We discussed what glibc Linux is, its history, how it functions, its features, its role in Linux, why it matters, its benefits and drawbacks, alternatives to glibc, and Linux Check glibc Version this blog.
What is glibc linux?
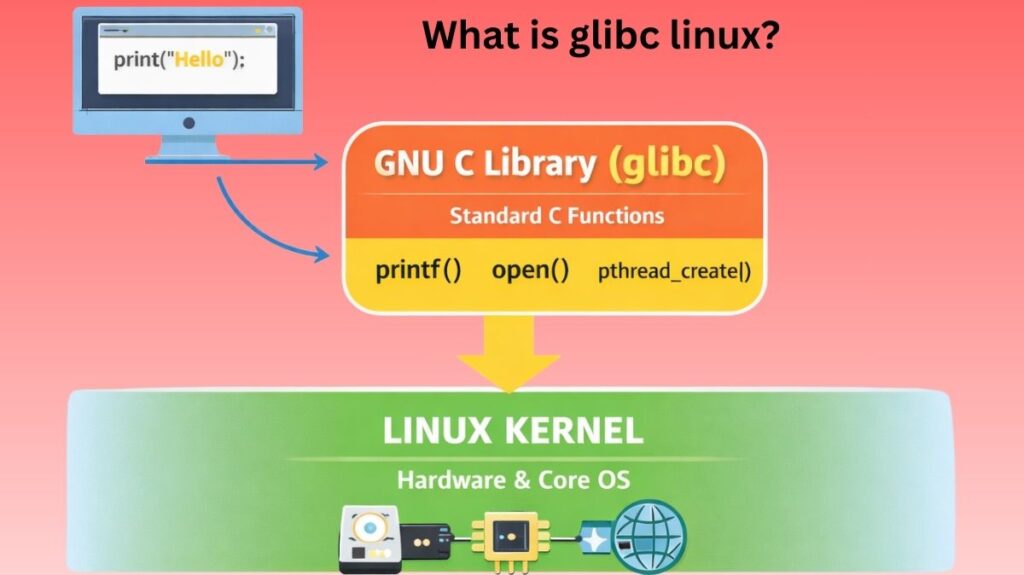
The GNU Project’s implementation of the C standard library is called the GNU C Library, or glibc. For application use, it offers a wrapper for the Linux kernel’s and other kernels’ system calls. Contrary to its name, it now supports C++ directly as well as other programming languages indirectly.
Simply put, glibc makes C and C-based software compatible with Linux. Without it, most terminal commands won’t run.
History
The GNU Project was the original source of glibc, which sought to provide an operating system that was entirely free and similar to Unix. There were already C libraries on early Unix systems, but many of them were restricted or proprietary. A powerful, free, and standard-compliant substitute was what the GNU developers were looking for.
Glibc was initially limited to the most important C functions. Glibc expanded along with Linux as it grew more sophisticated and popular over time. Gradually, support for contemporary hardware, threads, localization, and performance tuning was introduced. Glibc is being maintained by a global community and is regarded as one of Linux’s most reliable components.
How Glibc works
Glibc acts only in user space, not the kernel. Programs employ glibc functions to read files and allocate memory. Afterward, glibc turns the request into a kernel-friendly system call.
Glibc processes the outcome and gives it back to the application once the kernel has finished the task. This tiered strategy guarantees consistent behaviour across many systems and separates applications from kernel complexity.
Also Read About What Is Linux Kernel? Why It Is Important And Its Components
Key working steps:
- A glibc function is called by the application.
- A system call is prepared and issued by glibc.
- The kernel carries out the request.
- The application receives the result back.
Features
Although glibc provides thousands of functions, some are more crucial than others.
Core C functions
These consist of basic math, memory allocation, input/output operations, and string processing. These functions are utilized by all C programs, frequently without the programmer’s awareness.
