This article gives an Overview of Benefits Of Polkadot, Disadvantages, Applications, Features And How It Work’s.
Polkadot (DOT)
Polkadot (DOT), a popular blockchain project, was designed to construct decentralized Applications and other blockchain initiatives. Its goal is to construct a decentralized internet of blockchains, or Web3, by enabling middleman-free data transit and communication between blockchain networks. This inventive design addresses blockchain technology’s scalability, interoperability, and security challenges. Polkadot is a layer-0 metaprotocol that supports and formats a network of layer 1 blockchains, allowing it to forklessly update its codebase via on-chain governance.
Polkadot History and Founders
Peter Czaban and Gavin Wood, an Ethereum co-founder who first used the phrase “Web3” in 2014, founded Polkadot. Another co-founder is Robert Habermeier, a blockchain and cryptography researcher and developer. In 2016, Wood released the Polkadot white paper. Since its founding in 2017, the Web3 Foundation a nonprofit organization devoted to Polkadot’s advancement has raised more than $200 million from the sale of DOT tokens.
The first version of the Polkadot network was released on May 26, 2020, and the first five parachains were released on December 17, 2021, marking the network’s full debut.
How Does Polkadot Works: Core Architecture and Components
Polkadot is a sharded multichain network controlled by a Relay Chain. This architecture lets it process data and transactions on many chains, increasing its scalability. The network’s unique infrastructure includes several key components:
Relay Chain: The “heart of Polkadot” is the main blockchain. Network consensus, interoperability, and shared security are its main responsibilities. The Relay Chain processes transactions, obtains consensus, and verifies data, but it is intentionally less useful. Organization, governance, parachain slot auctions and leases, and staking are its main goals when giving functions to parachains.
Parachains (Parallel Chains): These specialized blockchains connect to the Relay Chain. Different use cases can require different governance, tokens, and functionality on each parachain. Connecting to the Relay Chain lets parachains use the network’s security without having to design their own. Few parachain slots exist; Polkadot can support 100–250 parachains, reports say. DOT tokens are used as collateral in “candle auctions” to lease these spots to projects. DOT tokens are locked for the parachain lease and returned at the end if a project succeeds. Parachains processed millions of transactions in 2024.
Parathreads: Parathreads, like parachains, offer a pay-as-you-go connectivity option for blockchains without a constant Polkadot connection. This helps scale the network by letting competitor parathreads share parachain slots.
Bridges: By allowing the transmission of data and tokens between parachains and parathreads and external blockchain networks like Bitcoin and Ethereum, these promote interoperability. Bridges enable the exchange of various coins and tokens without the need for a central exchange.
Substrate Framework: The blockchain development framework Substrate, offered by Polkadot, makes the process of creating new blockchains a lot easier. Developers can expedite development and time to market by customizing their chain architecture and plugging in necessary functionalities. Every chain constructed using Substrate is made to work with Polkadot’s environment.
Consensus Mechanism (Nominated Proof-of-Stake – NPoS)
Polkadot secures its network with a consensus method called Nominated Proof of Stake. This mechanism plays a number of important roles:
Nominators: Participants that designate their stake to reliable validators and stake their DOT tokens. A portion of the staking rewards produced by their selected validators are given to them. Validators can have a percentage of their staked DOT “slashed” for misconduct, therefore nominators are urged to choose their validators carefully.
Validators: These participants take part in reaching network consensus, stake their DOT, and verify collators’ evidence. They create new blocks, verify transactions from parachains on the Relay Chain, and guarantee the finality of transactions. Validators receive prizes for good behaviour and punishments (slashing) for bad behaviour.
Collators: They keep track of all legitimate parachain transactions and maintain complete nodes for their individual parachains. These transactions are combined by collators to create fresh block candidates that validators can then check on the relay chain. Because they recognise one another as peers on the Relay Chain, they are also essential for cross-chain messaging (XCMP).
Fishermen: These “watchdogs” keep an eye out for malicious collator activity or invalid transactions on the network and alert validators to them. They risk losing their staked tokens if their reports are incorrect, but they stake less tokens and get a significant payout if their reports turn out to be accurate.
Polkadot also employs a hybrid consensus technique that separates block production from finality. It is powered by two mechanisms: GRANDPA, which achieves on-chain finality, and BABE, which creates new blocks.
What is DOT Token
The DOT coin, the native cryptocurrency of the Polkadot network, has three main functions:
Staking: Network participants are encouraged to behave honourably by DOT, which serves as collateral for good behaviour. Users can receive rewards by staking DOT, and Polkadot is known for providing large yearly staking rewards estimated at more over 13%. According to one report, more than half of the DOT tokens that qualified were staked.
Governance: By voting on proposals and referenda, DOT holders are given the opportunity to take part in the network’s decentralized governance. The weight of their votes is determined by the number of DOTs they have staked. In order to give the community complete voting authority and do away with earlier centralised components like the Polkadot Council and Technical Committee, Polkadot launched OpenGov in June 2023. OpenGov allows any token holder to submit proposals, which are subsequently put to a vote. “Origins and Tracks” assigns a proposal’s priority in order to decide the proper safeguards and timeframes for deliberation.
Bonding: Parachain slots are leased and “coretime” is reserved through DOT. Projects vying for parachain spots at auctions also utilize it as security, with tokens locked for the term of the lease. In an effort to reduce entry barriers and enable more parachains, the Agile Coretime upgrade (September 2024) permits parachain developers to buy coretime in bulk and sell portions of it.
The DOT currency, which is intended to encourage the network and dynamically adapt based on staking participation rates, is inflationary, with an anticipated 10% annual rise in the amount of tokens. There were roughly 1.59 billion and 1.099 billion DOT tokens in circulation.
