Discover the best tools and practices for IoT hardware development. This comprehensive guide covers prototyping, embedded systems, and efficient IoT device creation.
What Makes Up Great IoT Hardware
Reliability
Having dependable IoT gear is essential to ensuring uninterrupted operations free from frequent malfunctions or outages. It must have a long lifespan and be resilient to a range of environmental factors. One way to guarantee failover methods in the event of hardware failures is to incorporate redundancy features.
Scalability
Scaling as the number of linked devices increases should be easy for successful IoT hardware. These designs’ modularity makes it possible to add more devices without requiring major system modifications. Therefore, scalable hardware makes it possible for IoT deployments to grow easily and handle growing numbers of connections and data volumes.
Interoperability
The compatibility of IoT devices with other systems is guaranteed by adherence to industry standards and protocols. Support for widely used communication protocols (such as MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP) makes it easier to integrate with many IoT platforms and applications. Easy data interchange and communication between non-uniform devices from various manufacturers are made possible by interoperable hardware.
Robust Security
As in any other industry, IoT hardware should be secure to prevent cyberattacks and data breaches. Hardware-based security mechanisms including secure boot, authentication, and encryption protect data. To correct vulnerabilities and keep the environment safe, apply security updates and patches regularly.
Optimized Power Consumption
For longer battery life, optimal power conservation is required because many IoT devices are battery-powered or run in remote areas. Sleep mode availability and low-power components are examples of energy-efficient hardware design that helps prolong device function and save energy
Data Processing Capabilities
It should be possible for IoT hardware to process data locally, minimizing latency and reliance on cloud services. At the device level, on-device analytics and edge computing facilitate real-time operations, analysis, and decision-making. Memory and high-performance CPUs are essential for the effective operation of machine learning models and algorithms on the edge.
Ease of Maintenance and Deployment
Deployment, configuration, and management of successful IoT hardware are simple, which lowers setup and maintenance complexity. Plug-and-play capabilities make installation easier and enable devices to connect to the network and start up fast. Without having to communicate directly, administrators may upgrade firmware, solve problems, and keep an eye on the health of their devices with remote device management features.
Cost-Effectiveness
Specially for large-scale projects, cost considerations are crucial to the success of IoT technology. At a competitive price, it should offer the required features and performance at a good value.
Energy usage, maintenance, and improvements are all significant factors in long-term operating expenses. They can sometimes be counterbalanced by excellent design, but other times they might become an overwhelming load on the system.
Adaptability
Performant Internet of Things hardware is flexible and can be used in a variety of sectors and use cases. Modular designs and adaptable configurations make it possible to integrate with a variety of applications and satisfy particular needs. Variability in hardware features, including form factors, communication protocols, and sensor compatibility, should facilitate a range of Internet of Things solutions.
User-Friendly Interface
Web dashboards and mobile apps are examples of intuitive user interfaces that improve end users’ ability to use IoT hardware. User experience is enhanced by intuitive controls, visualizations, and warnings. The popularity of products is increased and interfaces are improved to satisfy the needs of various user groups with the aid of usability testing and user feedback.
IoT Hardware Development
For IoT hardware development, process management is just as crucial as its more technical components. A business can guarantee a strong basis for the success of its product by considering its primary phases and creating a coherent plan. Let’s quickly review these vital processes.
