System Library in Linux
Introduction to System Libraries
System libraries are essential to the operation of Linux’s operating system and user applications. They serve as a layer in between the Linux kernel and application programs. Applications employ system libraries, which offer a common and secure method of accessing system resources, rather than interacting directly with the kernel. Linux is more effective, safe, and manageable because to this design.
What is system library in linux?
System libraries are sets of prewritten code that give programs access to frequently used features. File handling, memory allocation, process creation, input and output activities, and network communication are some of these functions. Programmers can avoid writing the same code over and over again by utilizing libraries. Rather, they make use of the system’s dependable and verified features.
Multiple programs in Linux typically share system libraries, which conserves disc space and RAM.
Role of System Libraries in the Linux Architecture
The Linux kernel and user-level applications are separated by system libraries. System libraries use system calls to communicate internally with the kernel, and applications call these libraries’ functions. This tiered strategy guarantees that applications adhere to defined guidelines while utilizing hardware or system resources while concealing from application developers the intricacy of kernel interactions.
Because apps are unable to directly alter kernel components, this structure also enhances system stability.
Also Read About What Is Btrfs File System In Linux? And Btrfs Vs Ext4 Vs XFS
Types of Linux System Libraries
Overview
Different system libraries exist in Linux. System functions like fundamental program execution, hardware interfacing, threading, networking, graphics, and mathematical operations are supported by many kinds of system libraries. Every kind of system library has a distinct function and facilitates safe, standardised application interaction with the Linux kernel. Gaining an understanding of these kinds makes it easier to see how Linux programs are developed and run.
- GNU C Library (glibc)
The most important Linux libraries are called core system libraries. On a Linux system, practically all programs rely on them sometime. Memory allocation, file input/output, process creation, and string manipulation are handled by these libraries.
The major system library is glibc. It is the main Linux kernel-user application interface. Programs use glibc functions to open files, start processes, and print output. Without critical system libraries, most Linux programs fail.
- Standard C Libraries
Functions specified by the C programming language standard are implemented by standard C libraries. These routines cover input/output, memory, text processing, and mathematical computations. There are different implementations for particular settings, including embedded computers, even though glibc is the most widely used implementation in Linux.
These libraries guarantee that C programs run uniformly on various Linux platforms. Additionally, they serve as the basis for numerous additional programming languages and libraries that internally depend on C.
- Mathematical Libraries
Beyond simple arithmetic, mathematical libraries offer more complex mathematical operations. Trigonometric computations, logarithms, exponential functions, and floating-point operations are some of these functions.
For these uses, Linux’s math library (libm) is frequently utilised. Mathematical libraries are essential to programs that carry out data analysis, engineering simulations, and scientific computations. Linux maintains programs’ modularity and efficiency by dividing these functions into specialised libraries.
Also Read About How Linux Works And Why Linux Is Important For Developers
- Threading Libraries
Threading libraries enable multithreading in a process. Threads let programs multitask, improving responsiveness and performance.
The most used Linux threading library is libpthread. It lets applications properly handle shared resources, produce threads, and synchronise. Modern applications like web servers, databases, and real-time systems require threading libraries.
- Dynamic Linking Libraries
Shared libraries can be loaded and linked at runtime with the help of dynamic linking libraries. Programs can use shared code to these libraries without having to include it in their executable files.
Libraries like libdl aid in controlling the dynamic loading of shared assets under Linux. This feature makes software more adaptable and expandable by enabling applications to load plugins or modules while they are operating. Because numerous programs can share the same library code, dynamic linking also lowers memory utilization.
- Hardware Interaction Libraries
Interfaces for regulated access to system hardware are offered by hardware interaction libraries. Without requiring direct access to hardware registers, these libraries enable applications to communicate with peripherals like discs, network cards, and input/output devices.
Applications stay safe and portable by utilizing these libraries, and the kernel keeps control over hardware access. System stability is increased and hardware resource abuse is avoided to this division.
- Networking Libraries
Functions for network communication, such as socket creation, data transmission and reception, and network connection management, are provided by networking libraries. Applications can connect over local networks and the internet to these libraries.
Web browsers, servers, email clients, and cloud services employ Linux networking libraries. They hide network protocol complexity so developers can focus on application logic.
