What is Decentralized communication?
Systems for data transmission, messaging, and phone calls that function without a central server or authority are referred to as decentralized communication. Rather, they use peer-to-peer (P2P) networks and blockchain technology to safely send data. Giving users total control over their data transactions is the goal of this strategy.
Decentralized Communication importance
Conventional online communication, like email or popular messaging apps like Telegram or WhatsApp, depends on central middlemen like servers that are owned and managed by the corporation. The controlling firm has enormous influence over user data, privacy, and even the potential to censor messages because to this centralized architecture. It generates dangers including censorship (blocking or monitoring messages), privacy violations (collecting and selling data), and single points of failure (the service ceases if a server goes down). Eliminating this one point of control is the goal of decentralized communication.
How Decentralized Communication Works?
Decentralized communication creates safe and trustless channels by combining P2P protocols, blockchain, and cryptography.
Important ideas and procedures consist of:
Networks that are peer-to-peer (P2P)
P2P networks are fundamental to decentralized communication. Users speak with one another directly or via a network of separate nodes rather than submitting messages to a central server. Every participant relays and processes messages in the roles of both a client and a server. By establishing several channels of communication, this strengthens the network against the loss of any one member. BitTorrent and the original internet concept are two examples.
Absence of central data storage or servers
Decentralized communication seeks for messages to predominantly reside on users’ devices or be routed over transient, dispersed networks, in contrast to traditional systems where messages are retained on business servers. This reduces the possibility of mass spying and data breaches. Nodes in the blockchain network manage message routing and validation in a decentralized system, taking the place of a central server.
Security of Cryptography
One essential element is end-to-end encryption (E2EE). Even if communications are intercepted, privacy is maintained because they are encrypted on the sender’s device and only the intended recipient can decrypt them. Users, not a business, create and maintain the encryption keys. Cryptographic key pairs (public and private keys) are frequently used to identify users rather than usernames or phone numbers. Communication between nodes is authenticated and secured by cryptographic means.
Resistance Against Censorship
It is significantly more difficult for governments or businesses to filter communications or limit access when there is no central authority to shut down or control the network.
Dispersed Ledgers
The underlying data (or metadata) can be stored on a distributed ledger, even while peer-to-peer communication takes place directly. This ledger, which is visible and continuously synchronized throughout the network, is kept in identical copies by each entity on the blockchain.
Mechanisms of Consensus and Broadcasting
When a user sends a message or starts a transaction, it is usually broadcast to all or many nodes on the network. Using a consensus technique, these nodes jointly verify the transaction or communication according to predetermined guidelines. This guarantees that all nodes eventually possess identical, precise data. In order for nodes to agree on the current state of the blockchain and ensure that the ledger is updated safely, decentralized communication protocols are essential for reaching consensus in blockchain networks.
Side-channel/off-chain operations
Certain conversations or transactions may take place off-chain, or outside the main blockchain, in temporary “side channels” in order to address scalability and privacy concerns. All that is subsequently reported to and documented on the main chain is the ultimate result or a synopsis of these exchanges.
Protocol for Gossip
Often, a “gossip protocol” is used to disseminate information among peers. In order to improve anonymity and hide the origin of transactions, this approach entails nodes individually adding delays when distributing transactions to their neighbors. It ensures that all nodes receive the same information and stay in sync by spreading new transactions and blocks around the network in a blockchain.
How Blockchain Integrates
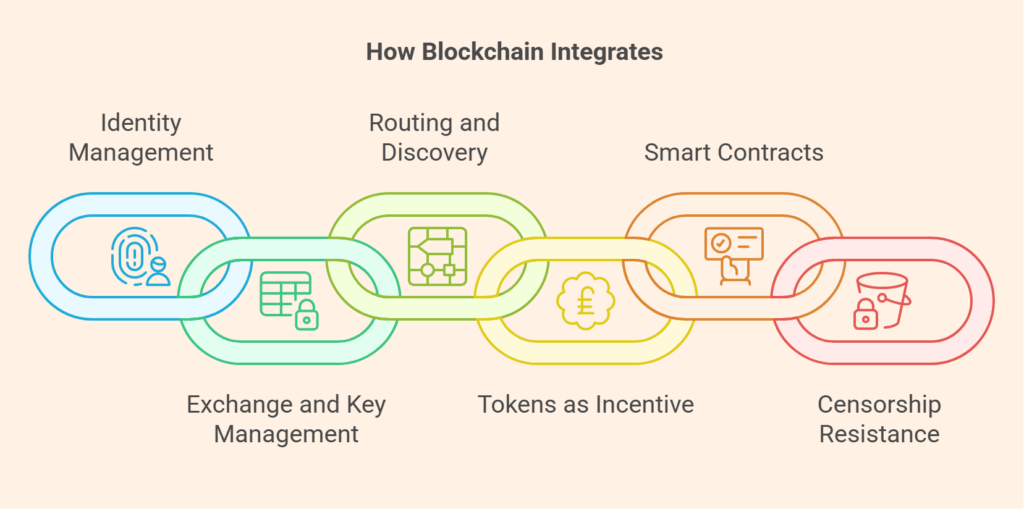
The blockchain serves a number of vital roles in facilitating and safeguarding decentralized communication, even if it is typically not used to store the actual message content (due to scalability and privacy concerns):
Management of Identity (Decentralized Identifiers, or DIDs)
For decentralized identities, blockchain can act as an impenetrable and safe ledger. A self-sovereign digital identity governed on a blockchain can be used by users in place of a centralized authority (such as Google or Facebook) to validate identity. DIDs on the blockchain can be connected to public keys for communication, granting users control over their online persona and enabling identification verification by third parties without the need for a central arbiter.
Exchange and Key Management
Blockchain makes it easier to handle and securely trade the cryptographic keys required for end-to-end encryption. On-chain management or recording of public keys or references to important content guarantees its availability and authenticity.
Routing and Discovery (Metadata)
Certain metadata like communication channels, user presence, or route information may be maintained on-chain even while message content is not. This facilitates node discovery and effective decentralized message routing without disclosing private information. Blockchain is frequently combined with protocols like the Gossip Protocol or Kademlia DHT (Distributed Hash Table) to facilitate node discovery and communication in a peer-to-peer network. Blockchain can hold durable discovery data or assist in bootstrapping these networks.
Tokens as an Incentive
Tokens are used by certain decentralized communication networks to reward nodes, or network participants, for storing data, relaying messages, and maintaining network infrastructure. In order to create a self-sustaining ecosystem, users may pay tokens for messages, and nodes receive tokens for rendering services.
Advanced Features with Smart Contracts
Blockchain-based smart contracts can control group chat memberships, impose regulations on conversation, or enable micropayments for particular communication services (such premium features or access to special channels).
Resistance to Censorship (Public Key Infrastructure/Registry)
Delisting a user or preventing them from communicating is made considerably more difficult by a blockchain’s decentralized, unchangeable record of public keys and identities. Users can take part as long as they have access to the decentralized network.
Also Read About What Is Astar Network, Advantages And Disadvantages
