What is a Linux shell?
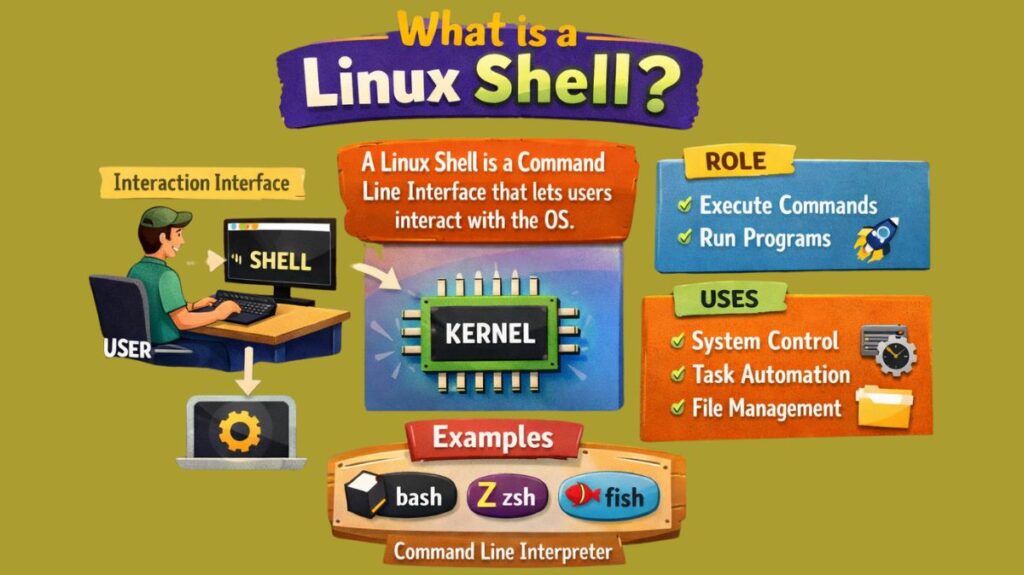
A Linux shell is a command-line interface (CLI) that enables users to interact with the operating system, execute commands, and automate procedures. It is a useful tool for daily computer use, system administration, and program development. The shell facilitates file access and manipulation, program execution, and system management by acting as a bridge between the user and the underlying operating system.
Functions of the Linux Shell
Command Interpretation
After reading user input, the shell deciphers each command’s meaning. It comprehends the required operation and deconstructs the command into its component pieces. Users can write commands in an easy-to-read format to its interpretation.
Program Execution
Both user and system programs are executed by the shell. It guarantees that programs run properly, controls execution, and generates new processes. In Linux, the shell is traversed by each command.
Input and Output Redirection
By using the shell, users can take input from files rather than the keyboard and redirect command output to files. This function facilitates efficient processing of big amounts of data and results saving.
Piping
One command’s output can be utilised as another command’s input to piping. This enables the combination of several commands to carry out difficult tasks in an easy manner.
Automation and Scripting
Because of the shell’s support for scripting, users can utilize shell commands to create programs. Repetitive processes like system monitoring, upgrades, and backups can be automated with the use of scripts.
Also Read About What Are System Utilities In Linux? Commands With Examples
Different types of shell in Linux
The two primary forms of shells are graphical user interface (GUI) and command-line interface (CLI).
Command-Line Interface (CLI) Shells
These are the most prevalent kind of “shells” in the Linux context and are the main means by which users communicate with the system using text commands.
Bash (Bourne Again Shell)
The most popular and standard shell in the majority of Linux distributions (such as Fedora and Ubuntu) is called Bash (Bourne Again Shell). With capabilities for scripting, job control, and command history, it is a powerful improvement over the original Bourne shell.
Zsh (Z Shell)
A sophisticated shell that is well-liked by power users due to its robust auto-completion, plugin support, and wide range of customisation possibilities. With more recent iterations of macOS, it is the default shell.
Fish (Interactive, Friendly Shell)
Features like syntax highlighting, auto-suggestions, and an integrated help system are all part of Fish’s user-friendly design.
Ksh (Korn Shell)
David Korn created the Ksh (Korn Shell), which is renowned for its effective scripting capabilities and integrated arithmetic operations. It integrates elements from the Bourne and C shells.
Sh (Bourne Shell)
The original Unix shell, Sh (Bourne Shell), was renowned for its portability and ease of use. Although it lacks interactive features like command history, it is the basis for many contemporary shells.