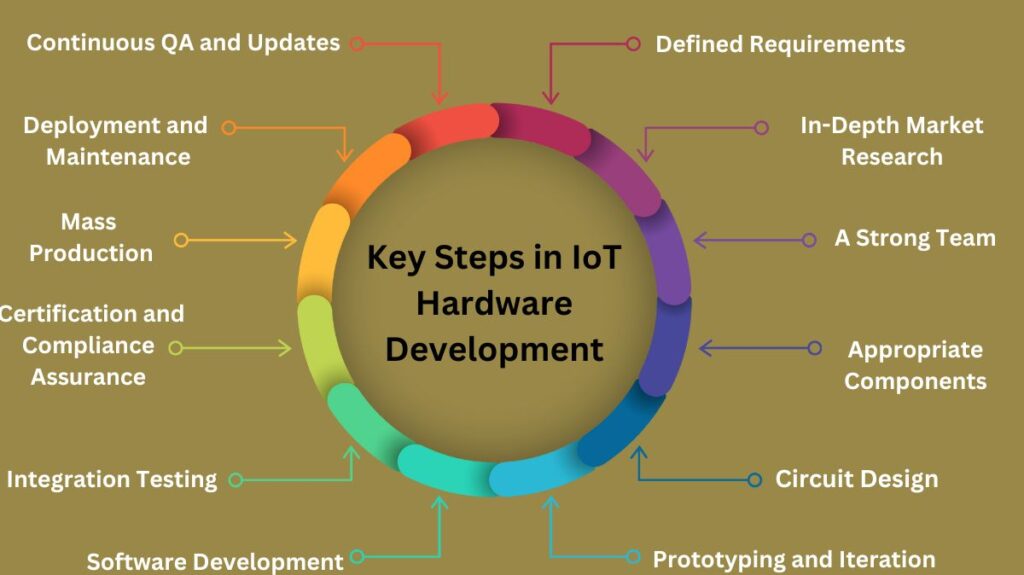
Step 1: Defined Requirements
Define the IoT device’s requirements precisely as the initial stage. This requires knowing the device’s purpose, operating environment, data it must collect, connectivity needs (cellular, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, etc.), and any size or battery constraints.
Step 2: In-Depth Market Research
Market research helps understand present products, competitors, and potential customers. To ensure a smooth post-production sales process, consider technical specs, expenditures, regulatory limitations, and consumer demand while assessing your IoT hardware project’s viability.
Step 3: A Strong Team
This need applies to every project including development. A team with data analytics, software development, hardware engineering, user experience design, and project management expertise is needed to develop IoT devices. Cooperate to meet company goals faster.
Step 4: Appropriate Components
The components required for the IoT device are selected by developers based on the needs. This comprises power supplies, sensors, actuators, communication modules, microcontroller or microprocessors, and additional auxiliary gear.
Step 5: Circuit Design
The circuit board layout is designed by engineers taking into account variables including signal integrity, power consumption, heat dissipation, and size restrictions. In order to generate the circuit board’s schematics and layout, CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software is used.
Step 6: Prototyping and Iteration
After the circuit design is finished, an IoT device prototype is constructed. This entails putting the device together after soldering parts onto a circuit board. Developers can test the device’s functionality, find any problems, and make the required changes gradually with the prototype.
Step 7: Software Development
In IoT devices, software engineering is just as important as hardware. This involves creating the firmware for the microcontroller or microprocessor of the device. The firmware regulates how the gadget communicates with other devices or servers, processes data, engages with sensors, and uses power.
Step 8: Integration Testing
To make sure the gear and software function as planned, the business then carries out a thorough testing process. Testing the device in various circumstances, examining its performance in various settings, and confirming its capacity to communicate with other devices or servers are standard procedures.
Step 9: Certification and Compliance Assurance
The market and application may determine which industry standards and regulations IoT devices must adhere to. Examples of certifications include those for data security, wireless communication standards, electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), and safety. When creating the budget for your IoT project, you must account for additional certification fees.
Step 10: Mass Production
Mass manufacture of the IoT gadget can begin after it has successfully completed all testing and certification criteria. This entails producing the hardware, putting the devices together, and maintaining constant quality control all the way through the manufacturing process.
Step 11: Deployment and Maintenance
In order to deploy the IoT devices to the users or locations they are meant for, you may need to configure devices, set up networks, and give user instructions. Frequent firmware updates and maintenance may also be required to guarantee the device’s continued security and proper operation.
Step 12: Continuous QA and Updates
Data analytics may be used to collect user input, track the effectiveness of the implemented solution, and uncover areas that require improvement. At this point, users anticipate frequent software upgrades, bug patches, and new features to improve your IoT hardware’s security and functionality.
Read more on What is IoT Hardware? & IoT Hardware Architecture Explained
