Let us discuss about the Disadvantages and Advantages Of Cryptocurrency including with it’s types.
Types of Cryptocurrencies
Ethereum (ETH): The native cryptocurrency and blockchain platform. It serves as the basis for numerous other tokens and dApps and is a perfect illustration of a utility token, which is used to pay for transaction fees and network gas.
XRP (Ripple): Primarily a payment cryptocurrency that financial institutions frequently use for quick and inexpensive international payments.
Litecoin (LTC): Considered the “digital silver” to Bitcoin’s “digital gold,” this payment cryptocurrency strives for quicker transaction confirmations.
Solana (SOL): An advanced blockchain system with its own cryptocurrency. Within the decentralized application area, it is a fierce rival to Ethereum and a useful token for its network.
USDC (USD Coin): A stablecoin that’s tied to the US dollar, specifically one that’s backed by money.
Dogecoin (DOGE): A well-known memecoin that began as a joke but quickly received a lot of support from the community.
Stellar (XLM): A cryptocurrency payment system intended to link financial institutions and facilitate cross-border transactions.
Chainlink (LINK): To pay for the data services it offers to smart contracts, a decentralized oracle network’s native token is a utility token.
Bitcoin Cash (BCH): The purpose of this Bitcoin fork is to create a payment cryptocurrency with bigger block sizes for quicker transactions.
Polkadot (DOT): A platform for blockchains that facilitates communication between them. Both a governance token and a utility token are its native tokens.
AVAX (Avalanche): A blockchain platform and network utility token like Ethereum and Solana.
Monero (XMR): Renowned for its robust anonymity characteristics, this coin is a leader in privacy.
Peercoin (PPC): Notable for being among the first to use both proof-of-work (PoW) and proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanisms, this cryptocurrency is older. It falls under the category of a cryptocurrency used for payments.
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and biggest cryptocurrency, it is mostly used as a store of value and a payment method.
Cardano (ADA): Research-driven development-focused blockchain platform. Both a governance token and a utility token are its native tokens.
Tether (USDT): Another popular stablecoin backed by fiat money and connected to the US dollar.
Binance Coin (BNB): The cryptocurrency that is native to the Binance Smart Chain and Binance exchange. It is a utility token with some governance features (for exchange fees, discounts, and involvement in the BSC ecosystem).
DAI: With the use of smart contracts and collateral, this algorithmic stablecoin seeks to keep its value steady in relation to the US dollar.
Stablecoins: As previously mentioned, the purpose of this particular category of cryptocurrency is to reduce price volatility. Tether, DAI, and USDC are particular instances in this category.
Altcoins: A catch-all phrase for cryptocurrencies other than Bitcoin. Ethereum, XRP, Litecoin, Solana, and all of the other individual currencies and tokens mentioned above are all regarded as altcoins.
Utility tokens: An ecosystem’s set of tokens that grant access to a certain good or service. This group includes, for instance, Polkadot, Chainlink, and Ethereum.
Memecoins: Internet memes served as the inspiration for this type of cryptocurrency. Shiba Inu and Dogecoin are two excellent examples, even though Shiba Inu wasn’t on your list.
Payment cryptocurrencies: A group of digital currencies that are mainly used for transactions. Strong examples are Bitcoin, Litecoin, XRP, and Bitcoin Cash.
Uniswap Labs: This is not a cryptocurrency in and of itself; rather, it is the organization or group that created the Uniswap decentralized exchange (DEX) and the UNI governance token that goes with it. It is a cryptocurrency, the UNI token. goods that are verifiable, such digital artwork or collectibles.
