Advanced encryption standard definition, its features, AES Operation Overview (Encryption Process), and its applications Of AES were all covered in this blog.
Advanced encryption standard definition
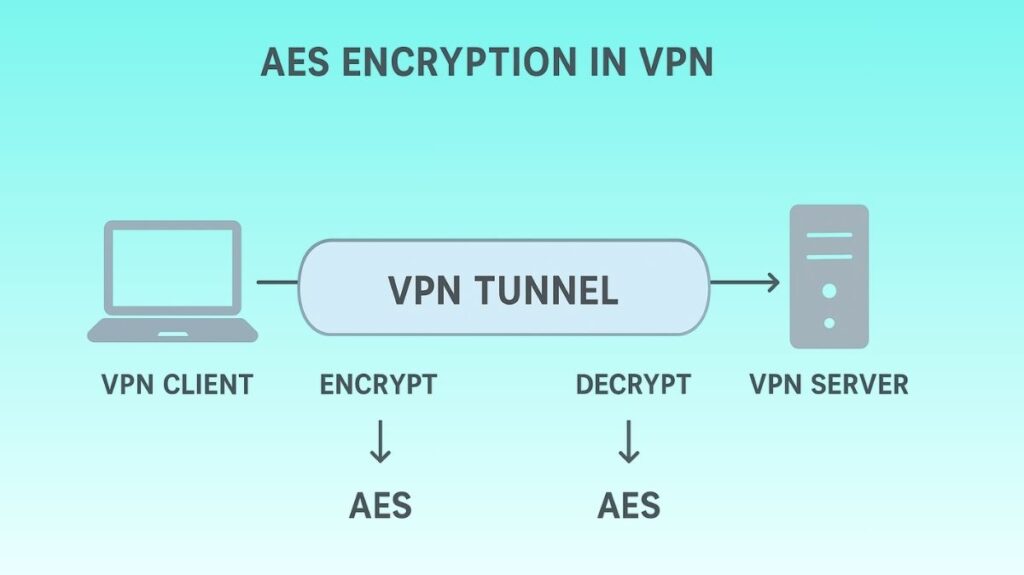
The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) is a basic cryptographic algorithm that is extensively used in contemporary networking protocols to guarantee confidentiality and safe data transfer.
The Data Encryption Standard (DES) was superseded by AES in 2001 by the U.S. National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST). Since DES’s limited key size left it susceptible to exhaustive key search attacks and Triple DES (3DES), its successor, was deemed too sluggish, a replacement was required. AES is extremely effective for software and hardware implementations in networking devices since it is noticeably faster and stronger than Triple DES.
Also Read About Common Network Security Vulnerabilities And Exploitation
Features of AES
Several essential cryptographic characteristics describe AES:
- Symmetric-Key Algorithm: AES encrypts plaintext into ciphertext and decrypts ciphertext back into plaintext using a single secret key.
- Block Cypher: It handles data in blocks, which are fixed-size units of 128 bits (16 bytes). It produces 128 bits of encrypted ciphertext after receiving 128 bits as input.
- Key Lengths: By supporting three different key sizes, AES offers flexibility and improved security.
- 128 bits (10 transformation cycles).
- 192 bits (12 transformation cycles).
- 256 bits (14 transformation cycles). The key length selected has a direct impact on the number of transformation rounds, Nr.
- Structure: AES is an iterative substitution-permutation network (SPN), not a Feistel cypher, in contrast to the more traditional DES method. To completely jumble the data, this structure employs a sequence of connected operations that include permutations (shuffling bits) and substitutions (changing inputs).
AES Operation Overview (Encryption Process)
Instead of using bits for calculations, AES uses bytes. The State, which is a 4×4 matrix of 16 bytes, represents the 128-bit plaintext block. A distinct 128-bit round key created from the original key using the Key Expansion Algorithm is used in each of the several rounds of encryption.
There are four main transformations in every round, with the exception of the last one:
SubBytes (Substitution)
Using a fixed substitution table called the S-box, this non-linear step replaces each of the 16 input bytes.
ShiftRows (Permutation)
The 4×4 State matrix’s rows are cyclically shifted to the left by a different offset for each row in the ShiftRows (Permutation) transposition phase (the first row remains untouched, the second is shifted one place, the third two, and the fourth three). In order to achieve diffusion by blending data across the columns, this step is essential.
Also Read About IPsec VTI: What is IPsec Virtual Tunnel Interface & Benefits
MixColumns (Mixing/Diffusion)
This transformation generates four entirely new bytes for each column of four bytes by applying a unique mathematical function (matrix multiplication). The last cycle skips this phase, which is meant to disperse the data throughout the block.
AddRoundKey
For that iteration, the relevant 128 bits of the round key are combined (XORed) with the resultant 128 bits of the State.
These four steps Inverse Mix Columns, Inverse Shift Rows, Inverse SubBytes, and Add Round Key, which is its own inverse are carried out in reverse order in the Decryption Process, which is comparable to encryption.
Applications of AES
Because of its high security and effectiveness, AES is the recommended option for protecting sensitive data while it is being transmitted. It is widely used in contemporary networking protocols:
Wireless Security (Wi-Fi)
An essential component of wireless network security is AES. It supports the most robust Wi-Fi security guidelines that the Wi-Fi Alliance has certified:
- AES encryption is used in the Counter Cypher Mode with Block Chaining Message Authentication Code Protocol (CCMP) in WPA2 (Wi-Fi Protected Access Version 2). Data integrity and confidentiality (encryption) are guaranteed by this protocol.
- Wi-Fi Protected Access Version 3, or WPA3, uses AES through the Galois/Counter Mode Protocol (GCMP), which incorporates AES counter mode encryption, to provide even more robust encryption. Specifically, WPA3-Enterprise requires the usage of a suite of 192-bit cryptography.
Also Read About TACACS+ Protocol Configuration And TACACS+ Vs RADIUS
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) and IPsec
In order to create private tunnels in VPNs, AES is essential:
- AES is one of the symmetric encryption algorithms frequently utilized by the Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) protocol in IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) to encrypt data.
- In IPsec, AES is utilised when security associations are negotiated, particularly for the encryption technique used in the IKE Phase 1 Policy and the IKE Phase 2 Transform Set.
- Despite being asymmetric, the Diffie-Hellman (DH) protocol produces symmetric keys, which are then used for mass encryption by algorithms such as AES.
Secure Communications Protocols
AES is frequently used to protect data confidentiality in a number of important communication protocols:
- Secure Communications: AES is used in protocols for voice/video conversations, email, instant messaging, and general internet communication (such TLS, which forms the foundation of HTTPS).
- Secure Shell (SSH): To safeguard user passwords and session data, this network protocol employs AES encryption.
- SNMPv3 (Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3): To protect device management communication, SNMPv3 offers optional encryption (privacy) using AES, which can be configured with 128, 192, or 256-bit keys.
Data Storage
AES is used to secure data on network-attached storage or devices in addition to transmission:
- File and Disc Encryption: To prevent unwanted access in the event of loss or theft, AES is used to encrypt private information kept on hard drives, USB devices, and cloud storage.
- Database Encryption: Sensitive information held in databases, such as financial records, can be encrypted using AES.
Also Read About Intrusion Detection System IDS Importance & IDS vs Firewall
