Hybrid Intrusion Detection System
A hybrid intrusion detection system design for computer network security
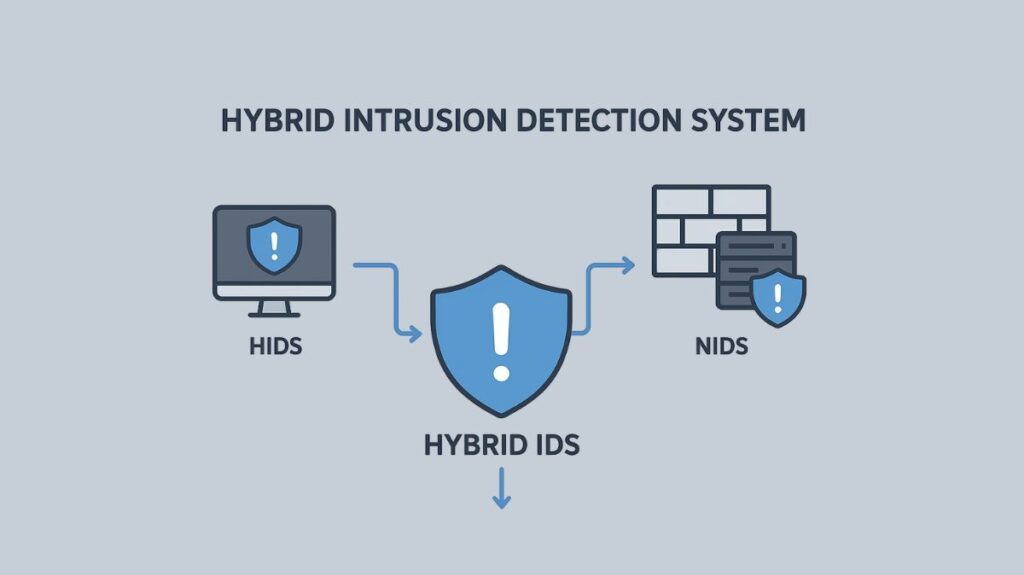
HyIDS is a security product that combines NIDS and HIDS characteristics to provide total protection. This hybrid technique combines host-level actions and network-level data to give more complete and precise detection than either system could alone.
Working Mechanism and Components
A HyIDS functions as a single, integrated system that keeps an eye on local systems as well as the network environment.
Typically, a hybrid IDS includes:
- Distributed HIDS Agents: On servers, other network hosts, and important endpoints, separate HIDS agents are installed. As indicated, these agents monitor each host’s file integrity, logs, processes, user activity, etc.
- Centralized NIDS Sensors: NIDS sensors are strategically placed at the perimeter, core network, and VLANs to monitor network traffic for unusual behavior, known attack signatures, and suspicious trends.
- The centralized administration and correlation engine links everything. HIDS agents and NIDS sensors send data and alarms to a central SIEM platform or IDS administration console. The correlation engine follows.
- Data normalization: HIDS and NIDS data formats are standardized.
- Correlates events: Examines seemingly unrelated network and host warnings to find a broader assault effort. For instance, an NIDS may identify a port scan directed at a server, while at the same time, the server’s HIDS may identify odd file access attempts or the initiation of a new process. An active attack can be seen much more clearly when these events are correlated than when either system is used alone.
- Minimizes false positives: A hybrid system can drastically cut down on false alarms by needing several verifying events from several viewpoints (host and network).
- Offers a cohesive perspective: Allows security analysts to observe and control all intrusion detection events from a single dashboard.
Also Read About What Is Inter VLAN Routing And How Inter VLAN Routing Works
Key Functions
The following crucial tasks are carried out by a hybrid IDS to guarantee end-to-end visibility:
| Monitoring Level | Function | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Host Activity Monitoring | HIDS Function | Tracks log files, system calls, and file integrity changes on endpoints. |
| Network Traffic Monitoring | NIDS Function | Detects suspicious patterns and anomalies in network packets. |
| Correlation & Analysis | Core Hybrid Function | Correlates data from multiple sources (hosts and network) to identify complex or distributed attacks. |
| Alerting and Reporting | Management Function | Generates alerts for both host-based and network-based intrusions. |
Also Read About Intrusion Detection System IDS Importance & IDS vs Firewall
Advantages of a Hybrid IDS
Comparing hybrid systems to stand-alone HIDS or NIDS solutions reveals several advantages:
Improved Detection and Visibility: They offer complete network and host visibility. They can identify a greater variety of attacks, including complex multi-stage threats that encompass both internal and external threats, to their all-encompassing perspective.
Reduced False Positives: Event cross-verification by the correlation engine reduces false positives by validating events from two different perspectives (host and network). This greatly reduces false positives and ensures only serious threats are notified.
Improved Context: Security teams can more easily comprehend the character and extent of an attack when alerts are enhanced with additional context.
Evasion and Resilience Resistance: HyIDSs prevent evasion. Even if an attacker encrypts communication to bypass the NIDS, the HIDS can detect malicious host activity. However, NIDS can identify network-level indications even if HIDS is corrupted.
Better Threat Hunting: Active scanning for dangers that may have eluded early automated detections is made easier by the pooled data.
Challenges
Hybrid IDSs have some operational issues despite their benefits.
- Complexity: Compared to a single-focus IDS, they are more difficult to design, implement, and maintain.
- Resource Consumption: They need a lot of storage space and computing power. The correlation engine requires a large amount of processing power and storage, while the HIDS agents need resources on separate hosts.
- Cost: HIDS agents, NIDS sensors, and a potent correlation engine or SIEM are required for the implementation.
- Latency: Latency may be introduced by data analysis.
Examples of Hybrid IDS Tools
Hybrid IDS tool examples include:
- Prelude Hybrid IDS
- AlienVault OSSIM
- Wazuh (often used with Suricata integration)
- Security Onion (which commonly combines tools like Snort or Suricata for NIDS functionality and OSSEC for HIDS functionality).
Also Read About What Is VLAN Trunking? How It Works, Advantages & Protocols