Benefits of Polkadot
Polkadot addresses “three significant obstacles hindering the growth of blockchain technology: decentralization, scalability, and security”.
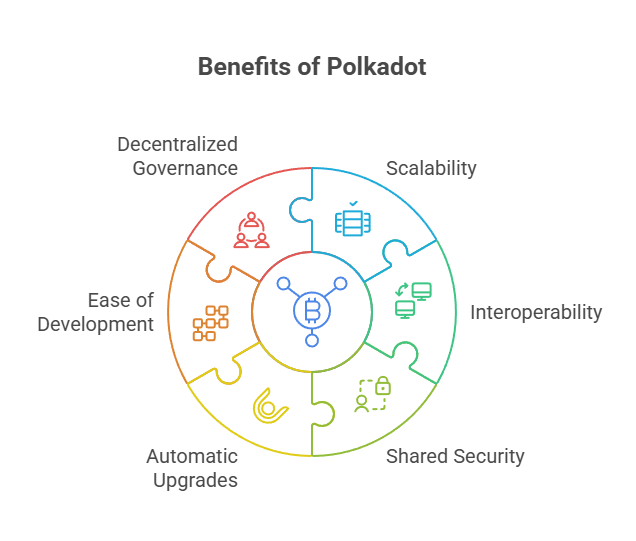
Scalability: Polkadot has a theoretical maximum of one million transactions per second (TPS), with an estimated 1,000 TPS. It can process more than 150,000 transactions per second. Its parallel processing and sharded architecture are intended to avoid congestion and bottlenecks, significantly increasing throughput.
Interoperability: Polkadot facilitates smooth, middleman-free communication and data transfer between disparate networks by allowing interaction between wildly disparate blockchain topologies. It can link oracles, permissionless networks, and public and private chains.
Shared Security (Pooled Security): The Relay Chain’s strong security benefits parachains by removing the need for separate projects to set up their own security measures.
Automatic Upgrades: Through on-chain governance, Polkadot may update its codebase on its own without the need for hard Forks, making bug patches and network evolution easier. It is hence very adaptive and flexible.
Ease of Blockchain Development: Because the Substrate architecture makes it easier to create new blockchains, developers can concentrate on improving their projects rather than creating infrastructure from the ground up.
Decentralized Governance: The network features an advanced user-driven governance structure that encourages decentralization by giving all DOT token holders a say in how the network is managed.
Polkadot Disadvantages
Limited Parachain Slots: Auctions are used to lease the limited amount of parachain slots, which are believed to be between 100 and 250. Smaller initiatives with less money may find it difficult to obtain their own parachain slots due to this competitive mechanism, which favours those with substantial financial resources.
Governance Concentration Risk: The governance structure is stakeholder-weighted despite being dispersed. Since DOT must be locked down in order to make, second, or vote on proposals, the people and businesses with the most DOT tokens have a big say in the initiative.
Stiff Competition: Other well-known and well-established blockchain platforms like Ethereum, Cardano, and Solana pose a serious threat to Polkadot.
Complexity: The Polkadot ecosystem is “interesting, but complicated” despite its creative nature.
Volatility and Uncertainty: It is difficult to forecast DOT’s price because, like all cryptocurrencies, it is influenced by economic factors and market sentiment. Like many blockchain projects, its future is uncertain.
What are some Use Cases of Polkadot
With multiple projects developing within its framework and spanning a variety of applications, Polkadot cultivates a thriving ecosystem:
Decentralized Applications (dApps): Polkadot gives developers the tools they need to create dApps and incorporate smart contracts over an interoperable network.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi): The ecosystem includes projects such as Acala, a stablecoin platform and cross-chain DeFi hub.
Oracles: As its main oracle provider, Chainlink is one of Polkadot’s notable partnerships with oracle technology.
Digital Collectibles (NFTs) and Gaming: Polkadot encourages the growth of initiatives in various fields.
IoT and Privacy: These industries can benefit from the platform’s versatility, which makes a range of use cases possible.
Cross-chain Solutions: Polkadot is made to make it easier for any kind of asset or data to move across shards, resulting in a seamless blockchain environment.
Alternative Payment Methods: Decentralized payments using DOT provide greater control over money and a substitute for costly and time-consuming international transfers.
A new era of cross-chain interoperability rather than separate protocols is being fostered by Polkadot, which is frequently viewed as enhancing current blockchains rather than competing with them.
Kusama: The Network of Canaries
Polkadot’s “canary network” or experimental development platform is another name for Kusama. Before features are released to Polkadot, it acts as a live testnet and proving ground for early deployments and battle-testing in real-world scenarios. For initiatives that wish to proceed swiftly or have a reduced financial barrier, Kusama is a good choice because it offers fewer economic barriers to entry and a faster governance speed than Polkadot.
How to Acquire and Store DOT
DOT tokens are available on a number of cryptocurrency exchanges, such as Binance, Coinbase, Kraken, and Gemini. You can use Cryptocurrency exchanges, peer-to-peer services, or cryptocurrency ATMs in some situations for direct purchases. Note that tokens that appear on some exchanges may be “wrapped or pegged versions of DOT” that were developed on a separate network.
Once obtained, your DOT can be kept in a variety of digital wallets. Software wallets like Fearless, Polkawallet, Polkadot-JS Plus, or Polkadot Vault (which can be loaded on an old smartphone for cold storage) and hardware wallets like Ledger (used with Polkadot-JS web wallet) are available options. You are in charge of your private key, which serves as a password to your money when you use a decentralised wallet.
