Taproot
In this article we learn about Taproot in blockchain, Purpose and Goals, Taproot Advantages, and Key Components
The Taproot upgrade is a significant enhancement to the Bitcoin protocol, activated on 14 November 2021, at block 709,632. It is considered the most important upgrade Bitcoin has experienced since the Segregated Witness (SegWit) activation in 2017.
Purpose and Goals:
The Taproot update aims to scale, optimize, and anonymize Bitcoin. Smart contract implementation enables Bitcoin decentralized financing (DeFi). Complex transactions, such as multi-signature or smart contracts, were previously clearly distinguished by their completely disclosed scripts prior to Taproot, which decreased privacy and increased their cost because of their larger size. Taproot solves these problems by presenting new cryptography tools and more intelligent script structuring techniques.
You can also read P2WSH Pay to Witness Script Hash: Bitcoin SegWit Transaction
Key Components (Three Interconnected BIPs)
The Taproot upgrade comprises three distinct Bitcoin Improvement Proposals (BIPs) that work together:
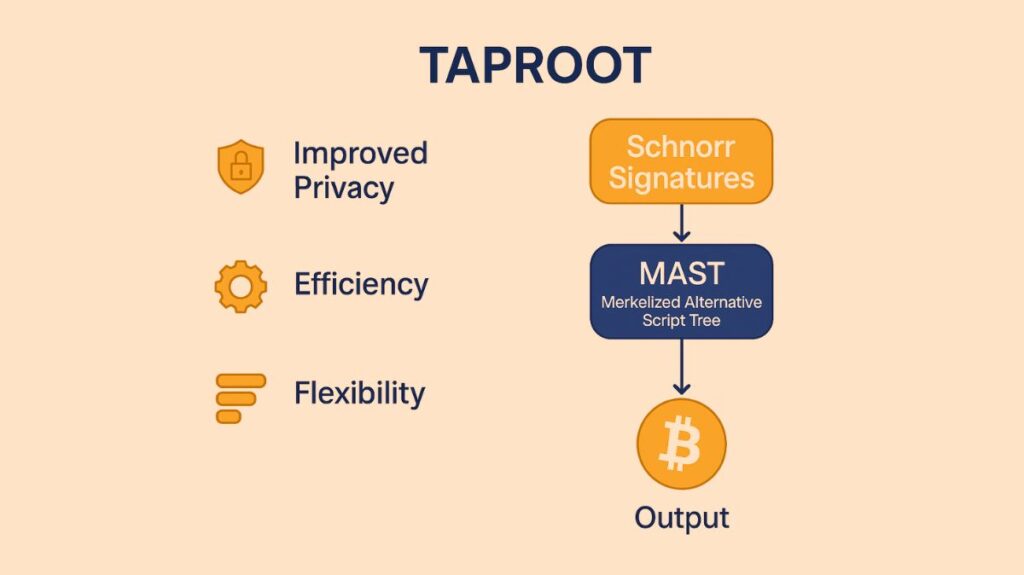
- BIP 340-Schnorr Signatures: This replaces the older Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm (ECDSA) with Schnorr signatures.
- Advantages: Schnorr signatures are described as faster, more secure, less data-intensive, and simpler to implement than ECDSA.
- Signature Aggregation: Their linearity property allows multiple collaborating parties to produce a single signature valid for the sum of their public keys. This means multiple signatures can be batched together and verified as one, which is particularly beneficial for multi-signature transactions.
- BIP 341–Taproot: This proposal introduces a new way to perform Bitcoin transactions by enhancing privacy and flexibility for users. It activates Merkelized Abstract Syntax Trees (MAST).
- MAST Functionality: MAST reduces transaction costs, boosts scalability, and minimizes memory usage by condensing complicated Bitcoin transactions into a single hash. Instead of committing the entire transaction or any unused spending conditions, MAST just commits the executed conditions of a complex transaction to the blockchain. This keeps certain script information hidden.
- Privacy Enhancement: It also introduces a new output type, Pay-to-Taproot (P2TR), which makes all transactions (simple or complex) look the same on the blockchain if the key path is used, significantly enhancing privacy.
- BIP 342–Tapscript: This is an upgrade to Bitcoin’s scripting language, which is used for Taproot script-path spends. It leverages Schnorr’s efficiency and enables more flexibility for future upgrades and the integration of new code. It also makes it possible to deploy the other two BIPs on Bitcoin.
