Decentralized communication examples
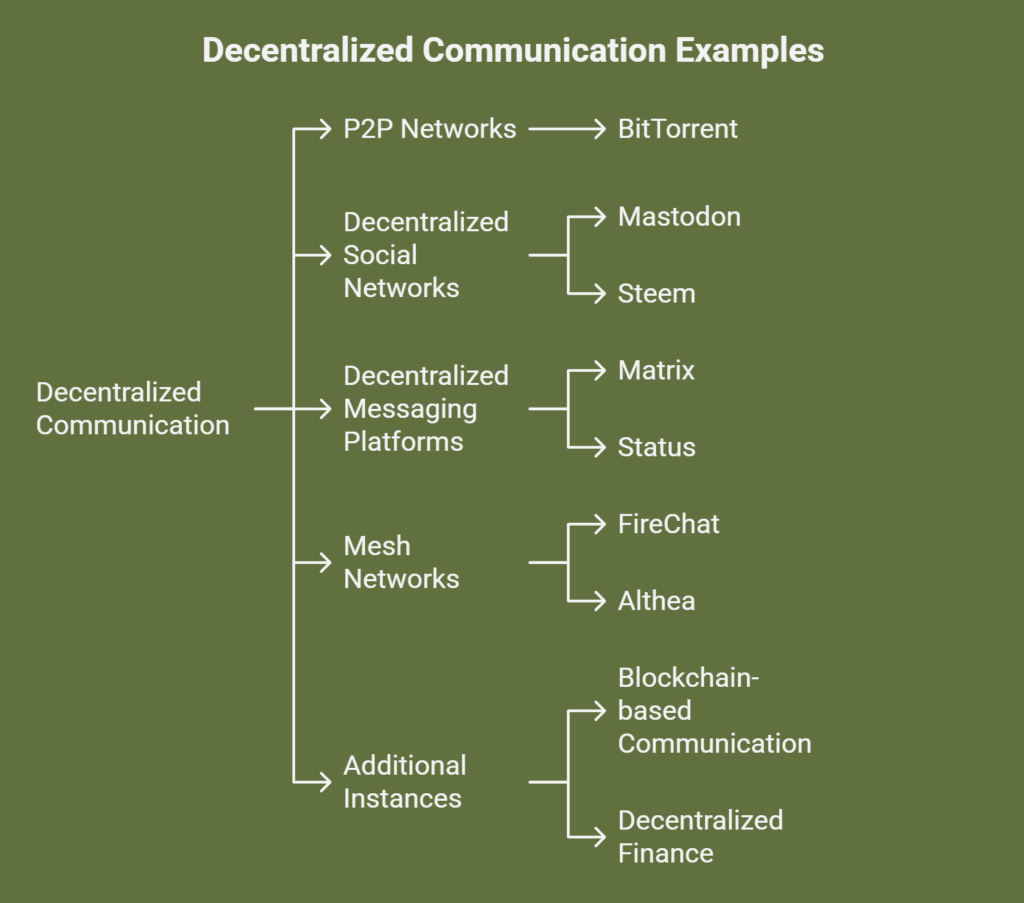
Decentralized communication examples include:
P2P (peer-to-peer) networks
BitTorrent: A well-known file-sharing protocol in which users download individual files from one another instead of a central server.
Decentralized social networks
- Mastodon: An open-source microblogging platform that allows users to operate their own servers, or instances, and communicate with other users on other instances, much like Twitter.
- Steem: A social blockchain in which users can get compensated for their participation and production of content.
Decentralized messaging platforms
- Matrix: An open standard that provides federation, bridging, and end-to-end encryption for decentralized, real-time communication.
- Status: Ethereum and the Whisper protocol are the foundations of a secure messaging app, browser, and wallet that facilitates private and secure communication.
Mesh networks
- FireChat: An app that uses nearby devices to relay messages so users can chat even if they don’t have internet access.
- Althea: A mesh networking-based decentralized internet service provider.
Additional instances
- Blockchain-based communication: Push Protocol, which makes it possible for AI-powered chatbots to provide decentralized communication, is one example of how blockchain technology can be utilized to establish safe and transparent communication channels.
- Decentralized Finance(DeFi): The DeFi space mostly depends on decentralized systems for financial transactions and interactions, even though it is not strictly a communication space.
Applications
Secure Messaging App
- Session: Offers robust privacy and anonymity by routing messages via an Oxen Network, a decentralised network of nodes.
- Status: An Ethereum-based mobile application that doubles as a Web3 browser and secure chat app.
