One of the most important elements of a successful network security program is user awareness. It aims to inform all users about cybersecurity risks and their part in safeguarding personal information and an organization’s information assets.
User Security Awareness

Raising user security awareness entails educating all users on the need of data confidentiality in protecting company information, as well as their own login credentials and personal information. It is a crucial component as, in the event that their credentials are stolen, users themselves pose a serious security risk. Many users do not have an IT background, thus they might not be able to identify vulnerabilities or completely understand the repercussions of their actions.
You can also read What Are The Common Network Security Vulnerabilities?
How User Security Awareness Works
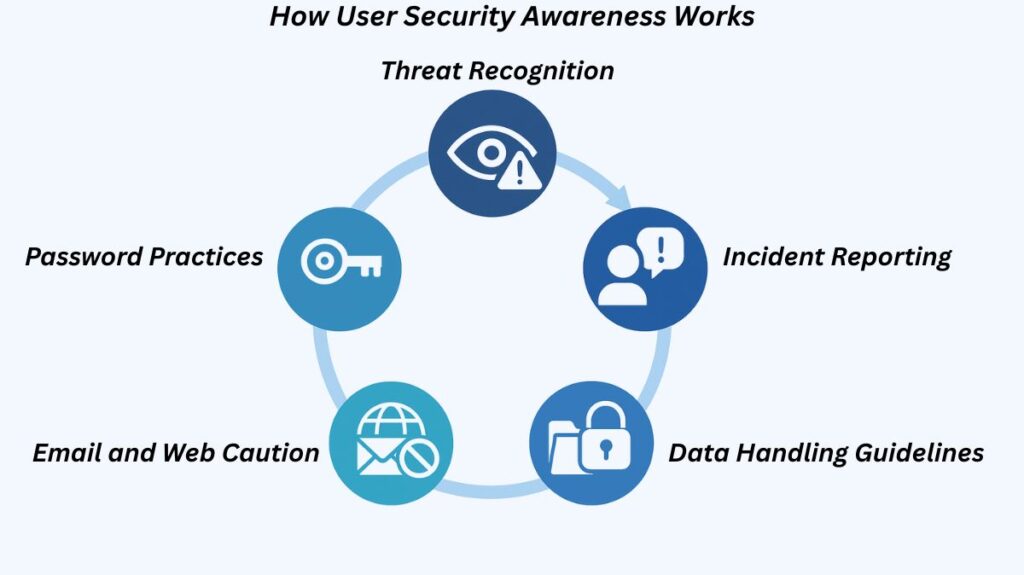
Raising user security awareness is achieved by instruction and the creation of precise policies and processes:
Threat Recognition: Potential dangers and deceptive tactics are alerted to users.
Incident Reporting: They are aware of the correct protocols for reporting security events.
Data Handling Guidelines: Tight instructions are given to avoid data loss. For instance, users should be told not to send sensitive data from cellphones, store it on unauthorized cloud services or external storage devices, or include it in emails or attachments.
Email and Web Caution: It is important to warn users not to click on links in emails, even if the sender seems trustworthy. The use of SSL/HTTPS (shown by a padlock icon or “https://” in the URL) and the importance of examining a website’s address bar to confirm its legitimacy should also be explained to them.
Password Practices: Acceptable password usage guidelines, such as when to use them, how to format them (e.g., using letters and numbers, making them at least six characters long, and avoiding common terms), and how frequently to change them should all be included in a security policy.
Why User Security Awareness is Important?
Because human weaknesses are commonly exploited by attackers, user security knowledge is crucial. A single human error, like clicking on a malicious link, can cause malware (like viruses or worms) to infect a user’s machine, open a backdoor, or otherwise negatively affect business operations. In the absence of sufficient security protocols and user awareness, the likelihood of a breach is greatly increased. The saying “an ounce of prevention here is worth a pound of forensics later if a compromise has occurred” implies that user education is a crucial component of threat mitigation. The willingness and ability of users to adhere to corporate policy is one of the most difficult security concerns of our time.
You can also read Types of Mitigation Techniques, How it Works and Advantages
Types of Threats Addressed
Countering attacks that take advantage of human trust and conduct is the main goal of user security awareness:
Social Engineering Attacks: Threat actors coerce victims into doing actions or disclosing private information in these attacks. Common methods include of:
- Phishing: Malicious invitations that pose as genuine requests (for example, through phoney websites or emails) in order to fool victims into divulging private information like passwords and usernames. Since phishing attempts are usually not stopped by antivirus or anti-malware software, the best defence is user awareness and training.
