What is Casper Network

With a significant emphasis on enterprise adoption and developer accessibility, the Casper Network is a Layer-1 Proof-of-Stake (PoS) blockchain. By providing capabilities that tackle typical issues encountered by current blockchain solutions, it seeks to close the gap between blockchain technology and conventional business requirements. This CasperLabs project launched on its mainnet in March 2021.
Fundamental Goals: Casper Network will solve old blockchain issues like low scalability, high energy consumption (a common issue with Proof-of-Work systems like Bitcoin), and business challenges when integrating blockchain technology or upgrading smart contracts. It’s scalable, energy-efficient, and future-proof to satisfy public and private sector needs.
Key Features of Casper Network
- The Proof of Stake (PoS) consensus model is used by Casper Network in contrast to the energy-intensive Proof-of-Work (PoW) blockchains. Accordingly, the quantity of CSPR tokens that validators “stake” as collateral determines which validators are selected to generate new blocks and validate transactions. This makes Casper a more ecologically friendly blockchain and leads to a much reduced energy consumption.
- Highway Protocol: the Correct-By-Construction (CBC) Casper research serves as the foundation for Casper’s unique consensus procedure. More finality criteria and flexibility are achievable with Highway than with traditional Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) models. Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) design allows it to function safely even if up to one-third of the validators are malicious or flawed.
- Dynamic Round Length: To promote effective message whispering and timely block additions, the Highway protocol dynamically modifies the duration of a “round,” or the time frame during which validators agree on a block.
- Upgradable Smart Contracts: Casper’s standout feature. An immutable smart contract is usually put on a blockchain. If developers and businesses need to repair issues, add functionality, or comply with new legislation, Casper lets smart contracts be changed without disruption or rebuild.
- Scalability: Casper’s design handles many transactions. Sharding transactions among smaller groups of nodes improves network efficiency and allows parallel processing.
- Security: Casper prioritizes security, using PoS and robust protocols to thwart attacks like as the 51% attack. Because cheating puts validators at risk of losing their staked tokens (slashing), they are financially motivated to operate honourably.
- Enterprise Focus: Casper is made especially for business use, whereas many blockchain systems are made mostly for cryptocurrency aficionados. With its scalability and upgradeability features, organizations can more easily incorporate blockchain technology into their operations without being constrained by a high learning curve. It provides tools for compliance and security and supports private or permissioned networks.
- Developer-Friendly: Popular programming languages like WebAssembly (WASM) and Rust are supported by Casper for creating smart contracts. Developers accustomed to mainstream languages will find it easier to expand on Casper as a result of the skill pool being expanded. Even a “Caspiler” tool for converting Solidity code to Rust has been developed by CasperLabs.
- Predictable Gas Fees: Casper wants to provide firms who must budget their operations without having to deal with fluctuating prices with consistent and predictable transaction (gas) fees. Gas reimbursements and even gasless transactions are covered by Casper 2.0 plans.
- On-Chain Governance: Casper allows CSPR token holders to participate in decision-making processes for the network’s evolution and upgrades, decentralizing control.
- Modular Architecture: Casper separates core blockchain functions (like consensus, data storage, and transaction execution) into distinct layers, enhancing flexibility, scalability, and efficiency.
You can also read Disadvantages of Zero Knowledge Proofs And It’s Applications
How Casper Network Works
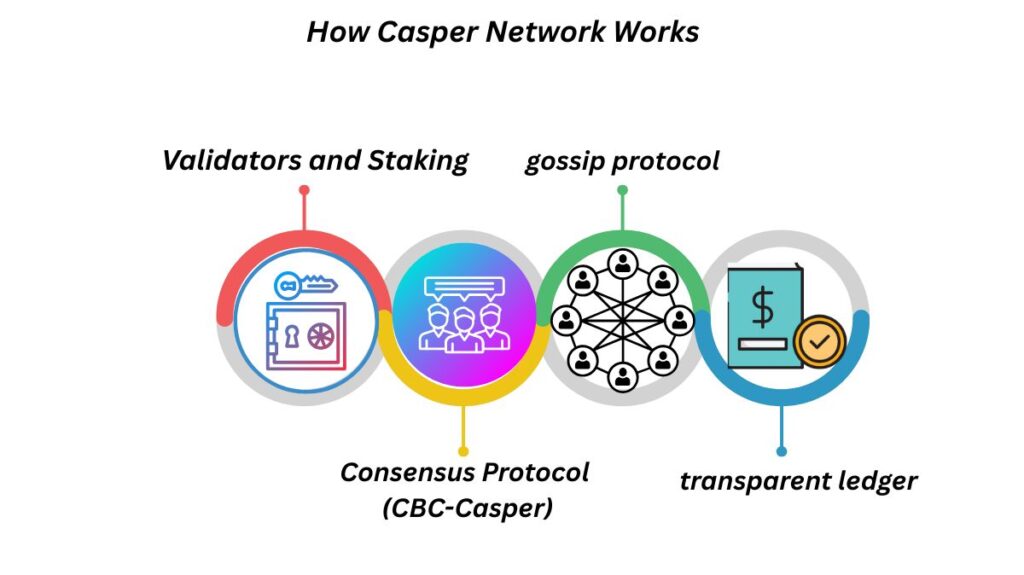
At its core, Casper Network operates on a Proof of Stake consensus model.