- Matrix.org is an open-source, decentralized communication system that facilitates safe and compatible messaging across a federated network of servers. It can be integrated with blockchain and decentralized identities.
- XMTP (Extensible Message Transport Protocol) is a decentralized, open, and safe communications protocol that is becoming more popular in the Web3 domain between blockchain addresses and wallets.
- Bitchat, developed by Jack Dorsey, is a completely off-grid, decentralized, and encrypted communication system that relays messages via Bluetooth mesh networks rather than the internet or blockchain.
- Bit message: Although not blockchain-based, this system is completely decentralized and cryptographically safe.
- At the expense of latency and bandwidth, Whisper (Ethereum) is intended for “dark communication” in order to prevent metadata leaks.
Decentralized Social Media
Social media platforms that are decentralized provide individuals greater control over their information and relationships.
IoT Communication
Secure and dependable communication between Internet of Things devices is made possible via IoT communication. For example, TeleHash is used by IBM and Samsung’s ADEPT platform to provide P2P device messaging.
Supply Chain Management
By documenting each stage and making data accessible to all parties involved, supply chain management ensures security and transparency in communication and data exchange.
Payments and Digital Currencies
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer digital currency that enables direct value transfers without the need for banks.
Web3 (Decentralised Web)
Initiatives such as IPFS (Interplanetary File System) seek to establish a decentralized World Wide Web for content delivery and storage. Another decentralized storage option is Ethereum Swarm.
Decentralised Identity (DID)
Lessens dependency on centralized suppliers by enabling users to manage and distribute their identity credentials selectively.
Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
Blockchain-based financial systems, such Decentralised Exchanges (DEXs), that function without the need for middlemen.
Decentralized Domain Name System (DNS)
Namecoin and other projects use a decentralized DNS that is censorship-resistant.
Battlefield Systems
In military applications, blockchain technology can provide dependable sharing of mission-critical data and secure communication.
Decentralized Microblogging
These sites can provide privacy and help with issues that centralized social media might cause.
Also Read About Ether Meaning in Blockchain, History, Functions, & Benefits
Benefits
Decentralized communication has a number of important advantages.
Enhanced Protection
It reduces the dangers of possible data breaches and single points of failure. These systems are more resilient to attackers because they distribute data and use strong cryptographic protection.
Improved Privacy
Because user data is dispersed throughout the network, it is more difficult for outside parties to access and manage it. Users can choose to remain anonymous, and they have more control over their privacy.
Decreased Censorship
Because no one organisation controls the flow of information, decentralized systems are more impervious to censorship.
Greater Openness
All participants can confirm the integrity of the communication process due to blockchain’s transparency. Every transaction is visible and auditable since each participant has an identical copy of the distributed ledger.
Enhanced Confidence
Decentralized communication can increase participant trust by reducing the need for a central authority. Because data integrity is guaranteed by the protocol and consensus procedures, it fosters a “trustless environment” in which participants do not necessarily need to trust one another.
High Resilience and Availability
There isn’t a single point of failure because it’s spread. The network can still function even if some nodes or perhaps a whole area of nodes go down.
Control by the User
Users are the owners of their data and identity.
Removal of Middlemen
By doing away with the requirement for reliable third-party service providers, customers may transact directly and keep total control over their data, which could result in lower costs and faster speeds. “Disintermediation” is the word for this procedure.
Also Read About Blockchain Moonbeam: Bridging Ethereum to Polkadot Parachain
Challenges and Limitations
Decentralized communication has a number of drawbacks despite its benefits:
Scalability
There are substantial scalability issues when managing millions or billions of messages in a genuinely decentralized, blockchain-supported fashion. Large volumes of data or transactions cannot be stored or processed by blockchains due to their inherent inefficiencies. Although certain Layer 2 solutions may restore a certain amount of centralization, solutions such as sharding and Layer 2 solutions (off-chain processing) are being explored.
Experience of the User
Compared to their centralized equivalents, current decentralized communication apps might be more difficult to use. Users frequently need to handle cryptographic keys, comprehend blockchain addresses, and occasionally put up with slower message delivery. They may be more difficult to operate and less polished.
Messaging Offline
Since there is no central server to store messages, it is difficult to guarantee that they are sent while the recipient is not online. Relying on other decentralized storage systems or implementing “store-and-forward” methods on a subset of nodes are common alternatives.
Also Read About What Is A Relay Chain In Blockchain And How It Works
Abuse and Spam
It is more difficult to stop abuse, malicious content, and spam when there is no central authority. Token-gated access or decentralized reputation systems may be the answer.