- Spear Phishing: Phishing that is more specifically targeted at a certain user demographic.
- Whaling: Focusses on prominent people inside a company.
- Vishing: Makes voice calls in order to engage in social engineering.
- Smishing: Uses SMS text messages as a means of social engineering.
- Pharming: Redirects a user’s URL from a reputable resource to a malicious one that seems authentic in order to obtain private data.
- Watering Hole Attack: Entails infiltrating a website that the target users visit regularly and installing malware that solely infects the targeted victims.
Password Vulnerabilities: User awareness campaigns draw attention to the risks associated with using default, weak, or simple passwords. Additionally, they address bad password hygiene, including writing passwords on sticky notes that are placed close to workstations.
Malware-Related Attacks: Many malware infestations, such as Trojan horses, worms, and viruses, start when users inadvertently open compromised files or click on harmful links. Preventing these first points of compromise is made easier by user knowledge.
Eavesdropping (Network Snooping/Packet Sniffing): At this point, hackers “listen in” on network activity. User awareness and security policies that require encryption for important traffic and prohibit the use of protocols known to be vulnerable to eavesdropping can mitigate the issue of network packets not being encrypted by default. In particular, wireless data is susceptible to being overheard by anyone nearby if it is not safeguarded.
User Security Awareness Advantages
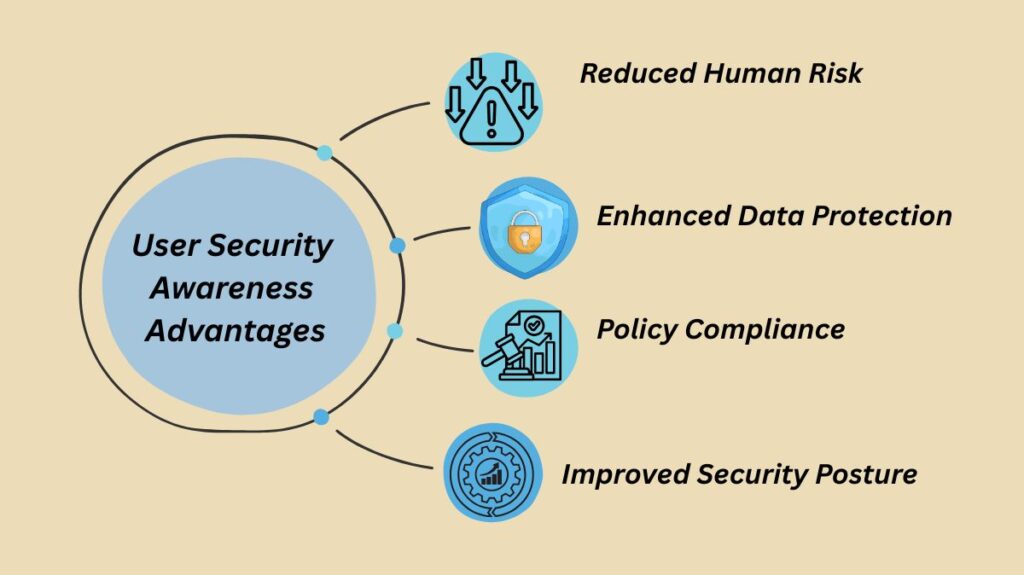
Reduced Human Risk: The probability of assaults that take advantage of human trust and conduct is greatly decreased by increasing user awareness, which makes users more watchful and knowledgeable.
Enhanced Data Protection: It directly helps to protect personal and business data by encouraging careful handling of sensitive data and understanding of data confidentiality.
Policy Compliance: Users are more likely to comprehend and follow company security policies and procedures when an awareness program is properly implemented.
Improved Security Posture: By tackling one of the most enduring weaknesses the human element it improves an organization’s overall security posture.
