We talked about IoT devices in this blog, including what they are, how they operate, why they are significant, examples, IoT device administration, and IoT device management protocol.
What Are IoT Devices?
Data-collecting sensors, gadgets, appliances, and other machinery are IoT devices. They can be integrated with other Internet of Things devices and are configured for specific uses. For instance, an Internet of Things gadget in your vehicle can recognize the traffic in front of you and instantly notify the person you are meeting of your upcoming delay.
How do IoT Devices Work?
While the functionality of many IoT devices vary, their operational mechanisms are all identical. First of all, IoT devices are actual physical objects that have the ability to sense physical events. They are often linked to a Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol server and have an integrated CPU, network adapter, and firmware. For it to work over the network, an IP address is also necessary.
A software program is used to configure and administer the majority of IoT devices. For instance, a smartphone app that allows you to manage your home’s lighting. Additionally, some smartphones come with built-in web servers, thus extra apps are not necessary. For instance, when you go into a room, the lights turn on right away.
Why Use IoT Devices?
AI and machine learning are increasingly being used by IoT devices to provide intelligence and autonomy to various systems and processes, including home automation, medical equipment, industrial smart manufacturing, and autonomous driving. Many of these gadgets are microcontroller-based systems with limited power and budget. More on-device processing, where data is handled on the IoT endpoint rather than using cloud-based technologies, is still required due to network bandwidth and consumer expectations about data protection and user experience.
Examples of IoT Devices
Home Security
IoT is the main force behind safe and intelligent homes. IoT connects a range of sensors, lights, cameras, and alarms that can all be operated from a smartphone to offer round-the-clock protection.
Read more on Applications of IoT in Smart Home Expanding Safety & Quality
Activity Monitors
Alerts and peace of mind are provided by smart home security cameras. Activity trackers are sensor devices with real-time monitoring and transmission capabilities for important health indicators. Your blood pressure, hunger, oxygen levels, and physical activity can all be monitored and controlled.
Industrial Security and Safety
To find trespassers, IoT-enabled cameras, sensors, and detecting systems can be installed in restricted locations. They can also spot minor chemical leaks and pressure buildups and address them before they become major issues.
Augmented Reality Glasses
Wearable, computer-enabled glasses that project 3D animations and films onto the user’s real-world surroundings are known as augmented reality (AR) glasses. The information can assist users in accessing Internet apps and is shown within the glasses’ lenses.
Motion Recognition
Motion sensors detect building, bridge, dam, and other significant structure vibrations. These methods find structural defects that can cause catastrophic collapses. They can be employed in earthquake-, landslip-, and flood-prone locations.
Read more on Eclipse Smart Home, Define And Explain Eclipse IoT Project
What is IoT device management?
Availability, scalability, power and processing capacity, security, and interoperability can hinder the implementation of an Internet of Things system and its components. Many of these challenges can be overcome with IoT device management using standard protocols or vendor services.
Device management provides capabilities essential to preserving the connectivity, security, and well-being of IoT devices over their whole lifecycles, assisting businesses in integrating, organizing, monitoring, and remotely managing internet-enabled devices at scale.
Onboarding devices, configuration, maintenance, diagnostics, and end-of-life management are among the distinct categories that make up IoT device management. Generally, device administration proceeds according to a pattern like this:
- Activation and registration.
- Authorization and authentication.
- Setup.
- Supplying.
- Diagnosis and monitoring.
- Troubleshooting.
- Upgrades to the firmware.
Lightweight Machine to Machine and Open Mobile Alliance device management are two instances of standardized device management protocols. Vendors including Amazon, General Electric, Google, IBM, and Microsoft all offer IoT device management software and services.
IoT device connectivity and networking
IoT Device Management Protocols
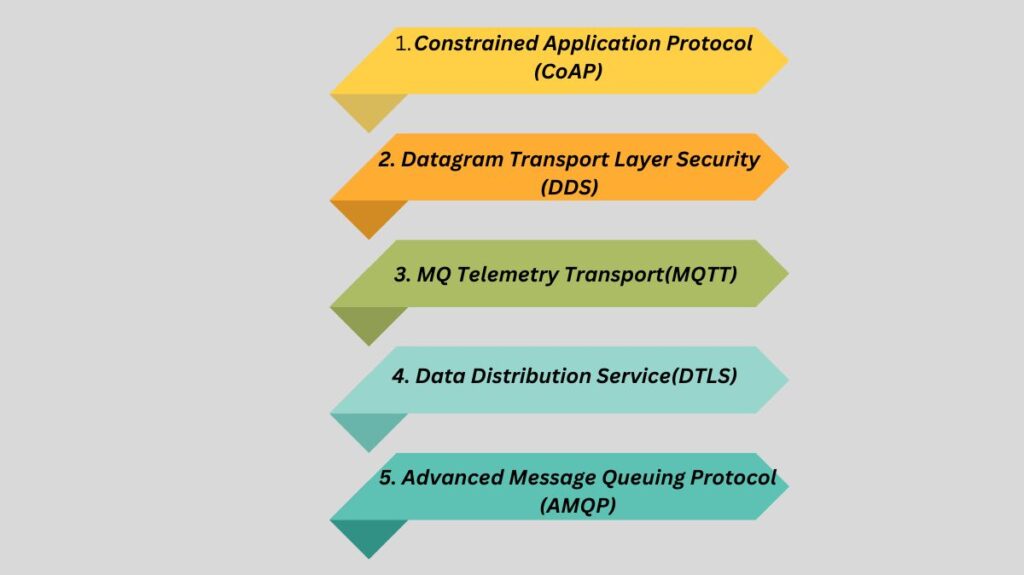
The IoT application affects internet-enabled device networking, communication, and connectivity protocols. IoT applications offer many connectivity and communication options, including:
- Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP)
- Datagram Transport Layer Security(DDS)
- MQ Telemetry Transport(MQTT)
- Data Distribution Service(DTLS)
- Advanced Message Queuing Protocol(AMQP)
Examples of wireless protocols:
- IPv6.
- Low Energy Zigbee Bluetooth.
- Z-Wave.
Read more on IoT Application Protocols And Importance of IoT Protocols
Other alternatives are Ethernet, Wi-Fi, satellite, and cellular.
Power consumption, range, and bandwidth must be considered when choosing devices and protocols for an Internet of Things application. Both high and low range, power consumption, and bandwidth are available.
IoT devices connect to a gateway or edge device to send data to the cloud or analyse it locally. Some devices have built-in data processing that reduces data transfer to the data centre or cloud. As more data is generated by IoT devices, this kind of processing which frequently makes use of machine learning features built into the device becomes more and more common.
IoT device trends and anticipated growth
More than 29 billion IoT connections are expected by 2027, according to the most recent IoT Analytics “State of IoT Spring 2023” report. The number of devices may vary according on chipset supply chains and the possibility of technological supply bottlenecks, even though this expansion will persist for years to come.
Read more on What Is IoT Operating Systems? And Key Features Of IoT OS
