Let us discuss DAI, How Does DAI Works, the History Of DAI, Advantages and disadvantages of DAI.
DAI is algorithmic and dollar-pegged stablecoin. It can be used for regular payments and financial activity because it was created to reduce price volatility in other cryptocurrencies. DAI is backed by digital assets and managed by MakerDAO, unlike many other stablecoins that are backed by fiat currencies and governed by centralized entities. DAI, an Ethereum-based ERC-20 token, may function decentralized, trustless, and permissionless.
Overview and History of DAI
Creation and Launch: In 2014, Danish entrepreneur Rune Christensen formed MakerDAO, which debuted DAI. The initial version, Single Collateral Dai (SAI), and its smart contracts were launched on Ethereum in December 2017. For the first year, SAI’s price stayed at $1 as ETH, its only collateral, plummeted.
Evolution to Multi-Collateral Dai (DAI): In 2019, the Maker Foundation released the Multi-Collateral Dai (DAI), replacing SAI. This was a huge development because it allowed collateral other than Ethereum.
Key Developments
- Andreessen Horowitz bought 6% of MKR tokens in September 2018 with a $15 million MakerDAO investment.
- Maker Foundation was created in Copenhagen to encourage Maker ecosystem.
- Andy Milenius, the Chief Technical Officer, left in 2019 because to internal conflicts about tighter integration with traditional banking systems, namely the desire of Rune Christensen to permit non-cryptocurrency assets as collateral.
- When the COVID-19 epidemic started in March 2020, DAI was hit by a deflationary deleveraging spiral amid erratic market conditions.
Decentralized Control
The Maker Foundation has since given up full control to MakerDAO, notwithstanding Rune Christensen’s creation, guaranteeing a genuinely decentralised governance approach.
How does DAI Works
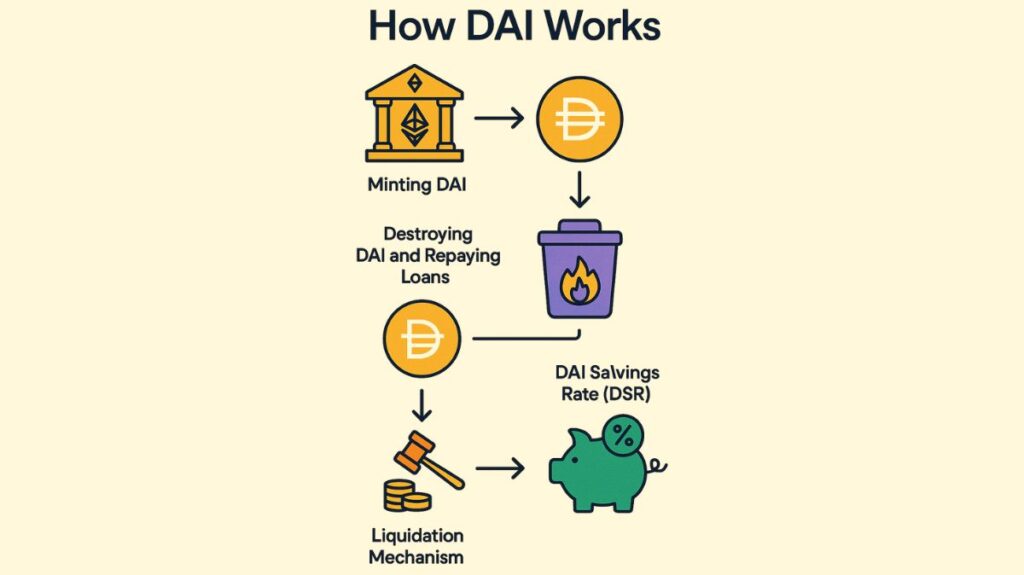
Through a system of overcollateralized loans and repayments made possible by MakerDAO’s Smart Contract, namely Maker Vaults (previously Collateralized Debt Positions or CDPs), DAI’s stability is mostly preserved.
Minting DAI
- In Maker Vaults, users pledge assets based on Ethereum that are supported.
- Because of the enforced 150% collateralization policy, consumers are required to secure at least 150% of the amount they plan to borrow. You would need to deposit at least $150 in collateral, for instance, in order to mint 100 DAI, which is equal to $100 USD. This over-collateralization protects against declines in the value of the underlying assets and acts as a volatility buffer.
- Following the deposit of collateral, the user receives a newly created DAI as a loan.
Destroying DAI and Repaying Loans
- The DAI that users borrow must be paid back in order to recover their collateral.
- Upon loan repayment, the collateral is made available for withdrawal and the returned DAI is automatically burned (destroyed).
- In addition, a stability fee which is comparable to loan interest is assessed when DAI is returned for collateral. By reducing the pressure on sellers, this fee, whose rate varies according to supply and demand, helps stabilise the price of the coin.
Liquidation Mechanism:
- In order to pay off a loan, the deposited collateral is liquidated or sold by force if the collateralization ratio drops below the minimum (for example, 150%).
- Keeper accounts are utilized in this procedure to pay off undercollateralized vault accounts and supply liquidity, which helps to maintain a consistent flow of DAI.
DAI Savings Rate (DSR):
- DAI holders who lock their DAI holdings in a DSR contract can receive interest on their holdings.
- The interest paid is financed by the stability fees obtained from loans, and MakerDAO controls the DSR.
Dynamic Supply
There is no set limit on the overall amount of DAI available; its availability is solely determined by demand. The supply of DAI Tokens fluctuates continuously depending on the quantity of collateral kept in the network, and users can create new tokens by using the CDP feature.
