Uncover the Advantages And Disadvantages Of cloud computing in healthcare, focusing on improved care delivery and data privacy challenges in this blog.
What is cloud computing in healthcare?
Using cloud-based services and technology to store, manage, and process medical data and applications connected to healthcare is known as Cloud Computing in Healthcare. This method improves patient care, operational effectiveness, and innovation by allowing researchers, organisations, and healthcare providers to safely and effectively access and share data.
Benefits of Cloud Computing in Healthcare
Lowered Healthcare Cost
The ability to access computer resources like processing power and data storage in real time is one of the main and most significant factors influencing healthcare organisations’ decision to use cloud services. In some situations, healthcare organisations are exempt from having to buy hardware for data storage. Additionally, there are no up-front fees associated with cloud computing, so healthcare organisations will only be charged for the resources they use.
Furthermore, cloud computing in healthcare includes apps that can provide the best possible cloud environment for scalability without incurring excessive costs. This means that a cloud system can store all of the patient data that comes in from many sources, including wearable technology, electronic medical records (EMRs), and other healthcare apps, while maintaining a low cost.
Interoperability Made Easy
Easy interoperability is another significant advantage of cloud computing in the healthcare industry. The idea of interoperability centres on creating data interfaces throughout the whole healthcare system, regardless of the patient’s data’s origin or location of storage. This indicates that interoperability enabled by healthcare cloud solutions allows the institutions to readily access patient data, share it within or outside the institution for medical emergencies, and derive appropriate insights from the data to support the provision of healthcare. In essence, cloud computing makes it possible for the healthcare sector to acquire patient data gathered from several sources and distribute it to key persons or stakeholders in accordance with appropriate delivery standards.
Ownership of Data by Patients
Cloud computing in healthcare has the potential to democratise medical data and empower patients to take control of it. This strategy aids in increasing patient involvement in health-related decision-making, teaching people about healthcare-related aspects, and promoting improvement. on essence, when digital data is kept on the cloud, cloud computing in healthcare makes it possible for medical data to be archived and then easily retrieved. This implies that data redundancy decreases as system uptime increases and that data recovery is made simpler when the system is not overburdened.
Improved Collaboration
Using cloud technologies in healthcare is crucial for improving teamwork and preserving electronic medical records. This implies that patients won’t have to bring their medical records to the doctor each time they see them. The doctors will be able to discuss information in real time, view the results of their prior treatments, and conveniently access patient data via the cloud system. In essence, combining cloud computing and healthcare can help physicians treat patients more precisely.
Enhanced Patient Experience
Cloud computing in healthcare gives physicians the ability to interact with patients more actively. Real-time access to test findings, doctor’s notes, and medical data makes this possible. Because they are better informed about their medical history, available treatments, and preventative actions, patients who receive this type of healthcare are able to take charge of their health. In addition, cloud computing in healthcare provides patients with appropriate care and protects them from being over prescribed medications or forced into needless testing.
Disadvantages Of Cloud Computing In Healthcare
Cloud computing has improved healthcare data storage, accessibility, and cooperation. However, downsides include:
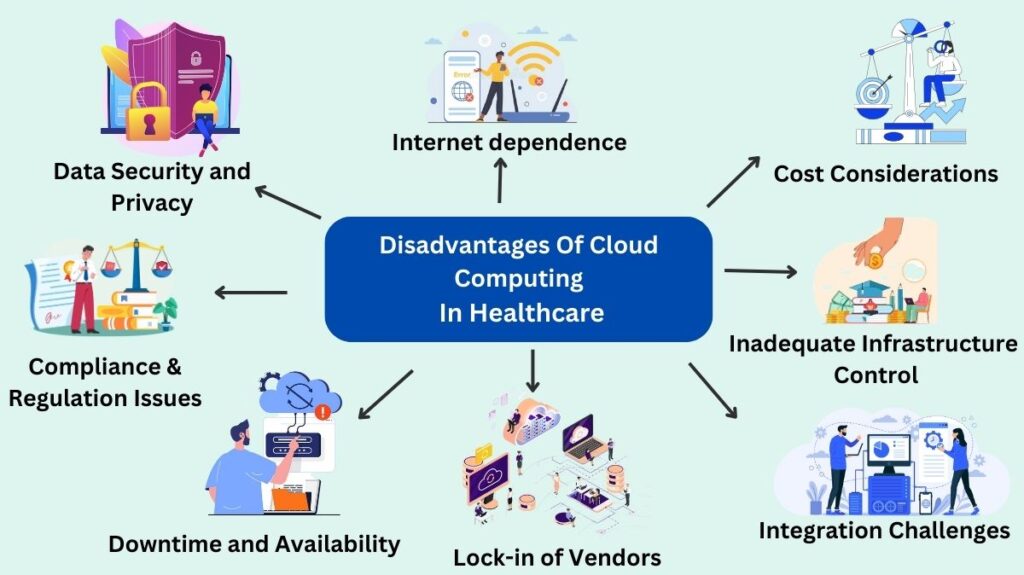
Issues with Data Security and Privacy
- Hacks and unauthorised access to cloud-stored patient data could breach GDPR or HIPAA.
- Ransomware, phishing, and hacks can compromise data.
Compliance and Regulatory Challenges
Healthcare institutions are subject to strict data protection regulations that differ by jurisdiction. Maintaining adherence to these rules in cloud systems can be expensive and difficult.
Downtime and Availability Issues
Cloud services depend on provider infrastructure. Downtime or service interruptions can disrupt hospital operations and patient care by preventing medical data access.
Dependency on Internet Connectivity
High-speed, dependable internet is necessary to access cloud-based solutions. Real-time data processing and access may be impeded in places with inadequate connectivity due to this dependence.
Lock-in of Vendors
Due to variations in platforms, data formats, and system integrations, switching cloud providers can be complex and may result in higher expenses and technical issues.
Cost Considerations
Even though cloud services can save money up front, unforeseen usage increases, data egress fees, or hidden costs may result in higher-than-expected costs.
Inadequate Infrastructure Control
Because the cloud infrastructure is run by the cloud provider, healthcare providers might not have much influence over it. Customisation, performance optimisation, and meeting certain operational requirements may be hampered by this.
Integration Challenges
Cloud system integration can be time-consuming and technically challenging when combined with traditional healthcare systems and on-premises infrastructure.
