Cisco Switch BPDU Guard
Cisco network switches often have BPDU Guard, however other vendors may offer similar functions. Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) topology is protected and dependability improved.
BPDU Guard, a Spanning Tree (STP) security feature, protects network architecture by blocking BPDUs on unexpected ports, such as end-user device access ports. A BPDU disables the port to prevent unwanted switches from interfering with the network and generating loops or topology changes. It is frequently activated in tandem with PortFast, which skips the listening and learning stages of STP and speeds up the transition of ports connected to end-user devices to a forwarding state.
BPDU Guard is regarded as a crucial component for preserving a secure and reliable STP environment.
Important Ideas
- STP and Rapid STP switches exchange BPDUs (Bridge Protocol Data Units). In order to avoid network switching loops, BPDUs are utilized to choose a root bridge and identify the optimal routes.
- By purposefully turning off specific paths, the link layer technology known as STP (Spanning Tree technology) guarantees an Ethernet network’s logical architecture is free of loops.
- PortFast/Edge Port: An edge port is one that is intended to connect to an end-user device, such as a PC, server, or printer, rather than another switch. By bypassing the typical STP listening and learning phases and going straight to the forwarding state, these ports expedite the end device’s network connectivity. Importantly, BPDUs should never be sent to edge ports.
Also Read About RSTP Attacks: What Is RSTP? Attack Mechanism And Types
How it works
Enforcing the STP domain borders and preventing unauthorized devices from altering the layer 2 network topology are the two main objectives of BPDU Guard.
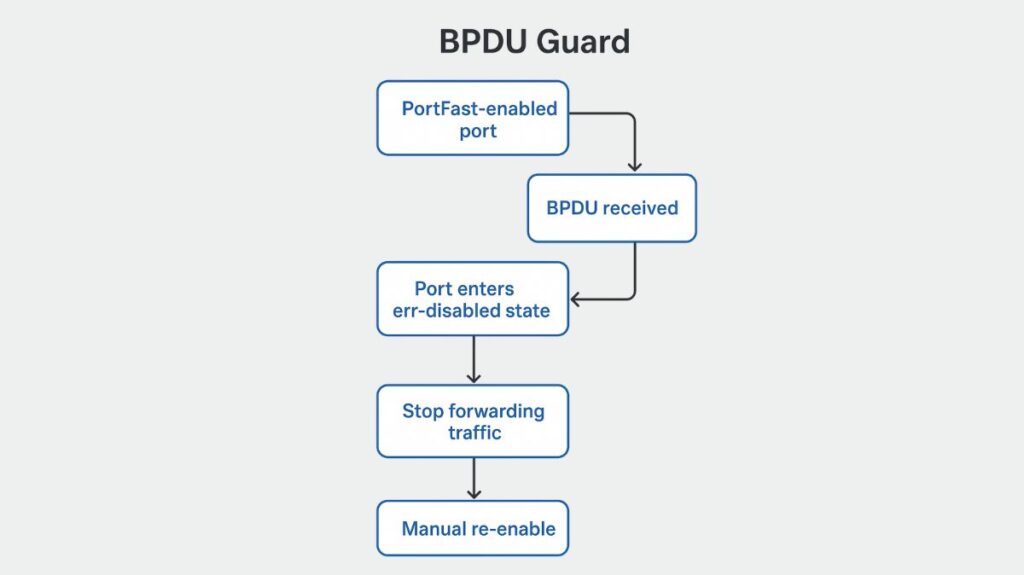
Context (Edge Ports/PortFast): BPDU Guard is usually set up on access ports, also known as edge ports. Configuring an edge port with PortFast lets it skip STP listening and learning and go straight to forwarding upon linkup. Only end-user devices like PCs, servers, and printers should connect to these ports, which should never receive BPDUs.
Detection (Trigger): These edge ports are monitored by the feature. Suppose a port equipped with BPDU Guard unexpectedly receives a Bridge Protocol Data Unit (BPDU), a message sent between switches taking part in STP. In that instance, it violates the “edge port” premise by signaling the connection of an unapproved device or a new switch.
Action (Security Response): The BPDU Guard logic instantly disables the offending port when it receives a BPDU. This is known as the action (security response).
Security: BPDU Guard blocks the port immediately to prevent the rogue switch from inserting STP. This prevents attacks that affect the STP topology, such as sending BPDUs with a higher or lower Bridge ID to become the root bridge or creating switching loops that could cause DoS or network instability.
Also Read About Cisco Gateway load balancing protocol GLBP, How GLBP works
BPDU Guard Configuration
On switches, BPDU Guard is usually turned off by default.
Configuration Techniques (Examples of Cisco IOS):
Configuration at the Interface Level
Use PortFast to apply BPDU Guard to a particular port:
Switch(config)# interface fastEthernet 0/1
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree portfast
Switch(config-if)# spanning-tree bpduguard enable
spanning-tree portfast→ Enables PortFast (treats the port as an edge port).spanning-tree bpduguard enable→ Enables BPDU Guard on that port.
Global Configuration (Recommended)
Turn on BPDU Guard by default on all ports that support PortFast:
Switch(config)# spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
In this manner, a BPDU will immediately put any PortFast-enabled port in an err-disabled state.
Verify Configuration
Verify that BPDU Guard is turned on:
Switch# show running-config | include bpduguard
Verify the port’s status
Switch# show spanning-tree interface fastEthernet 0/1 detail
Errdisable Recovery (Optional)
If you prefer automatic port recovery over manual intervention following a timeout:
Switch(config)# errdisable recovery cause bpduguard
Switch(config)# errdisable recovery interval 300
cause bpduguard→ Enables auto-recovery for BPDU Guard events.interval 300→ Wait time in seconds (default 300s = 5 minutes).
Also Read About NTP Server Configuration And How Does NTP Server Work?
Benefits of BPDU Guard
- Security: Protects STP topology from unauthorized devices and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- Maintaining STP domain borders keeps active network topologies stable and predictable.
- Network Reliability: Prevents loops brought on by rogue switches, improving overall network reliability.
Disadvantages
The user must go to the access switch’s CLI in order to disable the BPDU guard whenever they need an access switch port with a switch hooked into it.
Also Read About How Does A RADIUS Server Work, Architecture And Functions
