Middleware in NodeJS Express Functions
The Express.js framework relies heavily on middleware methods, which serve as a potent way to process requests before they are sent to the final route handler. These routines can access the following middleware function in the application’s request-response cycle, which is typically indicated by next, as well as the request object (req) and response object (res).
Custom Middleware
Since it’s just a function that takes as inputs req, res, and next, writing your own custom middleware is easy.
Logging Request Times, for instance Custom middleware is frequently used to log incoming request details, including the timestamp, HTTP method, and URL route. One way to do this would be to write a logger middleware that logs the current time, the request method (req.method), and the request URL (req.path or req.originalUrl) to a file or Console. To transfer control to the following method in the chain after logging, next() is invoked.
// Example of a custom logging middleware
app.use((req, res, next) => {
const now = new Date().toString(); // Get current timestamp
console.log(`${now}: ${req.method} ${req.path}`); // Log method and path
next(); // Pass control to the next middleware/route
});A permanent record of server activity can be created by extending this feature to write log messages to a file using Node.js’s fs module.
Common Use Cases for Middleware in NodeJS Express
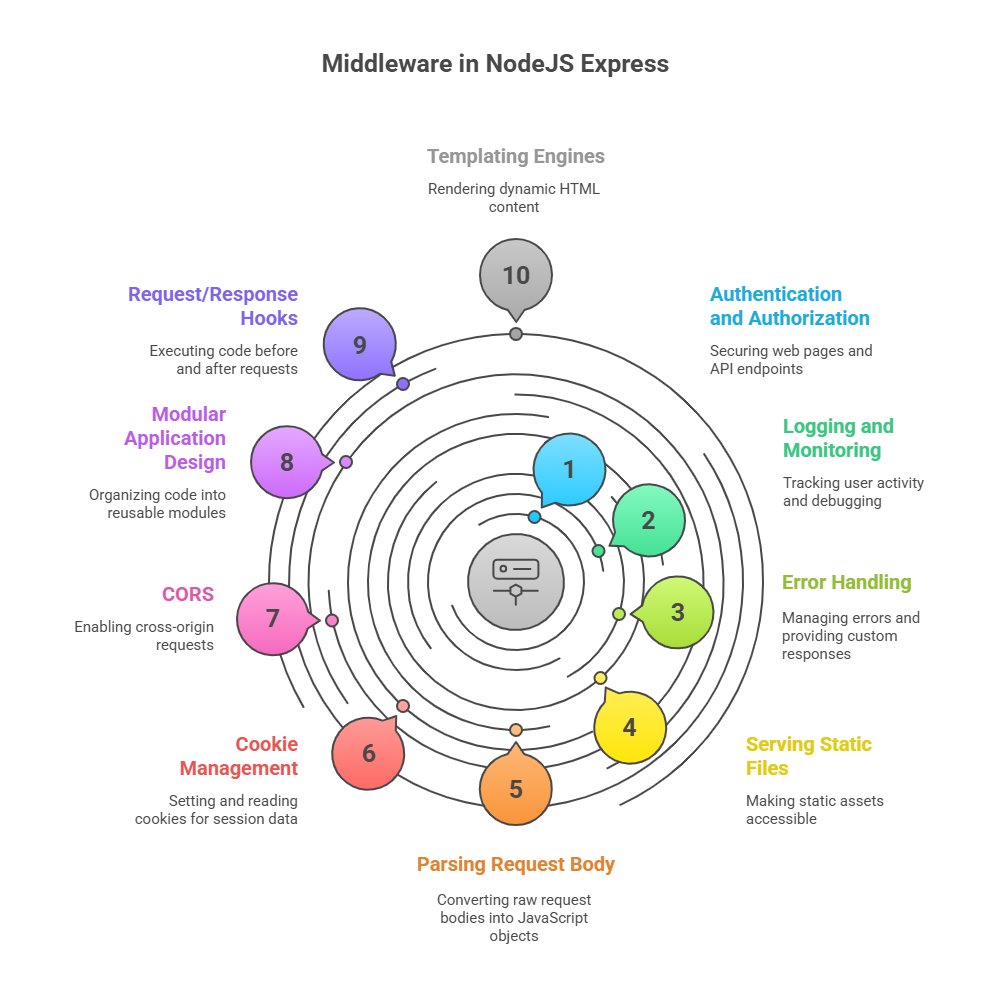
Middleware serves a number of functions and is essential to creating reliable Express applications.
- Authentication and Authorization: Middleware features are essential for protecting web pages and API endpoints. They can verify if a user is authorised (for example, using a session or JWT) before granting them access to a route. For example, the well-known module
passport.jsemploys middleware for authentication. In the event that authentication is unsuccessful, the middleware can send an HTTP 401 (Unauthorised) status without usingnext(), thus cutting off the request-response cycle. - Logging and Monitoring: Logging is a fundamental use case, as seen using bespoke middleware. This assists developers in tracking user activity, debugging problems, and monitoring the health of applications.
- Error Handling: When it comes to error management, Express offers a unique kind of middleware that is identified by its four arguments:
err,req,res, andnext. Usually defined at the very end of the middleware stack, these handlers are used to capture failures from earlier functions. They make it possible to render particular error pages (such a 404 “Not Found” page), log the error stack, and provide custom error answers. - Serving Static Files: With the
express.staticmiddleware, Express makes it easier to serve static assets (such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, pictures, etc.). Through the use of specified URLs, this middleware makes the contents of a directory accessible. Even more, you can define more than one static folder. - Parsing Request Body: Middleware such as
body-parseris necessary for managing data sent in the body of HTTP requests (such as POST, PUT, and DELETE). The raw request bodies are parsed into a JavaScript object that may be used by accessingreq.body. - Cookie Management: Setting and reading cookies is made simple for Express apps by the
cookie-parsermiddleware. For preserving session data or saving user preferences, this is essential. - Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS): Issues with Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) may occur when developing APIs that are used by apps across various domains. Enabling CORS support using middleware, such the
corsmodule. - Modular Application Design: The use of middleware, particularly in conjunction with Express’s
routerfactories, encourages the development of modular and reusable code. Large applications can be better organised by breaking them up into separate files (e.g.,user.model.js,user.route.js,user.controller.js,user.service.js). - Request/Response Hooks: Middleware can be used to execute code before any request and after any response. This is achieved by using
app.use()for ‘before’ actions and listening tofinishandcloseevents on theresobject for ‘after’ actions. - Templating Engines: The rendering of dynamic HTML content is made possible by the use of middleware to customise and integrate templating engines such as Jade (formerly Pug), EJS, Handlebars, Nunjucks, or Mustache.js.
Through the use of middleware, Express offers a versatile and strong foundation for creating web apps and APIs, simplifying and scaling complicated features.
