recording of in-game activities, asset management, and prohibiting changes to digital ownership, gaming tackles problems like fraud and manipulation in virtual gaming.
Challenges Confronting Hedera
Despite its advantages, Hedera faces several challenges:
- Competition: While ahead of first- and second-generation blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum, it faces competition from next-generation blockchains like Solana, which also offer quick processing speeds (3,000-4,000 TPS) and strong community support.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Cryptocurrency legislation vary by jurisdiction, which may hinder its governance model. The governance of Hedera may be too centralised, which may generate regulatory concerns or questions about its alignment with blockchain ideals. One problem is that the consensus procedure is overseen by a central organisation.
- Community Adoption: Ethereum and Solana are popular but hard to buy.
- Network Size Limitations: Hashgraphs perform poorly in small networks because they require many members.
- Complexity: The hashgraph technique demands a comprehensive grasp of virtual voting and gossip protocols, making it difficult for developers and consumers to create and use.
- Security Concerns: While offering greater security than conventional blockchain-based systems, it is not impervious to potential security attacks, such as a 51% attack.
- Lack of Track Record: Since this technology is still in its infancy, its scalability and effectiveness in extensive real-world scenarios are currently being assessed.
In order to take advantage of corporate demand across a range of industries, Hedera’s future depends on its capacity to use its cutting-edge technology, persuade businesses and regulators of its decentralisation, and foster wider community support.
You can also read Algorand Blockchain Overview And Algorand vs Ethereum