Characteristics and Benefits of DAI
For a number of reasons, DAI is distinct from other stablecoins:
Decentralization Guarantee: No centralized institution issues or manages DAI, as contrast to stablecoins backed by fiat reserves held by a central body. MKR token holders vote on changes to DAI, which is managed by MakerDAO, a distributed governance approach.
Multi-Collateral Functionality: Although the Maker Protocol initially only accepted Ethereum (ETH), it currently accepts a variety of Ethereum-backed assets as collateral, such as USD Coin (USDC), Compound (COMP), Basic Attention Token (BAT), and ETH. By diversifying, price stability is increased and user risk is decreased.
Stability and Security: The hybrid algorithmic nature of DAI, which codifies methods to preserve its value, and its multi-collateral make it one of the most reliable stablecoins. Especially in economies that are unstable, this enables customers to safely keep capital in a currency that is similar to the US dollar, protecting purchasing power from inflation or devaluation. Strong protection against theft and hacking is provided by DAI’s ability to be kept in safe, encrypted cryptocurrency wallets.
Interoperability and Accessibility: There are innumerable Ethereum-based Decentralized Application, wallets, protocols, and platforms that can work with DAI since it is an ERC-20 token. Because of its wide interoperability, it may be used for a wide range of purposes and promotes financial inclusion and innovation worldwide without the need for conventional middlemen like banks.
Disadvantages and Limitations of DAI
Notwithstanding its benefits, DAI has many innate drawbacks.
Partial Backing by Volatile Cryptocurrencies: The Cryptocurrency that support DAI, such as ETH, BAT, and WBTC, are impacted by market swings. However, over-collateralization and other stability measures are meant to reduce the danger of a depeg, which could result from significant price declines in these underlying assets.
Reliance on Centralized Stablecoins: DAI has a significant amount of support in USDC, a centralized stablecoin that is issued and administered by Circle. Due to the introduction of counterparty risk, the stability of DAI is contingent in part on Circle’s management and the soundness of the financial institutions who hold USDC’s reserves. Due to USDC’s reserves stored at Silicon Valley Bank, for instance, both USDC and DAI depreciated when the bank failed in March 2023.
Capital Inefficiency: Because customers must lock up more value than they borrow due to the necessity for over-collateralization (e.g., 150%), capital efficiency is decreased.
Uses of DAI
After being produced, obtained, or received, DAI can be utilized just like any other cryptocurrency. Its stability qualifies it for:
Avoiding Market Fluctuations: Users can protect themselves from significant price swings and market instability by using DAI. Stablecoins like DAI are frequently used by cryptocurrency traders, artists, and service providers to hedge their gains without having to switch to fiat money.
Everyday Payments: DAI enables blockchain-based payments for institutional and retail uses, including online and even in-person transactions, by acting as a substitute for fiat money.
Collateralised Loans: To obtain liquidity without having to sell their cryptocurrency, users can establish DAI by using their digital assets as collateral.
Savings and Earning Interest: The DAI Savings Rate (DSR) feature allows customers to lock their DAI and earn steady interest automatically. DAI is also frequently utilized in Decentralized Finance DeFi systems that provide interest-bearing funds, like Aave and Curve, which enable users to potentially receive yearly interest on DAI investments, sometimes even surpassing the cost of borrowing DAI.
Interacting with dApps and Services: In the Maker Protocol and other decentralized systems, DAI is utilized as an accounting unit. As examples, consider:
- Oasis.app: Frontend for making Dai and gaining access to the Maker Protocol.
- BuenBit: Dai may be bought and sold with ease by users throughout Latin America with this cryptocurrency exchange situated in Argentina.
- Blocklords: A grand strategy game that allows in-game purchases to be made with DAI.
Speculation: It enables people to make cryptocurrency speculations without having to sell their current cryptocurrency holdings.
Governance of DAI
As the Maker Protocol’s native stabletoken, DAI is controlled by Maker (MKR) token holders. It is the duty of MKR token holders to oversee the Maker Protocol and the monetary risks related to DAI. There is both on-chain and off-chain governance:
On-chain Governance: The Maker Protocol’s on-chain governance system, which includes Executive Votes and Governance Polls, is used by MKR token holders to cast their votes on proposals. Any MKR holder can take part and influence the direction of the protocol.
Off-chain Governance: Additionally, MKR stakeholders participate in public governance webcalls and forums to conduct off-chain votes with the community.
Security and Wallets
Being an ERC-20 token based on Ethereum, DAI is protected by the Ethereum Ethash Algorithm. Additionally, the Maker Protocol has an Emergency Shutdown Process that, if authorized by all signatories, can be initiated by a small number of reliable people who own global settlement keys. DAI holders can exchange their DAI for their original collateralized assets prior to the protocol’s termination if the Maker Protocol as a whole freezes. Since the system is open-source and decentralized, it might be re-deployed following the wind-down.
Among the choices available to users for storing DAI are:
Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets): These provide the safest choice for offline storage (e.g., Trezor, Ledger) and work best for bigger quantities.
Software Wallets: These come in desktop or smartphone apps and are simple to use and free. For lesser sums or inexperienced users, they might be either custodial or non-custodial.
Online/Web Wallets: Although they are free and available through web browsers, these are typically regarded as less secure than software or hardware wallets. For lesser sums or regular trades, they work well.
Crypto Exchanges: A digital wallet is created for consumers by platforms like as Firi or Kriptomat, which provide safe storing options in addition to trading capabilities.
