Linux Distributions
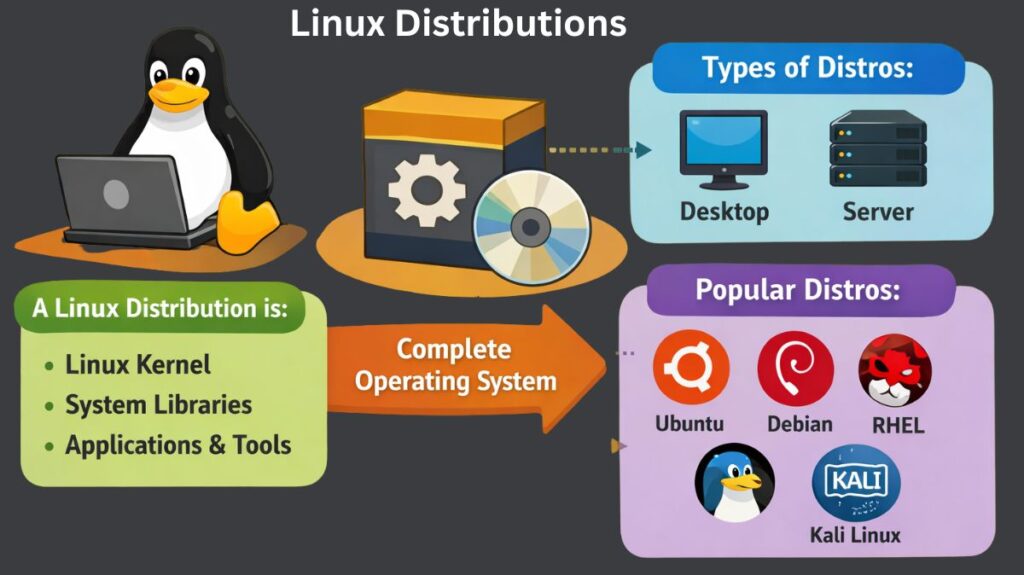
The Linux kernel is used to create Linux distributions, which are whole operating systems that also include extra programs, hardware, and system utilities. Hardware and system resource management is solely the responsibility of the Linux kernel. A distribution adds libraries, package managers, apps, and configuration files to the kernel to make Linux useable for actual users.
Linux distributions exist because different users have different needs. Some users want a simple desktop system, while others need a stable server platform or a security-focused environment. Linux is flexible and adaptable to all of these needs to distributions.
What Is Linux Distribution (Distro)?
A packaged version of Linux that comes with the Linux kernel, system libraries, utilities, and application programs is known as a Linux distribution, or distro. Additionally, it has a package management system that makes it simple for users to install, update, and uninstall software.
Linux distributions vary in look, software availability, update frequency, and target customers, although using the same kernel. For instance, while certain distributions stress security or stability, others concentrate on usability. Users can choose the distribution that best fits their needs to this versatility.
Components of a Distribution
A distribution is a collection of interconnected modular components rather than a single software package.
- Linux Kernel: The Linux kernel is the central component that controls hardware (CPU, memory, and peripherals) and permits software to communicate with it.
- Bootloader: The initial application (such as GRUB) that loads the kernel into memory when the computer is turned on.
- Init System: The initial process (such as systemd) that launches following kernel loading. It controls daemons, or background services.
- Display Server: The subsystem (such as X11 or the more recent Wayland) that creates graphics on your screen.
- Desktop Environment (DE): The graphical user interface (GUI) that you use, such as windows, taskbars, and icons (e.g., GNOME, KDE Plasma, Xfce).
- Package Manager: The Linux equivalent of the “App Store” is Package Manager. Software is installed, updated, and removed (e.g., DNF for Fedora, APT for Ubuntu).
Features
- Open Source: You can view, edit, and distribute the source code for free.
- Multi-User & Multitasking: Built from the ground up to support numerous users and processes at once without crashing.
- Security: It is intrinsically more malware-resistant than Windows due to its stringent permission-based architecture (Root vs. User).
- Package Management: Software is validated and updated with ease to centralized repositories.