You can also read What Is A Network Security Threat? History, And How It Works
User Security Awareness Disadvantages
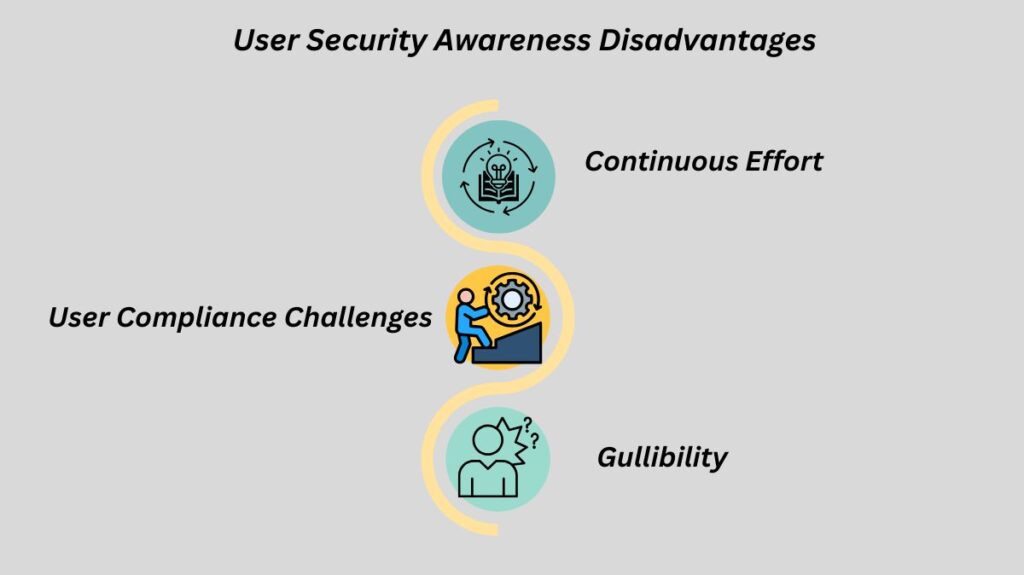
Continuous Effort: Being security conscious is a continuous process. In order to keep people aware, social engineering tactics and threats must be updated on a regular basis and require ongoing formal training.
User Compliance Challenges: Users may find security regulations inconvenient, even with training, which could result in shortcuts or deliberate policy circumvention, including attempting to escape history records by using old passwords.
Gullibility: One of the most difficult security problems of our time is human vulnerabilities since users can still be tricked even with awareness.
User Security Awareness Applications
An essential component of any all-encompassing corporate security program is user security awareness. It functions in tandem with a number of technical security tactics and mechanisms, such as:
Formal Security Policies: On top of formal security rules that specify acceptable behaviour and security criteria for users, staff, and business partners, awareness programs are developed and reinforced.
Access Control: Because credentials are essential for gaining initial access to network devices, user awareness helps access control methods by holding users accountable for safeguarding them.
Endpoint Security: Because endpoints (laptops, desktops, servers, IP phones, and employee-owned BYOD devices) can become infected with malware through web browsing or email, user awareness helps avoid these early infections.
Network Access Control (NAC) and Identity Service Engine (ISE): In order to supplement user knowledge, these systems can enforce policies that check devices for compliance with security criteria (such as virus scanning tools, patches) before granting network access.
You can also read How Is The IEFT Related To The IRTF, History & Types Of IETF
Compared with User Training
User training is a separate but closely connected component. While user awareness aims to raise awareness among people, user training entails scheduled, structured sessions in which all users must attend in order to become acquainted with all corporate security regulations. For its users, staff, and business partners, the company must also create and disclose these formal security rules.
All users must be aware of their responsibility to maintain security in a corporate network, which goes beyond its own boundaries to include external users and business partners. A user may misbehave even in perfect, closed systems, which is why continual training is essential.
Implementing a Security Awareness Program
A successful program for raising security awareness is a continual process that includes:
Initial Assessment: Determine which dangers are most important and which areas require the greatest training for users.
Tailored Content: Provide training materials that are appropriate for the intended audience. For instance, a financial team may want more specialized training on wire transfer fraud, whereas an IT team may require more technical information.
Regular Training: Regularly hold training sessions, such once a year or every three months. To maintain user engagement, use a variety of forms, such as interactive modules, brief movies, and simulated phishing assaults.
Simulated Phishing: In a controlled setting, simulated phishing campaigns are an effective way to gauge user awareness. Clicking on a link is not a security event; rather, it is a teaching moment.
Reinforcement and Communication: Remind people about security on a frequent basis through internal mailings, newsletters, and posters. As new threats appear, disseminate knowledge and reinforce important ideas.
Measurement and Feedback: To assess the program’s efficacy, monitor KPIs like the proportion of users who fail simulated phishing exams. Over time, use feedback to make the training better and more efficient.
Organizations can create a robust human firewall to protect against a constantly changing array of cyberthreats by involving everyone in security and giving them the necessary resources and expertise.
You can also read Advantages And Disadvantages Of Malware & Types Of Malware