- Graphics and User Interface Libraries
Graphical application development is easier with graphics and user interface libraries. Window management, graphics, and keyboard and mouse input are handled by these libraries.
Libraries utilised by application toolkits and graphical desktop environments are two examples. These libraries enable the development of user-friendly graphical applications that rely on the underlying system for display management and hardware interaction.
- Security and Cryptographic Libraries
Functions for encryption, decryption, authentication, and secure communication are offered by security and cryptography libraries. These libraries are necessary to guarantee secure communications and safeguard private information.
These libraries are necessary for applications that deal with passwords, secure file storage, or encrypted network connection. Linux guarantees standardised and tried-and-true security measures for all applications by centralizing security services.
- Utility and Support Libraries
Other support functions that do not fit into core categories are offered by utility libraries. These could comprise libraries for localisation, logging, compression, and configuration management.
These libraries enhance program functionality and user experience, while they are not usually essential for system launch. They are extensively utilised in contemporary Linux services and applications.
Also Read About What Is Ext4 File System In Linux? Features And Advantages
Why System Libraries Are Important
The following reasons make system libraries crucial:
- Encourage uniformity and code reuse
- Limit kernel access to increase system security
- Cut back on storage and memory usage
- Make the process of developing applications simpler
- Allow updates and enhancements for the entire system
- Linux would be more difficult to create, scale, and maintain without system libraries
Library Management in Linux
Linux speeds up loading by keeping track of accessible shared libraries in a cache. This cache is updated and the required symbolic links are created by the ldconfig command. Configuration files like /etc/ld.so.conf include the list of folders that contain shared libraries.
Programs can find the right versions of the libraries they require when libraries are managed properly.
Examples of Linux System Libraries
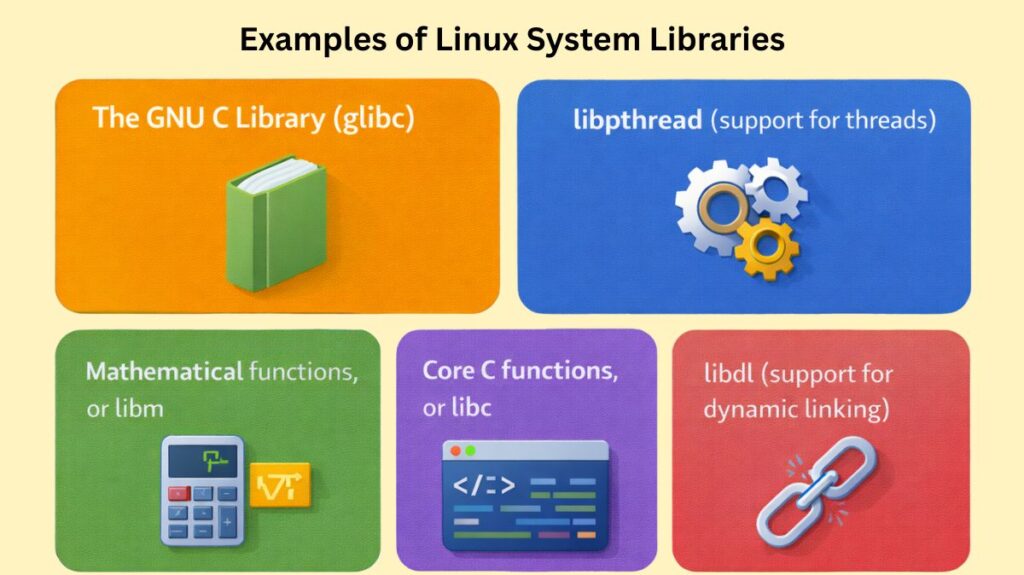
Among the frequently used Linux system libraries are:
- The GNU C Library (glibc)
- libpthread (support for threads)
- Mathematical functions, or libm
- Core C functions, or libc
- libdl (support for dynamic linking)
Numerous applications demand unique functionality, which each of these libraries offers.
In conclusion
An essential component of the Linux operating system are system libraries. They give apps a consistent way to access system resources while preserving stability and security. System libraries make software development easier and increase overall system efficiency by managing complicated processes and providing reusable functions. Anyone learning Linux internals, system management, or application development must have a solid understanding of system libraries.
Also Read About Linux Architecture Layers: Kernel, Shell, And Hardware