Taproot Advantages
Taproot Advantages
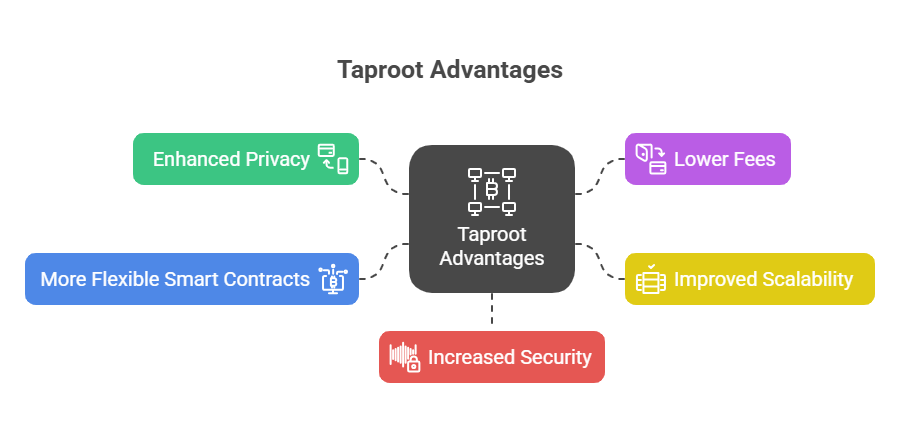
- Enhanced Privacy: Taproot makes it difficult to distinguish between multi-signature and single-signature transactions, or even complex smart contracts and simple peer-to-peer payments. This reduces the ability of outside observers to tell what kind of spending conditions are used, thereby making it harder to identify participants’ transaction inputs where private data is stored. While not making Bitcoin a completely private currency, it significantly increases anonymity.
- Lower Fees: Taproot reduces the size of complicated transactions by aggregating signatures and storing less data on the blockchain, which results in faster and less expensive transactions. The block saves the most space this way as well.
- Improved Scalability: Signature aggregation and MAST optimize block space, allowing the network to process more transactions faster. This removes a key Bitcoin adoption barrier.
- More Flexible Smart Contracts: Taproot is a game-changer for Bitcoin’s utility, making smart contracts cheaper and smaller. It empowers Bitcoin’s ability to host smart contracts on the base chain, positioning it as a competitor to platforms like Ethereum for DeFi applications. It allows for more advanced scripting possibilities while preserving privacy.
- Increased Security: Schnorr signatures are more secure than ECDSA. Taproot also addresses signature malleability, a known security risk that could allow alterations to a transaction’s signature before confirmation, potentially leading to double-spending.
You can also read P2SH-P2WSH: Understand Nested P2WSH Bitcoin Transactions
Development and Adoption:
Developer Greg Maxwell of Bitcoin Core initially proposed Taproot in 2018. Pieter Wuille wrote Taproot’s three BIPs. Developers Tim Ruffing, A.J. Townes, and Jonas Nick joined in 2020. Miners agreed 90% on June 12, 2021. The upgrade was a soft fork, like Bitcoin Cash after SegWit in 2017, keeping it backward compatible with older software and not splitting into two blockchains. Like SegWit, its adoption is projected to grow gradually despite strong support.
Impact on Bitcoin’s Value:
Taproot may be a technical improvement, but it may have a big impact on Bitcoin’s value in the long run. Although it’s hard to forecast future price effects, analysts say it helped boost network confidence and the value of Bitcoin around the time of its activation. Long-term investors will have additional options as the upgrade increases the usefulness of DeFi and provides the technological basis for speeding it up on the Bitcoin network.
Because it will provide a more stable and effective framework, it should give investors greater trust in the fundamentals of Bitcoin. Since Bitcoin is mostly used as a speculative investment rather than a widely accepted payment method, some reports say the upgrade has had minimal immediate influence on its price.
In essence, Taproot represents a crucial advancement for Bitcoin, addressing long-standing issues of privacy, efficiency, and scalability, and significantly enhancing its capabilities for smart contracts.
Summary Table
| Feature | Taproot |
|---|---|
| Activated | Nov 14, 2021 |
| Main goals | Privacy, efficiency, smart contracts |
| Key improvements | Schnorr signatures, MAST, P2TR |
| Benefits | Better privacy, lower fees, advanced scripting |
| Address format | bc1p… (bech32m, for P2TR) |
| Use cases | Simple payments, multisig, smart contracts |
You can also read P2WPKH (Pay to Witness Public Key Hash), new Bitcoin Address