Advantages of Cryptocurrency
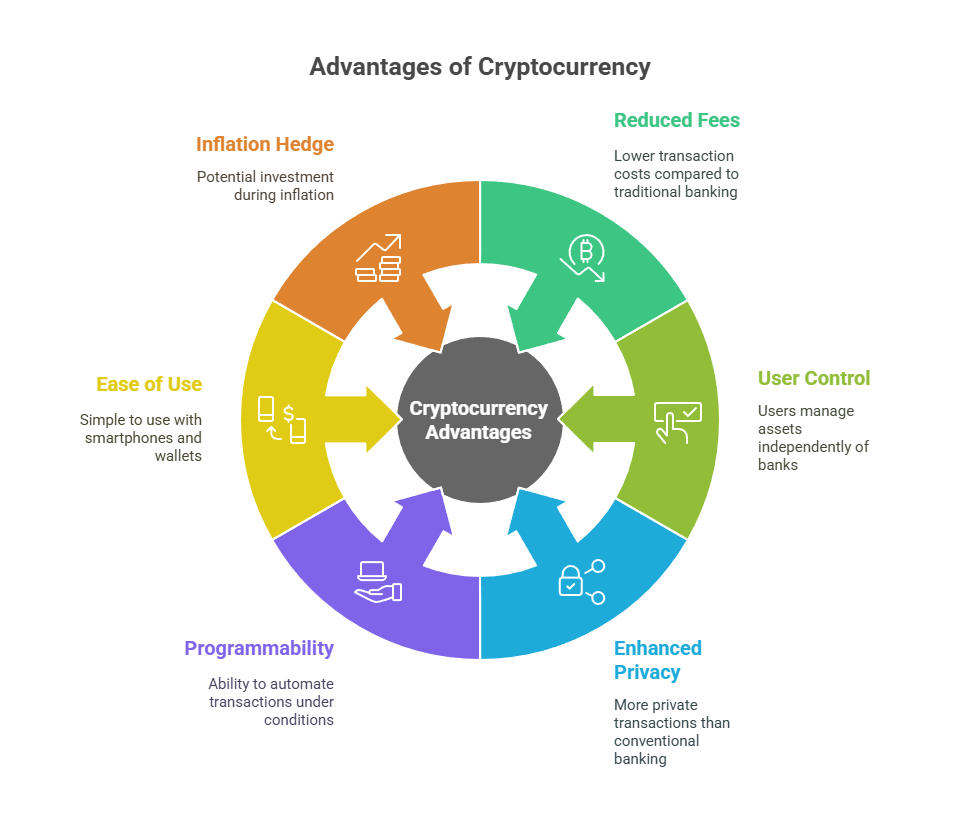
Reduced Transaction Fees: For international payments, cryptocurrencies can reduce transaction fees compared to traditional banking.
User Control and Autonomy: Users are in charge of their assets without any direct limitations from banks or the government. They do business outside the purview of banks and municipal government.
Enhanced Privacy: Even though they are pseudo-anonymous, they provide more private transactions than conventional banking.
Programmability: Because they may be programmed to do automatic transactions under certain conditions, they are incredibly adaptable.
Ease of Use/Portability: Simple to use with a smartphone and wallet, and portable (on a phone or by remembering a key word).
Inflation Hedge: The restricted supply of cryptocurrencies has led some to conclude that they can be a viable investment during inflation.
Disadvantages and Risks
Cybersecurity Issues: Blockchain technology is vulnerable to fraud and hacking, as seen by the many high-profile theft events. Money can be lost forever if private keys are not protected against malware, data loss, or physical media destruction.
Price Volatility: Given that supply and demand alone determine their worth, the excessive price volatility is a big worry for investors and businesses alike.
Lack of Regulation: Without strict regulation, they are more vulnerable to speculation and put investors at more risk because there is no central authority to defend users against fraud or disputes.
Scalability Concerns: Rapid adoption may cause transaction delays because some blockchains are slow, which prevents them from competing with payment giants like Visa in terms of transaction volume.
Limited Acceptance: Despite their increasing numbers, they are still not as commonly used as traditional currencies as a mode of payment.
Energy Consumption: Carbon emissions and electronic waste emerge from proof-of-work cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin’s huge electricity demand.
Illicit Activities: Transaction anonymity makes them desirable for tax evasion, money laundering, and extremist financing.
Difficulty in Legal Recourse: Courts may not provide assistance to victims of fraud if there is no central authority or legal evidence.
Storing Cryptocurrencies
Cryptocurrency wallets are interfaces that hold the public and private keys (also known as seeds) that are used to receive and spend cryptocurrency. No gadget actually contains the cryptocurrency itself; the wallet is a way to keep track of assets on the blockchain and initiate transactions. Wallets of many kinds include:
Paper Wallets: Store that is offline and uses paper keys.
Hardware Wallets (Cold Wallets): Electronic gadgets that are offline and maintain private keys securely. The only time they are online is when they are sending or receiving cryptocurrency. In terms of security, these are the best.
Digital Wallets (Hot Wallets): Software programs on computers (desktop or mobile) that save wallet data online. They are susceptible to hacking, although they are nearly always free.
Custodial Wallets: It is stored by a third party, such a cryptocurrency exchange, which frequently uses both hot and cold storage. This is thought to be the most user-friendly and straightforward approach.
Regulatory Landscape
Countries have very different legal statuses for cryptocurrency. Some nations have outright permitted their usage, while others have restricted or outright prohibited use. For example, although the Supreme Court lifted a ban on cryptocurrency investment in 2020, India still does neither forbid or permit it, albeit a clear regulatory framework is still being considered. All bitcoin transactions are prohibited in China as of September 2021. El Salvador legalised Bitcoin first in June 2021.
Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and IMF are advocating for regulation of “virtual asset service providers” (VASPs), which are similar to financial institutions, including KYC and AML requirements, to promote coordinated and comprehensive supervision. Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) was passed by the EU to regulate digital assets. To strike a balance between prohibiting illicit transactions and promoting sector growth, the US is also creating regulatory frameworks.
