This is a comprehensive description of decentralised enterprises and the decentralisation idea behind the blockchain: What it is, its Characteristics, advantages, decentralized organization disadvantages, and the Hybrid Method are all discussed below.
What is a decentralized organization?
In the context of blockchain, a Decentralized Organisation (DO) is a kind of organisational structure that is implemented as a blockchain-based software application. In essence, these are software representations of conventional physical organisations, based on the idea of real organisations with personnel and procedures. Importantly, one of the main differences between DOs and Decentralized Autonomous Organisations (DAOs) is that DOs rely on human input to carry out their business logic, in contrast to completely automated organisations.
In a broader sense, a decentralized organisation is one that automates decisions and streamlines transactions without the need for a central authority by using an open computer program or platform and electronically preset rules. It denotes an organisational system in which medium or lower-level subordinates have been given decision-making authority by upper management. As a result, decisions can be made at lower levels of power without consulting higher-ups or centralised authorities.
Characteristics of decentralized organization (DO)
Software-Based Entity
A DO is essentially a software program that functions as a system in which separate computers coordinate and communicate with one another, giving the impression to the user that they are one single unit.
Blockchain Foundation
By utilising a blockchain’s built-in Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), DOs function on top of it. By ensuring data replication over several nodes, this allows participants to communicate with one another without depending on a single central authority. DOs are supported by the fundamental advantage of blockchain technology, decentralization, which enables platforms with numerous leaders selected by consensus processes and no middlemen.
Dependency on Human Input
One important difference between DOs and DAOs is that the former lack complete autonomy and rely on human input to carry out their business logic, whilst the latter strive for complete automation.
Capital and Ownership
DOs are usually “owned” and have “capital” attached to them.
Legal Status
Like other blockchain-based organisations like DAOs and Decentralized Autonomous Corporations (DACs), the legal status of DOs is still up for debate in a number of jurisdictions.
Expense
When compared to DAOs, DACs, and Decentralized Applications (DApps), the expense of implementing a DO is deemed to be “High”.
Relationship with DApps
DApps are software applications that run on a decentralized network, frequently a distributed ledger. DOs are seen as a more general category of DApps. DApps, which stand for developments in decentralization technology, include DAOs, DACs, and DOs.
Differentiation from Decentralized Autonomous Organisations (DAOs)
Although they both use blockchain technology, DOs and DAOs vary mainly in how much human intervention they require:
Human Input vs. Complete Automation
The primary distinction is that DOs lack complete autonomy and depend on human input for their business logic. A Decentralized Autonomous Organisation (DAO), on the other hand, is intended to function entirely or in part through decentralized computer programs. Voting and financial management are handled by decentralized ledger technology, such as a blockchain, and the organisation frequently strives for no human administrative interaction after it is placed into operation.
Decision-Making in DAOs
Since DAOs lack a central authority, community members usually token holders who vote share power. Transparency is ensured by posting all votes and DAO activities on a blockchain. Once the necessary number of votes is obtained, DAOs use smart contracts to automate group decisions. These contracts can even automate token transfers from a treasury. The amount of tokens owned is frequently correlated with voting power.
Security and Governance Issues in DAOs
DAOs’ immutable blockchain code makes bug patches difficult and exposes security holes to exploitation, causing security and governance difficulties. Ethereum flaws allowed the 2016 DAO breach to steal $50 million in bitcoin. The network was fixed via a controversial Ethereum hard fork after this hack.
Furthermore, token concentration may result in power concentration, which could jeopardise distributed governance and leave it vulnerable to hostile takeovers. The DAO subsequently offered stocks in violation of U.S. law, according to the U.S. stocks and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Advantages and disadvantages of decentralized organization
Decentralized organization advantages
General benefits of decentralization apply to different organisational forms, including blockchain-based DOs:
- Empowerment and Motivation: Flexibility and responsibility enhance morale, job satisfaction, and production. Valued workers have input on corporate operations.
- Exploration and choice increase creativity and innovation by embracing varied perspectives and ideas.
- Lower-level decision-making accelerates market and customer adjustment. This reduces bureaucratic bottlenecks.
- Decentralization improves communication by allowing direct system-human connection.
- Expansion: Local businesses’ understanding of the area might help growing companies.
- Better control and supervision: Lower-level managers can locally change task allocations and production schedules.
- Decreased Stress and Bureaucracy: Top executives can concentrate on important strategic decisions rather than pointless ones when there are fewer levels of hierarchy, which speeds up decision-making.
- Top management can take time off and the absence of a team member has less of an impact on production because pressure is shared.
- Scaling is easier when local workers handle daily tasks and high management doesn’t have to oversee everything.
- Encouragement to decide improves leadership.
- Increased Customer-Centricity: Teams closer to customers may respond to input and make changes faster, providing specialised customer care and a competitive edge.