Also Read About What Is A Shell Script In Linux? How It Works And Examples
Linux Distribution Types
The use and purpose of Linux distributions can be used to classify them.
Certain distributions have graphical user interfaces and commonplace apps and are intended for desktop users. Others are built for server environments, focusing on stability, performance, and long-term support. Additionally, specific distributions have been developed for applications including lightweight computing, system recovery, and penetration testing.
Without needless complication, this classification aids users in determining which distribution best suits their requirements.

Popular linux distributions
Numerous Linux distributions have become more well-known over time as a result of their features, dependability, and community support. Within the Linux ecosystem, each of the following distributions fulfills a certain function.
Ubuntu
One of the most popular Linux distributions worldwide is Ubuntu. It is known for its simplicity, ease of installation, and strong community support. Because it offers a seamless learning experience and has numerous preinstalled programs, Ubuntu is frequently suggested for novices.
Ubuntu has a regular release cycle and is based on Debian. Servers, laptops, desktop computers, and even cloud platforms use it. Because of its balance between usability and performance, Ubuntu is suitable for both personal and professional use.
Debian
Debian is one of the oldest and most respected Linux distributions. Stability and the ideals of free software are highly valued. Debian systems are a popular option for servers because of their reputation for dependability.
Debian places a higher priority on extensive testing than other distributions that concentrate on the newest software. Because of this, it adopts new features a little more slowly yet is incredibly reliable. Debian is the foundation for many other distributions, such as Ubuntu.
Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL)
A commercial Linux distribution made specifically for business settings is called Red Hat Enterprise Linux. Organizations that need security upgrades, long-term stability, and expert technical assistance frequently employ it.
RHEL follows strict testing standards and offers guaranteed updates over many years. Large-scale manufacturing systems, financial organizations, and corporate data centers frequently use it since it is subscription-based.
Also Read About What Is The Difference Between Linux And Windows? Explain
CentOS
CentOS was traditionally a free, community-supported distribution built from the source code of RHEL. It provided stability at the enterprise level without requiring a commercial license.
For servers and business apps, CentOS gained a lot of traction. CentOS is still a crucial distribution for comprehending enterprise Linux settings, despite changes in its development methodology over time.
Fedora
Red Hat is the sponsor of Fedora, a community-driven Linux distribution. It focuses on innovation and modern technology. New software versions and features are frequently released by Fedora before enterprise deployments.
Fedora is well-liked by developers and Linux fans who wish to have access to the newest tools and technologies as a result. Additionally, it acts as a platform for testing technologies that might eventually be included in RHEL.
Kali Linux
A specific Linux distribution called Kali Linux was created for penetration testing and cybersecurity. It comes with many preinstalled tools used for security auditing, vulnerability testing, and digital forensics.
Security experts, ethical hackers, and students studying cybersecurity are the main users of Kali Linux. It is not meant to be used on a desktop for general purposes.
Desktop Linux vs Server Linux
Daily users are the target audience for desktop Linux distributions. They emphasize programs like web browsers, office software, and media players, as well as graphical user interfaces and ease of use. The goal of these distributions is to make the user experience comfortable.
Performance, stability, and security are the main priorities of server Linux distributions. They are designed for functions like web hosting, databases, and network services and frequently operate without a graphical user interface. The primary distinction is not in the Linux kernel itself, but rather in setup and intent.
| Feature | Desktop Linux | Server Linux |
| Interface | Full GUI (Windows, icons, mouse) | Headless (Command line only) |
| Hardware | Supports Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPU | Supports RAID, Multi-core CPUs |
| Stability | Optimized for app responsiveness | Optimized for 100% uptime |
| Resources | Uses more RAM for visuals | Lightweight; minimal RAM usage |
Also Read About What Are System Utilities In Linux? Commands With Examples
Common Use Cases
For Beginners & General Use
- Distros: Ubuntu, Linux Mint, Pop!_OS
- The reason for this is that “it just works.” To facilitate the switch from Windows/Mac, they include pre-installed office suites, browsers, and drivers.
For cloud and server distributions
- Distros: Debian, RHEL (Red Hat), Ubuntu Server
- Why? Because of its “rock-solid” solidity. As the foundation of the internet, they power the majority of web servers and frequently lack a graphical user interface (GUI) to conserve resources.
