What is a pharming attack?
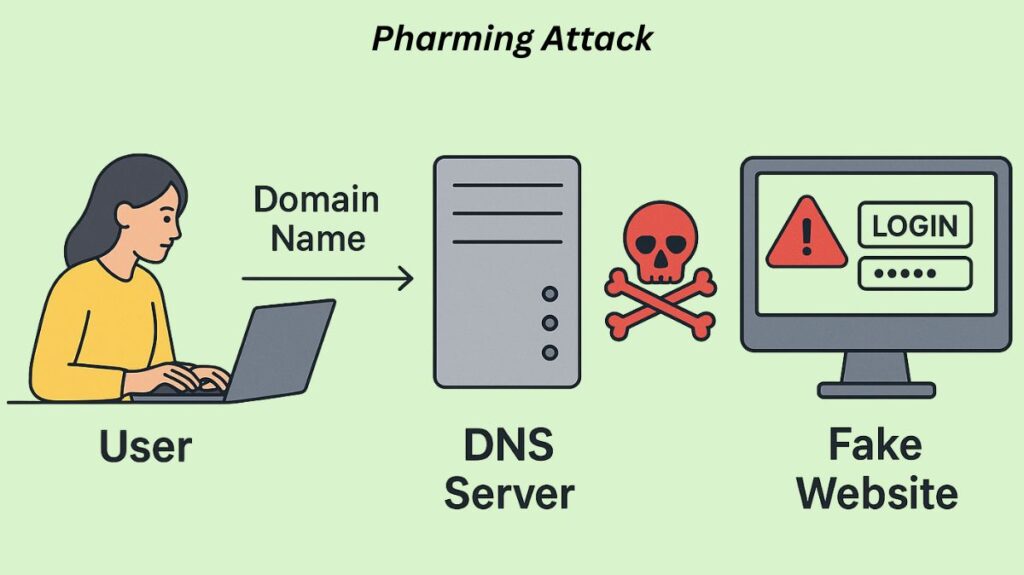
One type of online fraud or cyberattack that aims to divert website visitors to a phoney website is known as pharming. The user is not informed of or gives their approval for this.
Passwords, financial information (such as bank account or credit card numbers), login credentials, and other personally identifiable information (PII) are among the sensitive data that pharming aims to obtain. The phoney website that imitates the look and branding of a genuine one (such as online banking or e-commerce sites) deceives victims into divulging this private information.
A neologism, “pharming” is derived from the terms “phishing” and “farming,” which allude to the extensive gathering of personal information. A more sophisticated and hazardous kind of phishing is pharming.
How Pharming Works
DNS pharming converts URLs like www.example.com into numeric IP addresses that computers use to find websites. Attackers can swap network or computer settings to send victims to their server instead of the website.
Two main techniques are employed to carry out a pharming attack:
Host File Modification (Malware-based Pharming)
This technique usually targets the PC of a single user:
Installation of Malware: A Trojan horse or virus is often downloaded accidentally through fraudulent emails or software downloads.
File Alteration: The malware causes changes to the local “hosts” file on the computer. By using a local mapping, the hosts file avoids the typical DNS lookup.
Redirection: Even if the user enters the right URL, the attacker’s counterfeit copy will be immediately accessed by any legitimate request for the targeted website once the hosts file has been altered.
Also Read About What is WAN Security & Advantages of Wide Area Network Wan
DNS Poisoning / DNS Server Compromise
Due of its focus on network infrastructure, this approach is typically more popular and effective.
DNS Server Exploitation: The software used by DNS servers, which convert Internet names into IP addresses, has flaws that attackers take advantage of.
Cache Corruption: The attacker inserts a fake DNS entry into the DNS server’s cache or table, corrupting it.
Widespread Impact: Anyone depending on that DNS server to visit the authentic website will be unintentionally diverted to the fake site since the DNS server has been compromized (also known as “poisoned”). Thousands or hundreds of users may be impacted at the same time.
Router Compromise: A local network router compromise is a particularly concerning vector since it provides clients with a trusted DNS. Any changes made to the router’s firmware or settings will contaminate lookups for the whole Local Area Network (LAN).
Pharming attack vs Phishing
Both attacs seek to steal data, although pharming differs in its attack vector and level of sophistication: steal data, pharming is distinguished by its sophistication and attack vector:
| Feature | Phishing | Pharming |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Relies on social engineering, typically via deceptive email or text, to trick the user into clicking a malicious link. | Attacks the underlying systems (DNS or hosts file) to route web traffic. |
| User Action Required | The user must consciously click a link or open an attachment. | No link clicking or interaction is required; the user is redirected automatically after the malicious code is installed or the server is compromised. |
| Deception | Relies on making a link or email look trustworthy. | Redirects the user even if they type the correct, legitimate URL into the browser. |
| Scale | Generally targets individuals or small groups via direct messages. | Can victimise larger numbers of computer users simultaneously, particularly through DNS poisoning. |
Also Read About Advantages, Disadvantages Of Routers & How Do Routers Work
How to prevent pharming attacks
User awareness and technical safeguards are both necessary for effective pharming protection:
Use Secure Connections (HTTPS): The “https” at the beginning of the URL should be checked by end users to make sure they are accessing privacy-sensitive websites via Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS). This makes traffic encrypted. While helpful, depending only on the padlock emblem is not infallible because SSL certificates can also be used by fraudulent websites.
Strong Password Practices for Routers: On consumer-grade routers and wireless access points, change the administrative passwords right away. Default passwords are a huge weakness.
Use Security Software: Install and update antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and halt host file altering programs. DNS server poisoning cannot be prevented with conventional antivirus software, thus you may need specific tools or DNS protection.
Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enabling MFA adds an additional layer of protection, preventing the attacker from accessing the account without the second factor, even in the event that credentials are taken via a pharming attacks.
Use Reputable DNS Services: Change the DNS settings on your router or device to Cloudflare or Amazon to avoid DNS server poisoning.
Vigilance and URL Checking: Keep an eye out for mistakes or odd spellings in URLs because pharmers frequently use little alterations to hide their websites. It’s also advised to use bookmarks for websites that are visited regularly.
Also Read About DHCP Server Conflict, DHCPv4 Operation & DHCPv6 Operation
