Direct Attached Storage Definition
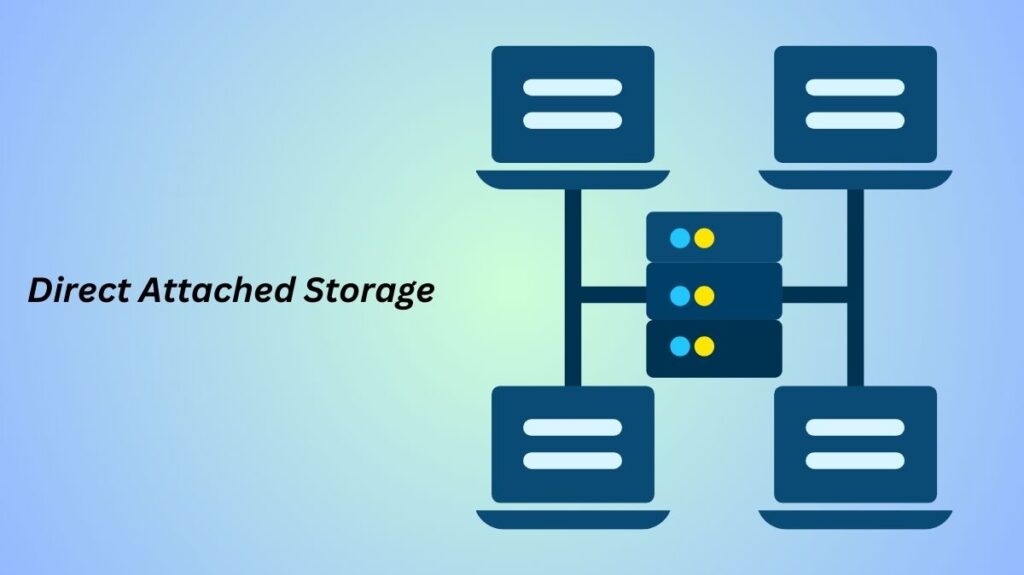
One kind of digital storage device that connects straight to a computer, workstation, or server without using a network is called direct-attached storage (DAS). DAS is only connected to one device, therefore other systems cannot access it unless they connect via the host computer. DAS includes internal and external hard drives, SSDs, optical media (CDs and DVDs), and tape storage. DAS is often used for local data storage when files on one device need rapid access.
Direct Attached Storage DAS Purpose?
DAS gives servers and PCs internal or external storage. Besides motherboard-connected HDDs and SSDs, USB drives and external hard drives are DAS. Small and medium-sized organizations (SMBs) frequently employ DAS as file servers, providing specialized storage for certain workstations or servers. It is also utilized in data centers when certain servers or applications require dedicated storage. To improve performance and capacity, larger businesses may combine DAS with networked storage systems like Storage Area Networks (SAN) or Network Attached Storage (NAS).
DAS is frequently used in scenarios that call for high performance and big storage capacity, which makes it perfect for SMBs that want easy, affordable storage without necessitating data sharing throughout the company. Additionally, compared to more complicated choices like SAN and NAS, external DAS systems may be expanded at a cheaper cost.
Define Direct Attached Storage?
Direct-attached storage (or “DAS”) is immediately connected to the computer or server. The device to which it is physically linked may access the storage, not the network. An external storage enclosure that is directly linked to a server or hard disc drives or SSDs that are placed within a computer or server chassis can make up a DAS system.
- DAS is a group of external discs directly attached to a server using FC, SAS, SATA, or SCSI connections.
- DAS enables storage access without Ethernet, Fibre Channel, or network infrastructure such hubs, switches, or routers, unlike network-attached storage systems.
How does DAS Works?
DAS does not require a network connection to connect to the host computer or server, and it can be either internal or external. Internal DAS usually uses a high-speed host bus adapter (HBA) to connect a storage device internally to a server or personal computer.
- At least one internal DAS drive, which can be either a speedier SSD or a conventional HDD connected via a SATA port, is included in every personal computer. Likewise, internal storage on servers can be connected via SATA, SCSI, or SAS connections.
- Examples of external DAS include external hard drives and drive enclosures that can hold many drives. Connection interfaces like USB, eSATA, SAS, or SCSI are used to connect these to workstations and servers.
- The DAS is managed and controlled by the computer to which it is attached. Instead of immediately accessing the data, networked computers must communicate with the computer hosting the DAS.
Why Use Direct-Attached Storage For Storage?
Direct-attached storage (DAS) provides a number of strong benefits to consumers looking for economical and effective storage options:
High Performance
Because DAS links directly to the computer or server that requires the data, it offers quick access to the data. By reducing latency, this direct connection guarantees speedy read and write operations. DAS maintains continuously excellent performance since it is not impacted by network congestion or connection problems, in contrast to network-attached storage (NAS) or storage area networks (SAN).
Simple Setup
DAS is simple to set up and configure. When placed in a computer or server, internal DAS, such as solid-state drives (SSDs) or hard disc drives (HDDs), are usually operational right away. External DAS devices, like external hard drives or USB drives, are made to be “plug and play,” meaning that users can attach them to a USB port and begin using them immediately without having to go through complicated setup steps.
Low Cost
When compared to NAS and SAN systems, which need extra hardware and software for maintaining and running the storage infrastructure, DAS is a more affordable storage option. Users can avoid the higher expenses associated with networked storage systems by using DAS, which only requires them to purchase the disc drives and drive enclosures they need. DAS is a sensible option for consumers that value cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and performance in their storage configuration.
When Direct-Attached Storage DAS Should Be Used?
Direct-Attached Storage (DAS) may be the better option in the following situations:
Budgetary Limitations
DAS is cheaper than SAN or NAS, which can cost hundreds to millions of dollars. DAS is a low-cost storage alternative for small and medium-sized organizations with high storage needs but limited funds. Acquiring the required storage devices and, if required, extra enclosures is part of setting up a DAS system. If more storage is required, it is simple to integrate and acquire.
Easy Storage Solution
DAS is beneficial for organizations without large network infrastructures or those that do not require considerable internal data exchange. DAS provides these companies with an easy-to-implement storage solution that requires little IT assistance. It is essentially a workable solution for companies with limited resources or those seeking a simple, affordable storage solution free from the hassle of sophisticated network setups or demanding data sharing needs.
