This article discusses Ethereum 2.0’s definition, main objectives, motivation, features, development stages, Ethereum 2.0 Price , relationship to Ethereum 1.0, and intermediate solutions, which are displayed below.
What is ethereum 2.0?

Multiple stages were used to update Ethereum 2.0 (Serenity). This upgrade’s scalability, performance, safety, and energy efficiency made Ethereum a better “World Computer”. Blockchain enthusiasts call the update “Ethereum” rather than “Ethereum 2.0” and welcome it as evolution.
Core Goals and Motivation
The fundamental blockchain design trade-offs drive Serenity. Vitalik Buterin’s 2015 plan optimised only two of a blockchain’s three important characteristics: decentralisation, scalability, and security (consistency). Ethereum 2.0 balances eWasm, sharding, and PoS.
The main Serenity growth objectives are:
Scalability
Ethereum 1.0 can only process a limited number of TPS, causing peak congestion and expensive fees. Ethereum 2.0 shard chains support multiple transactions. This dramatically boosts network capacity and scalability.
Energy Efficiency
Ethereum 1.0’s PoW mining demands a lot of computational power and energy. PoS uses less energy than PoW in Ethereum 2.0. Instead of solving complex mathematical puzzles, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on their cryptocurrency stake.
Security
The network’s security is mostly dependent on miners, and PoW is vulnerable to specific kinds of attacks and flaws. Proof Of Stake(PoS) improves security by making validators pledge collateral, which they risk forfeiting in the event of malevolent behaviour. This lowers the risk of centralisation and increases the cost of attacks.
Decreased Transaction costs
The Ethereum network is costly to use due to high transaction costs, which are sometimes caused by heavy demand. Ethereum 2.0 seeks to reduce transaction fees and make the network more accessible to users by utilising the enhanced transaction capacity and efficiency that shard chains and PoS provide.
Better Network Performance
Inefficiencies and slower transaction times might result from network congestion. Ethereum 2.0 enhances overall performance and speeds up transaction processing times by distributing the burden over several shard chains and streamlining the network protocol.
Key Features of Ethereum 2.0
Serenity modifies the Ethereum protocol in a number of important ways:
Mechanism for Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Consensus
Ethash, the Proof-of-Work (PoW) consensus model that powers the majority of the current Ethereum mainnet, uses a lot of energy and has a limited capacity for processing transactions. Ethereum 2.0 will switch between PoW and PoS. It is anticipated that this change will greatly lower power usage by up to 99.9% and increase the network’s decentralisation and efficiency. Before they may generate blocks under PoS, nodes known as “bonded validators” in Casper, an algorithm created to replace PoW in Ethereum must pay a security deposit, or stake Ether from Ethereum 1.0. Two-thirds of the staked validators must agree for the network to be secure. In the PoS context of Ethereum 2.0, the “Greedy Heaviest Observed SubTree (GHOST)” protocol more precisely, LMD GHOST is modified to identify the canonical chain.
Sharding
Scalability can be achieved by sharding the network into “shard chains” to execute transactions simultaneously. Sharding parallelises data, consensus, and execution to improve transaction performance and instantaneity. Because each segment is protected by fewer validating copies, sharding can lower security even when it improves efficiency.
EWasm (Ethereum WebAssembly)
As previously mentioned, eWasm (Ethereum WebAssembly) is an Ethereum-flavored version of WebAssembly that is being developed as a backup backend environment for running Ethereum programs in addition to the EVM. It is intended to use the WebAssembly toolchains and optimisations already in place to enable smart contract execution at almost native speed. Faster smart contract execution will be possible in Phase 2 since each shard chain will have its own eWasm EVM.
Beacon Chain
Founded in Phase 0 of development, this is a fundamental system chain that serves as the framework for the whole Ethereum 2.0 chain system. It keeps the network in sync and gives all shard chains consensus. The main links in charge of synchronisation, block attestation, and giving validators vital information are beacon nodes.
Also Read About Sharding In Blockchain: How It Works And Types Of Sharding
Development Phases (Roadmap)
Ethereum 2.0 will be developed in phases:
Phase 0 (Beacon Chain): In late 2020, the Beacon Chain became the central PoS chain, selecting block proposers, validators, and consensus rules. It runs alongside Ethereum 1.0. In order to reward validators, this phase also presents the idea of ETH 2, a new digital currency for Ethereum 2.0. To become validators on the Beacon Chain, users must deposit Ethereum 1.0 (ETH) into a deposit contract on the Ethereum 1.0 chain.
- The creation of shard chains and blocks, including their cross-linking to the Beacon Chain, is the main objective of Phase 1 (Shard Chains), which is slated for 2020 (according to the timeframe provided by the source).
- Phase 1.5 (“The Merge”): In this stage, the Ethereum mainnet will change into Ethereum 2.0, most likely by becoming a shard chain of Ethereum 2.0. It is not specifically numbered as a complete phase in all sources, although it is referred to as “the merge.” The goal of this merge is to create interoperability bridges while integrating the current Ethereum 1.0 chain “as is” into the Ethereum 2.0 Beacon Chain.