- Validators and Staking: Users become validators when they “stake” (lock up) a specific quantity of CSPR, the native token of the network. Being selected to suggest the next block is more likely the more tokens are staked. In exchange for honest validation, validators receive CSPR tokens, but if they attempt to cheat, they risk losing their staked tokens.
- Consensus Protocol (CBC-Casper): The backbone of Casper’s communication is its CBC-Casper protocol, a variation of PoS ensuring consensus among validators securely. This protocol validates and secures transactions while allowing the system to evolve.
- Communication between validators takes place using a gossip protocol, which effectively disseminates block proposals and transaction data around the network.
- All validators have access to the same transparent ledger, which is updated in real time. They collaborate to agree on new transactions.
Benefits and Why It’s Gaining Attention
- Reduced Energy Consumption: By using PoS, Casper consumes significantly less energy, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Lower Transaction Fees: Casper’s PoS system enables lower transaction fees compared to older blockchains, making it more accessible for users and businesses.
- Future-Proofing: Smart contracts’ upgradeability and developer-friendliness meet organizational needs and technology.
- Business Applications: Casper’s design accommodates government, healthcare, finance, and supply chain management.
- Solves Older Blockchain Issues: Casper aims to overcome fundamental compromises (e.g., speed sacrificing decentralization/security), complex code, high/unstable transaction fees, and archaic tooling found in older layer one blockchains. It offers scale without sacrifice, is minimal risk and easy to use, provides flexibility (public, private, or hybrid solutions), and is low cost.
CSPR Token
CSPR is the native utility token of the Casper Network. It is used for:
- Paying transaction costs and executing smart contracts.
- Staking is used to protect the network and generate income.
- Voting on protocol decisions is an example of governance participation.
Use Cases of Casper Network
Casper is positioned for a wide range of real-world applications, including:
- Marketplaces for decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Real-world asset tokenization.
- Governments and corporations can use enterprise blockchain technologies.
- NFT marketplaces and platforms for digital identities.
- Improved traceability and transparency in supply chain management.
- Intellectual property management includes safeguarding digital assets and expediting the patent registration process.
- Financial services include safe lending platforms, automated financial procedures, and the facilitation of international transfers.
- Supplying a scalable and adaptable platform for in-game assets and digital collectibles in gaming and NFTs.
How to Get Involved with Casper Network
There are several ways to engage with the Casper Network:
- Invest in CSPR Tokens: Leading cryptocurrency exchanges allow you to purchase, sell, or trade CSPR tokens. Staking tokens to validate transactions and receive rewards is made possible by holding CSPR.
- Build on Casper: Developers can build smart contracts and dApps in its developer-friendly ecosystem.
- Join the Community: Casper has a vibrant community with developer events, social media, and online forums. Casper Wallet and other compatible wallets are ways for developers to connect
Technology solutions company Calibrant recognizes Casper Network as a major paradigm shifter in the blockchain space that presents potential and innovation.
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Layer-1 Blockchain |
| Launch Year | 2021 |
| Consensus | Proof of Stake (PoS) — CBC-Casper |
| Native Token | CSPR |
| Key Strengths | Energy-efficient, enterprise-ready, upgradable smart contracts |
| Programming | WebAssembly (Wasm), developer-friendly |
| Use Cases | dApps, DeFi, NFTs, enterprise solutions |
You can also read What Is Tether (USDT)? How To Invest In Tether In Blockchain