Also Read About What Is Solidity In Blockchain? Introduction To Overview
To efficiently allocate resources, autonomous teams may assess their needs, eliminate waste, and ensure projects have the right people working on them at the right time.
Decentralized organization disadvantages
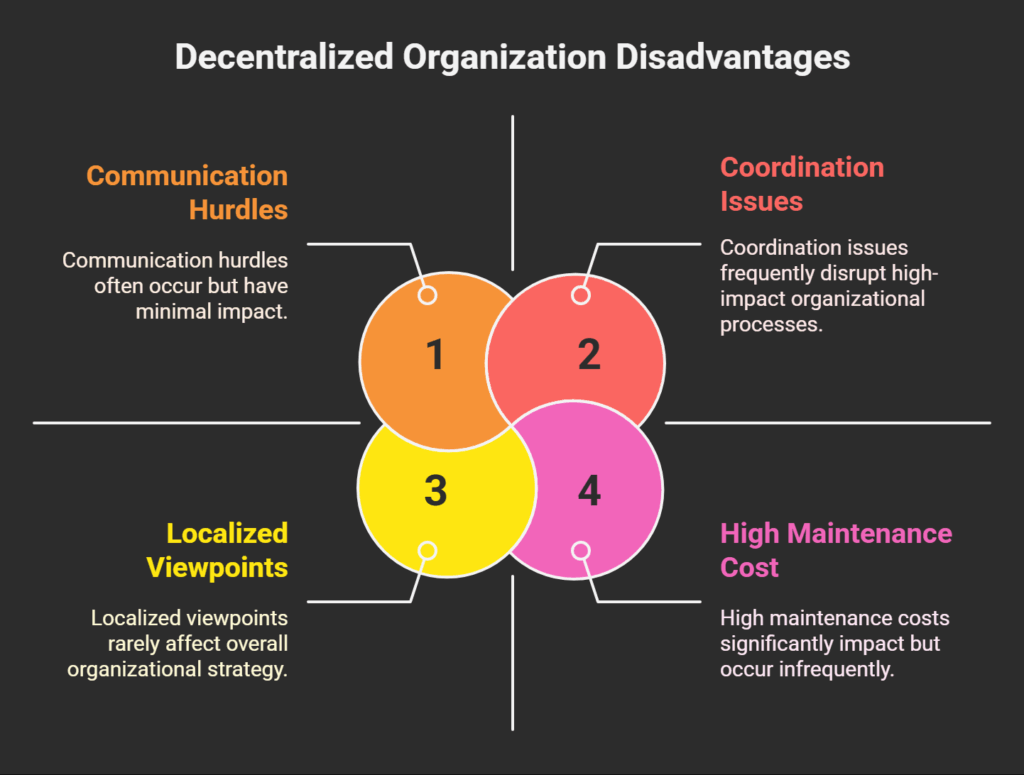
Coordination Issues
When teams or divisions have too much autonomy, coordination issues may arise.
High Maintenance Cost
Decentralized networks can be expensive to build up, maintain, and operate. Errors committed by accountable workers can also be expensive, and seasoned workers who can accept accountability may be paid more.
Concerns about Central Control and Consistency
Businesses that need rigorous compliance or consistent brand messaging may be at danger from a reduction in central control and overall consistency. If decisions are not appropriately led, they may conflict with the company’s basic strategy.
Organisational Silos
Units or teams may separate and concentrate only on their own aims, which can be harmful to cooperation amongst teams and the pursuit of common objectives.
Risks of Poor Leadership
Although it promotes leadership, inexperienced leaders may make poor choices that harm the company’s standing.
Communication hurdles
Although excessive autonomy may allow for free-flow, it can also result in ambiguity and communication hurdles because of disparate approaches.
Higher Team-Wise Expenses
Hiring and operating costs go up when managers are needed to oversee operations across many teams at all levels.
Waste of Resources by Service Functions
Serving personnel at various levels may necessitate separate teams, which results in redundancies and excess resources.
Localised Viewpoints
Local managers’ decisions may solely address the demands of a single branch, which could prolong the operation of unprofitable branches longer than intended.
Information Silos
Knowledge transmission across units may be minimised if important information or effective processes stay local.
Distinct Procedures
The company’s overall quality standards may be challenged if several teams or branches implement completely distinct procedures.
Hybrid Method
In order to balance the benefits and drawbacks of each strategy, many organisations really use a hybrid method that combines aspects of centralization and decentralization. This seeks to design a framework that best meets their unique requirements and objectives. Central control is frequently maintained over functions that are essential to the organization’s protection (such as legal and risk), development of its value agenda (such as branding and strategy), and sharing of economies of scale (such as payroll, IT, and accounting). Instead of demanding control, leaders in decentralized organisations must take a different approach, serving as mentors and educators, creating a common goal, and offering context.