- Phase 2 (Execution Environments, eWasm): This phase is anticipated to take place in 2021 and is centred on the enhancement of execution environments. With each shard having its own eWasm EVM for quicker execution, it offers the capability to run and interact with smart contracts on shard chains. Developers might create unique execution environments for particular use cases during this phase.
- Phase 3 (More Scalability and Improvements): Previously scheduled for 2022, this phase entails ongoing upkeep and enhancements for the fully functional Ethereum 2.0 network. This includes Proto-Danksharding (EIP-4844), which was introduced in the Dencun upgrade on March 13, 2024, which greatly reduced the cost of Layer 2 networks by introducing “blobs” for less expensive, temporary data storage. Future updates such as Pectra, which is anticipated to be released in the middle of 2025, would enable Externally Owned Accounts (EOA) to utilise smart contract features and significantly raise the staking amounts per validator.
Impact on Performance and Costs
Significant advancements are anticipated with the switch to Ethereum 2.0:
Transaction Throughput
Ethereum 2.0, with sharding, intends to process thousands of transactions per second (TPS), but Ethereum 1.0 is limited to about 12 to 30 TPS, which is much lower than Visa’s 1,700 TPS average. “1000s of TPS” are recommended by some sources for Blockchain 3.0 (which includes sharding and DApps).
Lower Gas Prices
To offset the high transaction costs that the existing Ethereum network incurs, Ether is used as “gas” to cover the cost of computation. Since miners will play a smaller role in Ethereum 2.0’s transition to PoS, petrol prices may decrease or even disappear. Gas prices are even set to zero in permissioned networks such as Quorum.
Energy Efficiency
The Ethereum network’s energy usage will be significantly decreased by switching from PoW to PoS.
Ethereum 2.0 price Chart
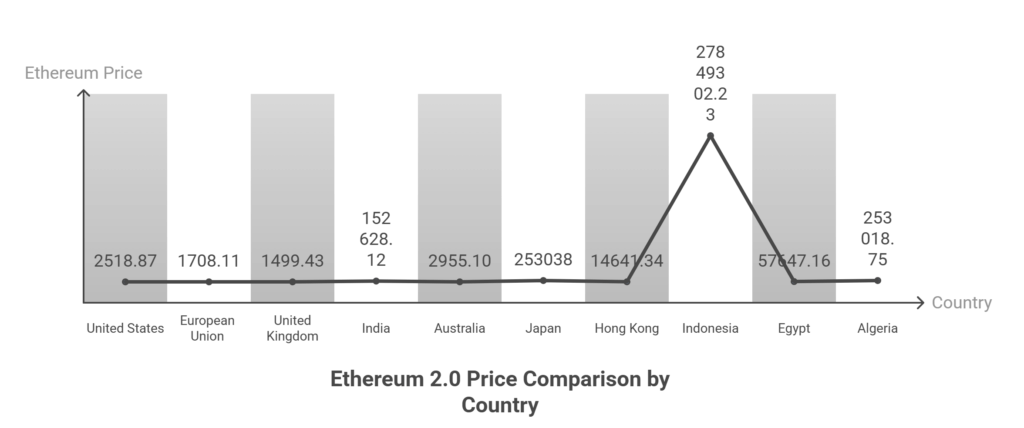
| Country / Currency | Symbol | ETH Price (approx.) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | USD | $2,518.87 | Latest from crypto markets |
| European Union | EUR | €1,708.11 | From latest market data |
| United Kingdom | GBP | £1,499.43 | As per £ latest quotes |
| India | INR | ₹152,628.12 | Market rate ₹ value |
| Australia | AUD | A$2,955.10 | From CoinGecko listing |
| Japan | JPY | ¥253,038 | CoinGecko 1 ETH to yen |
| Hong Kong | HKD | HK$14,641.34 | Converted via RatesViewer |
| Indonesia | IDR | Rp27,849,302.23 | From RatesViewer |
| Egypt | EGP | E£57,647.16 | From RatesViewer |
| Algeria | DZD | د.ج253,018.75 | From RatesViewer |
Relationship with Ethereum 1.0 and Intermediate Solutions
At first, the new Beacon Chain will function in tandem with Ethereum 1.0. The mainnet will eventually switch to Ethereum 2.0 as a result of the merge. Layer 2 alternatives including side channels and state channels have been investigated during this transition to address urgent scaling issues. By removing trusted party transactions off the main chain, these solutions lighten its load and allow for faster transaction rates. Layer 2 solutions are seen as a “very powerful stepping stone” prior to the complete deployment of PoS and sharding.
YUL, an intermediate language that can compile to several backends, including eWasm, also facilitates the creation of WebAssembly-based smart contracts. This allows developers to focus on eWasm or the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) according on their needs.
Ethereum 2.0 is a major overhaul to improve the network’s scalability, sustainability, and efficiency to keep it a top decentralised application platform.
