This article explains about the Meaning And Context In NLP.
Since meaning and context are intricately linked to the fundamental components of language, comprehending language in Natural Language Processing (NLP) requires battling these ideas.
Meaning in NLP
The ultimate goal of NLP systems is sentence understanding. Context, lexical information, parsing findings, and common sense reasoning all play a part in the intricate process of understanding meaning.
Semantic analysis in general linguistics is the study of interpreting words, fixed expressions, entire sentences, and words in relation to their context. Translating original words into a semantic meta-language or comparable representational system is frequently the approach. In NLP, semantic analysis seeks to understand words, phrases, and sentences in their literal sense. But for many real-world NLP applications, depending only on truth-conditional meaning generated from philosophical logic is frequently too limited. An object’s meaning might be derived from its context in common knowledge or from its name, which can be taken literally.
Among the crucial elements of meaning analysis in NLP are
- In the NLP pipeline, semantic analysis comes after lexical and syntactic analysis. Meaning representation is its focus. When a deeper comprehension of context and semantics is needed for activities like question answering, language translation, and content summarization, semantic analysis is essential. Applications such as machine translation, text summarization, information extraction, and retrieval also benefit from it.
- Word senses and other word meanings are included in lexical semantics. In lexical analysis, a fundamental objective is to relate morphological variants to their lemma, which contains semantic information that is constant.
- Logic is frequently used to convey compositional semantics, which is the process of creating meaning from syntax. The meaning of a sentence or phrase, for example, is made up of the meaning of its constituent elements when using a compositional method.
- Using formalisms such as predicate logic, semantics can be abstractly represented as a logical form. To describe the meanings of lexical items and text-meaning representations, ontologies can also be used to construct concepts.
- Ambiguity: Given that words may have numerous meanings (lexical ambiguity) or phrase patterns may be interpreted in different ways (scopal, referential ambiguity), ambiguity is a significant difficulty in NLP. The same string may have multiple meanings in natural languages, which is rife with ambiguity.
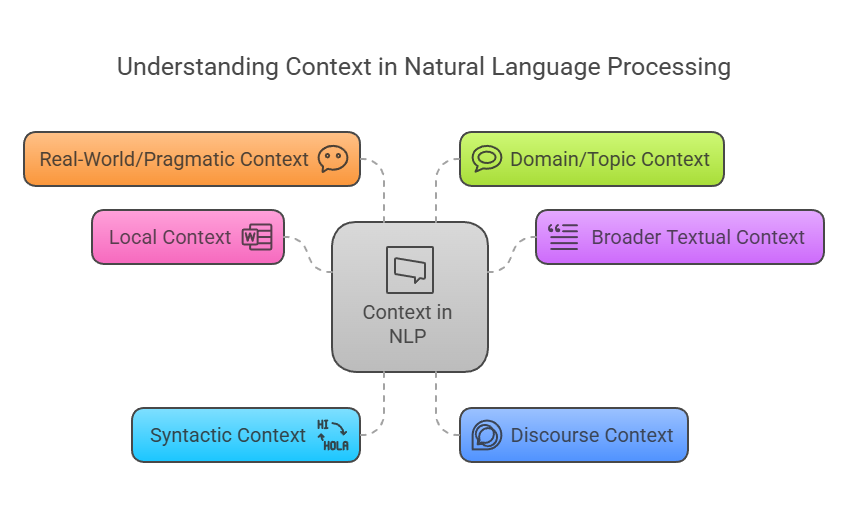
Context in NLP
Resolving linguistic ambiguity and figuring out the intended meaning of words, phrases, and sentences depend heavily on context.
NLP uses various levels and kinds of context:
- The words that are immediately surrounding the target word within a narrow window are referred to as the “local context.” Ordered phrases that are close to a word are known as local collocations, and they might offer semantic context for disambiguation. In particular, local context is helpful for activities such as part-of-speech tracking.
- The full sentence, paragraph, or page in which a word appears can be considered the “broader textual context.” Determining a word’s semantic sense inside a section of speech can frequently be accomplished with the help of distant content terms in the larger context.
- Syntactic Context: Data that demonstrates the links between words in a sentence by utilising its grammatical structure, or parse tree. In terms of semantic interpretation, this can be extremely important.
- Discourse Context: The preceding and following sentences might influence a sentence’s meaning. How the present sentence’s meaning connects to the text or discussion at hand is processed through discourse integration.
- Real-World/Pragmatic Context: Interpreting the text or utterance in the context of the particular circumstance in which it occurs. Applying practical analysis entails reinterpreting statements in light of existing information.
- Domain/Topic Context: The general subject or domain of the text might reveal a word’s most likely meaning.
The Relationship: Meaning in Context
The Distributional Hypothesis, which states that a word’s meaning can be deduced from its context, is central to statistical natural language processing. This implies that words with comparable meanings are frequently found in instances that are similar. A large portion of statistical NLP research is grounded in this philosophical stance, which is consistent with Wittgenstein’s use theory of meaning. Word-context matrices, which represent words as vectors depending on the circumstances in which they occur, are one technique that captures these distributional features.
The comprehension of meaning in context is specifically required for several NLP tasks
- Finding the meaning of an ambiguous word in a given context is known as word sense disambiguation, or WSD. WSD is thought of as a contextualised similarity task that tells you a word’s meaning in many contexts.
- Named Entity Recognition (NER): This method recognizes and categorizes names of people, places, organizations, etc., often requiring context.
Semantic similarity: comparing context and meaning in two texts
Context plays a major role in contemporary NLP techniques, especially those that use deep learning. Word or token meanings in their particular textual context are represented by contextual embeddings, which are produced by pre-trained language models. The general meaning of a word type was expressed by prior “static” embeddings, which are different from these. These days, contextual embeddings are essential to contemporary algorithms for tasks like Word Sense Disambiguation and other uses where contextual word meaning comprehension is necessary.
Meaning is the ultimate goal of language comprehension, but context offers the crucial details required to clear up ambiguities and correctly interpret that meaning in everyday language use.
