What is Blockchain CAPTCHA?
A security measure called CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is intended to differentiate between automated bots and human users. CAPTCHA is mainly utilized in blockchain systems as a defense mechanism to guard against automated abuse or attacks, particularly in situations that call for human participation, such voting, airdrops, or Decentralized Applications (DApps).
Why CAPTCHA is Needed in Blockchain?
Anyone can engage with smart contracts or use services on blockchain platforms, especially public blockchains and DApps, which are meant to be open. Despite its advantages, this openness leaves them open to other automated attacks:
- Bot-attacks
- Sybil attacks: In order to get undue control or influence, tamper with voting in a Decentralized Autonomous Organisation (DAO), hoard airdropped tokens, or disrupt consensus processes, a single malevolent actor fabricates a large number of fictitious identities (nodes or accounts).
- Spam transactions: Automated bots that submit fraudulent transactions or misuse platform resources might be blocked.
- Airdrop farming: To obtain free tokens, bots signup in bulk.
- Cryptojacking: CAPTCHAs can also aid in preventing cryptojacking, or malicious cryptocurrency mining, by making it more difficult for bots to access resources.
The goal of implementing CAPTCHA systems is to restrict access to actual people exclusively, which will increase equity, lower fraud, and conserve network resources.
How CAPTCHA Works in Blockchain
The following steps are usually included in the steps:
- A user starts an interaction, like claiming an airdrop or registering for a blockchain-based service.
- The user is prompted to complete a task (such as choosing a picture or entering text) as part of a CAPTCHA test.
- The smart contract or DApp processes the request if the test is successfully completed.
- The interaction is halted if the test is not correctly solved.
The fact that CAPTCHA is a web technology and cannot be used directly within smart contracts should not be overlooked. It is instead implemented off-chain, that is, on a backend or front-end server for the web. The user can sign and send a blockchain transaction through the backend after the off-chain verification is successful. In certain sophisticated situations, human identity is cryptographically verified on-chain using proof-of-humanity systems or zero-knowledge proofs (ZK-CAPTCHAs).
Using CAPTCHA as a Proof-of-Personhood (PoP) method
“Proof-of-Personhood” (PoP) is one of the main uses of CAPTCHA in blockchain technology. By guaranteeing that every participant is a distinct human being rather than an automated script or bot, this idea immediately counters the Sybil attack. This aids in:
- By ensuring that free tokens are provided equitably to individual users rather than being taken by bot farms, we can prevent airdrop abuse.
- Securing Governance: CAPTCHA can confirm that every vote in DAOs or community-governed projects comes from a distinct person, preventing a single entity from influencing proposal outcomes by using several wallets.
- Sybil-Resistant Faucets: These ensure that tokens are available for legitimate use by stopping bots from draining testnet faucets that provide free tokens for development.
CAPTCHA as a Less Common Proof-of-Work (PoW) Mechanism
Although less popular and more theoretical, some academics have looked into utilizing a riddle similar to CAPTCHA as a Proof-of-Work method. The premise is that a human, not a machine, would carry out the necessary computational “work” here. For instance, a little, CPU-intensive job may run in the background on a user’s device. The total computing cost for a bot attempting to spam a network could become unaffordable, even though it would be insignificant for one user.
However, there are serious problems with this strategy:
- User Difficulty: A “proof-of-work CAPTCHA” may cause a user’s computer to lag or deplete their battery, which would make the experience less pleasant.
- Accessibility Problems: For those with disabilities, visual or auditory CAPTCHAs pose serious accessibility problems.
- Scalability Issues: Since a reliable third party could be required for verification, incorporating such a mechanism into a high-throughput blockchain network may result in latency and perhaps centralize control.