System call wrappers
Glibc wrappers manage things like file access, creating processes, and communicating across processes. These wrappers shield applications from low-level faults and kernel modifications.
Thread and concurrency support
Glibc enables software to effectively utilize multiple CPU cores by supporting multithreaded programs.
Localization support
Programs can accurately display text in several languages and regional formats to glibc.
Also Read About Linux Architecture Layers: Kernel, Shell, And Hardware
Role of glibc in Linux
Glibc specifies the interface between Linux and user-space applications. Everything, from a basic ls command to sophisticated server programs, depends on glibc to work.
Glibc guarantees uniformity throughout the system since it is shared by all programs. One of the primary causes of the consistent behaviour of Linux software across distributions is this.
Why glibc is so important
Linux would essentially cease to function if glibc were eliminated or damaged. It is essential to the graphical environment, background services, package management, and shell.
Glibc’s backward compatibility is another factor that makes it crucial. Due to glibc’s meticulous preservation of earlier behaviour, programs compiled many years ago frequently continue to function on contemporary platforms.
Benefits
Glibc is the recommended C library for general-purpose Linux systems due to its many benefits.
- Rich functionality: Facilitates intricate workloads and applications.
- Standards compliance: Guarantees compatibility with Unix-like systems.
- Optimised performance: Adapted to contemporary hardware.
- Widespread adoption: Excellent documentation and community support.
- Glibc is appropriate for desktops, servers, and cloud platforms because of these benefits.
Drawbacks
Glibc has several drawbacks in spite of its advantages. In settings with constrained system resources, its size and complexity may be a disadvantage.
- Big footprint: Unsuitable for embedded or basic systems.
- Complicated internals: May be more difficult to modify and debug.
- Updates must be made carefully: The system as a whole may be impacted by errors.
- Alternative libraries are used in some specialized systems due to these reasons.
Alternatives to glibc
Although glibc is the most used C library on Linux, there are other options for certain applications. These substitutes frequently have an emphasis on ease of use, compact size, or quicker startup times.
They are frequently utilised in minimal Linux environments, containers, and embedded systems. They might not, however, have all of the sophisticated features that Glibc offers.
Licensing and Community Support
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) governs the release of glibc. This license guarantees that updates to the library itself stay free while permitting the usage of glibc in both open-source and proprietary software.
A worldwide developer community maintains the library by providing security updates, performance enhancements, and bug fixes.
Linux check glibc version

Glibc itself is a library, so users do not “run” it directly like a command. However, Linux provides several commands that interact with glibc and help us understand how it works in real systems.
Checking the Installed glibc Version
Every Linux system has glibc installed by default. To check the version currently in use, the following command is commonly used:
ldd --versionThis command works because ldd is part of glibc. The output shows the glibc version along with copyright information. System administrators often use this command when diagnosing compatibility issues.
Finding Which glibc a Program Uses
To see which shared libraries (including glibc) a program depends on, the ldd command is used:
ldd /bin/lsThis command lists all shared libraries required by the program /bin/ls. One of the entries will point to libc.so.6, which is the core glibc shared library. This helps developers understand runtime dependencies.
Locating glibc Files on the System
Glibc libraries are stored in system library directories. You can locate the main glibc file using:
ls /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6On some systems, the path may differ depending on architecture, but libc.so.6 is always the central glibc library.
How glibc Handles a Simple Program
Consider a simple C program that prints text on the screen.
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
printf("Hello, Linux\n");
return 0;
}Although this program looks simple, glibc performs many tasks behind the scenes.
In conclusion
One essential component of Linux operating systems is the GNU C Library (glibc). It offers crucial features that make it possible for apps to communicate with the kernel in a secure, uniform, and effective way. Its significance in contemporary computing is demonstrated by its features, history, benefits, and difficulties.
Developers and system administrators can better understand how Linux functions and why it continues to be a dependable and popular operating system by being familiar with glibc.
Also Read About What Is The Difference Between FAT And NTFS File Systems?