Csh (C Shell) / Tcsh (TENEX C Shell)
Programmers are drawn to Csh (C Shell) and Tcsh (TENEX C Shell) because of their comparable syntax to that of the C programming language. With facilities for history and command-line editing, Tcsh is an improved version of Csh.
Dash (Debian Almquist Shell)
Because of its low resource consumption, this lightweight and quick shell is frequently used as the default system shell for running system starting scripts in Debian-based distributions.
Graphical User Interface (GUI) Shells
With windows, menus, and icons, these offer a visual environment. In the Linux environment, some examples are as follows:
GNOME Shell
Many popular distributions, including Fedora and Ubuntu, use the GNOME Shell as their default graphical user interface.
KDE Plasma
Frequently the default in distributions like openSUSE and Kubuntu, it is renowned for its adaptability and wide range of customisation possibilities.
Also Read About What Is Linux Kernel? Why It Is Important And Its Components
Components of a Shell
A Linux shell acts as an interface between the user and the kernel. It is made up of several key components that work together to execute commands.
1. Command Interpreter
- Reads and interprets user commands
- Converts commands into instructions for the kernel
- Executes both internal and external commands
Example:
ls2. Prompt
- Displays a symbol indicating the shell is ready
- Shows user, host, and current directory
Example:
user@linux:~$3. Environment Variables
- Store system-wide and user-defined values
- Control shell behavior
Examples:
PATH
HOME
USER4. Command History
- Stores previously executed commands
- Allows reuse and editing
Example:
history5. Input and Output Redirection
- Redirects command input or output
- Supports pipes for chaining commands
Examples:
ls > files.txt
cat file.txt | grep "linux"6. Job Control
- Manages background and foreground processes
Examples:
bg
fg
jobsAlso Read About Most Commonly Used C Standard Library Functions On Linux
Basic Command Examples
Several basic commands are shared by most CLI shells, regardless of the particular one.
- ls: Enumerates a directory’s contents.
- cd: The current directory is changed with cd.
- pwd: The path to the current working directory is printed using pwd.
- mkdir: A new directory is created with mkdir.
- cp: Makes copies of directories or files.
- mv: Renames or moves directories or files.
- Files or directories are deleted with the rm command.
- cat: Shows a file’s contents.
Benefits and drawbacks of Shell
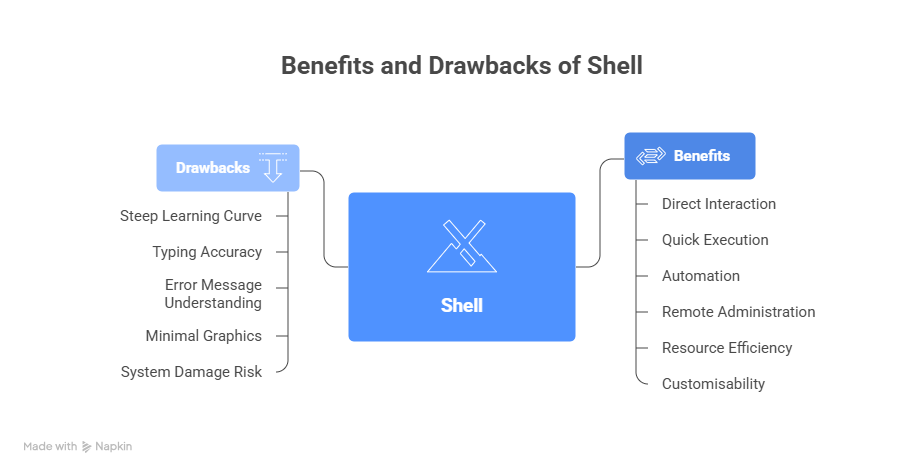
System administrators and users can benefit greatly from the Linux shell.
Benefits of Shell
- Direct interaction with the operating system
- Quick and effective command execution
- Strong automation with scripts
- SSH-based remote system administration
- Uses relatively little system resources
- Adaptable and customisable
Drawbacks of Shell
The shell has certain drawbacks despite its strength.
- Steep learning curve for novices
- Accurate typing is required for commands
- Understanding error messages might be challenging
- Minimal use of graphics
- Danger of system damage in the event that commands are abused
What is the Best Linux Shell Overall?
| User Type | Best Shell |
|---|---|
| Beginner | Fish |
| Developer / Power User | Zsh |
| System Administrator | Bash |
| Script Writer | Bash |
| Customization Lover | Zsh |
| Minimal Systems | Bash |
Also Read About Linux Check glibc Version: What Is glibc And Why It Matters