Common Use Cases of CAPTCHA in Blockchain
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Token Airdrops | Prevent bots from mass-claiming free tokens. |
| DeFi Applications | Protect platforms from automated trading bots abusing protocols. |
| Governance Voting | Ensure that votes are coming from real users, not bot farms. |
| Web3 DApps & Games | Stop automation in play-to-earn or NFT-based games. |
| Anti-Spam Measures | Avoid spam transactions in blockchain-based forums or messaging systems. |
Benefits of Blockchain-based CAPTCHAs
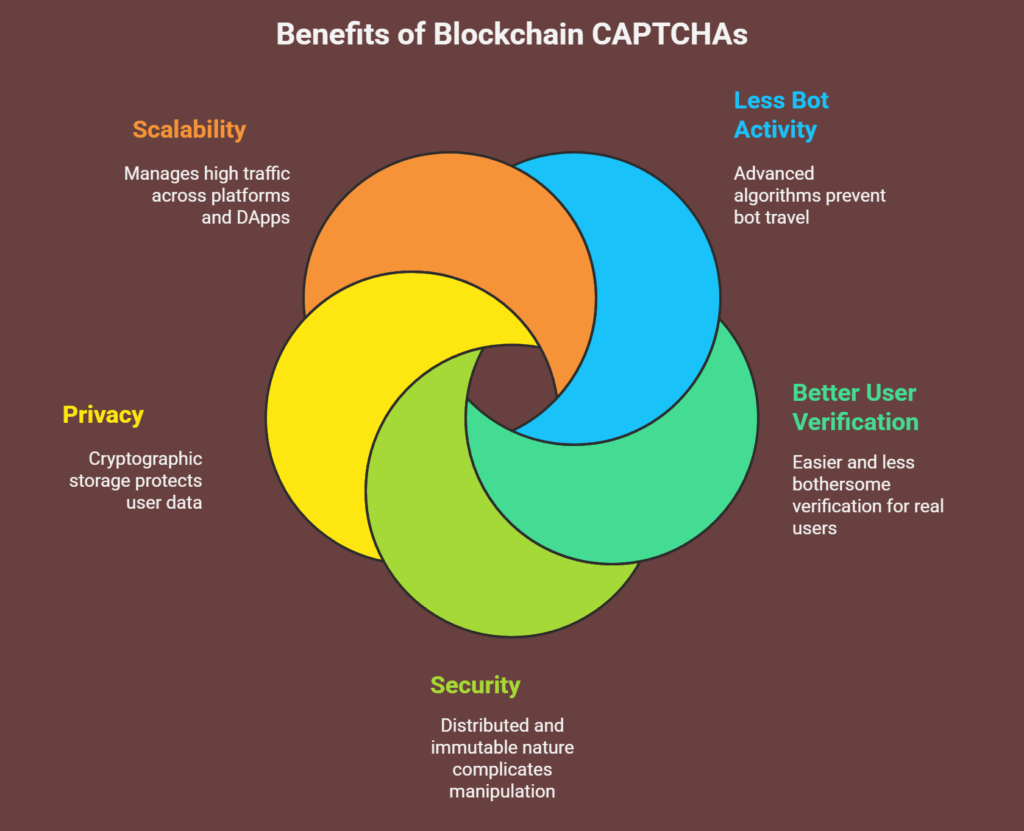
CAPTCHAs have many benefits when combined with blockchain principles:
- Less Bot Activity: Advanced algorithms and decentralised validation make bot-travel impossible.
- Better User Verification: Real users find verification easier and less bothersome.
- Security: Blockchain’s distributed, immutable nature complicates CAPTCHA manipulation.
- To protect user privacy, several blockchain technologies store data cryptographically.
- Scalability: Many platforms and DApps can manage high traffic.
Alternatives to Traditional (Centralized) CAPTCHA in Web3
Blockchain initiatives are actively investigating decentralized solutions that are more in line with the Web3 philosophy, since standard CAPTCHAs, such as Google reCAPTCHA, are centralized. These consist of:
- Proof of Humanity (PoH): A decentralized registry for people who have been verified through social verification and identity evidence.
- BrightID: A decentralized identity verification system designed to demonstrate each user’s individuality.
- hCaptcha/Arkose Labs: Web3 wallets and DApps use privacy-friendly CAPTCHA services.
- Worldcoin’s World ID: A proof-of-personhood system based on biometrics that confirms each person’s individuality.
Limitations of CAPTCHA in Blockchain
Despite its benefits, CAPTCHA has drawbacks and is not a perfect fit for the decentralized world.
- The most widely used CAPTCHA services are centralized, which poses a risk of centralization. The fundamental blockchain tenets of decentralization and trustlessness are incompatible with depending on a single, private entity for verification.
- Attack Vulnerability: “CAPTCHA farms,” where human workers are paid to solve CAPTCHAs, enable bots to get around the system, and sophisticated bots can frequently solve multiple CAPTCHA variations.
- Privacy Issues: For users who seek anonymity, several CAPTCHA services watch user behavior to establish whether they are human.
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Centralization | Many CAPTCHA services are controlled by centralized entities like Google. |
| Accessibility | Some CAPTCHAs are not accessible to visually impaired users. |
| Bypass Methods | Advanced bots and CAPTCHA farms can bypass basic CAPTCHA systems. |
| Off-chain Dependency | Smart contracts can’t process CAPTCHA logic directly relying on off-chain verification. |
Essentially, even though CAPTCHA is an essential defense against automated misuse in decentralized systems and aids in the fight against Sybil attacks, its use frequently results in a certain amount of centralization and security and privacy trade-offs that may be at odds with the core principles of a decentralized ecosystem.
Consider CAPTCHA in blockchain as a special secret handshake at a club’s door that is exclusively open to members. It is intended to prevent imposters (bots) from trying to overrun the club or take advantage of its resources by limiting access to only real members (humans). However, the club’s “decentralized” structure may be compromised if the secret handshake is controlled by a single central authority or if it becomes too simple for con artists to imitate, leading to the adoption of more complex, unreliable identification verification methods.