For Hacking & Cybersecurity
- Distros: Parrot OS, Kali Linux
- Why? Because it comes with hundreds of tools for ethical hacking, digital forensics, and penetration testing.
For Software Developers
- Distros: Arch Linux and Fedora
- Why: Before other distributions, these offer the most recent versions of compilers and libraries (Python, Ruby, C++). “Power users” who wish to create their own operating system from scratch should utilize Arch.
For Privacy & Anonymity
- Distros: Qubes OS, Tails
- Why? Because Tails operates solely on a USB stick and sends all traffic via the Tor network, it doesn’t leave any evidence on the computer that uses it.
Also Read About What Is Linux? A Brief History And Evolution Of Linux
Benefits vs Drawbacks
| Benefits | Drawbacks |
| Cost: Most distros are free for personal and commercial use. | Learning Curve: Requires getting comfortable with the Command Line Interface (CLI). |
| Stability: Can run for years without needing a reboot; rarely “freezes.” | Software Gaps: Some professional software (Adobe Suite, MS Office) is not natively available. |
| Privacy: Does not track user data or “phone home” like proprietary OSs. | Hardware Drivers: Newer or very niche hardware might lack driver support. |
| Revival: Lightweight distros can make a 10-year-old laptop feel fast again. | Gaming: While improving (via Steam/Proton), some games with anti-cheat software don’t work. |
Choosing the right Linux distribution
Selecting the best Linux distribution in 2026 is more about matching a Linux “flavor” to your unique hardware, technical proficiency, and objectives than it is about figuring out which one performs best.
The fastest way to narrow your choices is to define your primary mission.
| If you are a… | Recommended Distro | Why? |
| Windows Switcher | Linux Mint | Features a familiar “Start Menu” layout (Cinnamon) and rock-solid stability. |
| Software Developer | Fedora Workstation | Offers the latest compilers and tools; it’s the primary choice for many upstream developers. |
| Gamer | Bazzite or Pop!_OS | Bazzite offers a SteamOS-like experience for handhelds; Pop!_OS has excellent NVIDIA driver support. |
| AI / ML Engineer | Pop!_OS | Comes pre-configured for CUDA, TensorRT, and modern GPU-heavy workflows. |
| Cybersecurity Student | Kali Linux | Pre-loaded with over 600 tools for penetration testing and digital forensics. |
| Absolute Purist | Arch Linux | You build the system from scratch, piece by piece. Great for learning. |
Also Read About What Is A Linux Shell? And Different Types Of Shell In Linux
Matching Your Hardware
- Some “heavy” distributions will be instantly disqualified by your hardware criteria.
- Contemporary PCs (8GB+RAM): You can run “heavy” and elegant desktops like KDE Plasma or GNOME (available in Ubuntu/Fedora).
- For older laptops with 4GB RAM, consider “mid-weight” solutions such as Xubuntu or Linux Mint (XFCE Edition).
- For older hardware (less than 2GB of RAM), use Lubuntu or Puppy Linux. By using only RAM, these may revitalize a laptop that is fifteen years old.
Understanding Update Cycles
- The most important technical decision you will make is this one. It establishes the frequency at which your system “changes.”
- Every two years, you receive a significant update under Fixed/LTS (Long Term Support). Versions of the software remain constant, so nothing breaks without warning.
- Examples are Debian Stable and Ubuntu 24.04 LTS.
- Rolling Release: There aren’t any “major versions.” Every day, the most recent software is installed on your system.
- Manjaro, Arch Linux, and openSUSE Tumbleweed are a few examples.
The “Try Before You Buy” Strategy
- You don’t have to make a rash commitment in 2026. To test a distribution, use these two techniques:
- DistroSea: A website that allows you to test-drive hundreds of Linux distributions without downloading anything.
- Live USB: You can flash the installer to a USB device with the majority of distributions. Without touching your hard disk, you can utilize the entire operating system in “Live Mode” when booting from the USB.
Also Read About How Linux Works And Why Linux Is Important For Developers