Interoperability
Ensuring seamless communication between various decentralized communication protocols and applications is a persistent challenge.
Intricacy
Compared to conventional centralized systems, decentralized communication solutions can be more difficult to develop, install, and maintain.
Costs of Computing and Storage
Due to significant data redundancy, requiring each participant to have a complete copy of the ledger may result in expensive data storage expenses. It’s possible that some participants lack the requisite processing and storage power. Large files are typically not well-suited for direct blockchain storage; instead, specialized decentralized storage solutions are frequently employed.
The Byzantine Fault System
Reaching consensus and preserving system integrity can be severely hampered by malicious or defective nodes.
Latency
The speed at which information spreads can be impacted by latency introduced by communication between geographically separated nodes.
Trade-offs
Decentralization is not a “all-or-nothing” notion, and determining the right level of decentralization frequently requires striking a balance with aspects like performance and usability.
Aslo Read About Proof Of Membership In Blockchain: Mechanisms, Verification
Decentralized Communication Protocols
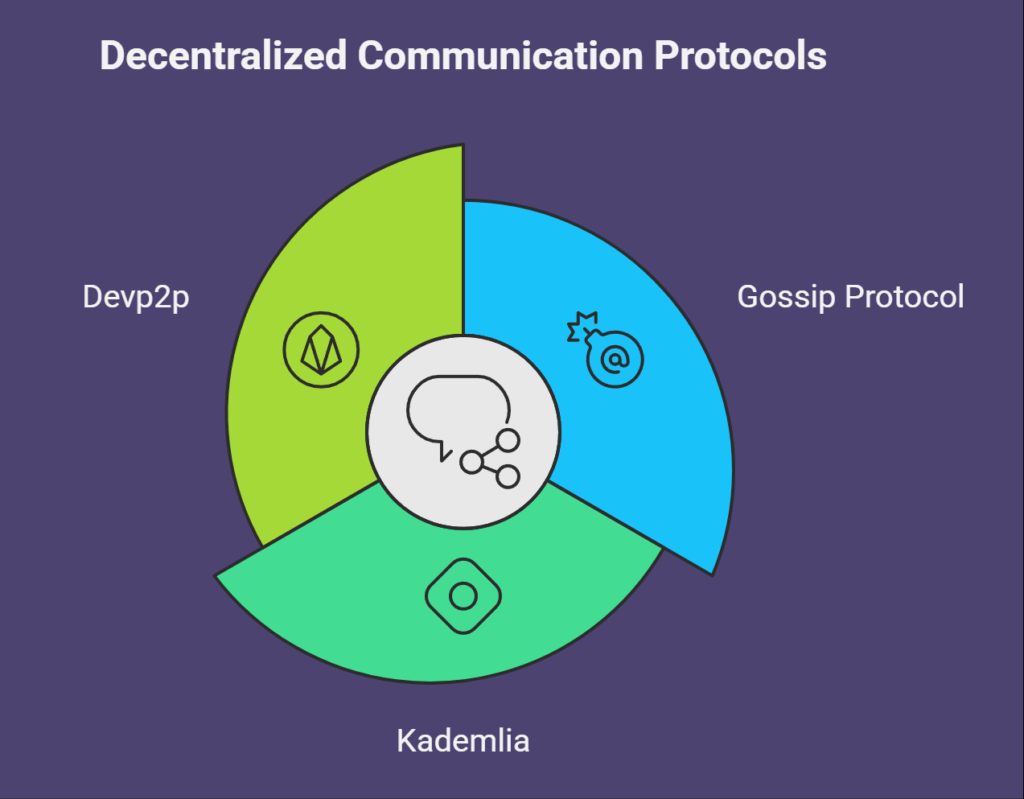
Blockchain networks make use of particular decentralized communication protocols to guarantee that messages are received in an interpretable manner and reach their intended receiver. For routing and formatting, they use communication logic and messaging standards.
Here are a few typical examples:
- One of the most widely utilized protocols in blockchain networks is the gossip protocol. Every time a node receives a new block or transaction, it broadcasts information to a select group of other nodes. The procedure is then repeated by these recipient nodes, causing a “gossip” effect in which information circulates throughout the network until it reaches every node. Because only a minority of nodes need to acquire information prior to propagation, it is incredibly efficient.
- Decentralized protocols such as IPFS use Kademlia, a distributed hash table (DHT). It offers a structure for nodes to group together and interact as a network. Using User Datagram Protocol (UDP) to transmit messages, communication takes place through “node lookups” to determine a node’s position. Because Kademlia only contacts a logarithmic number of nodes during a search, it is incredibly efficient.
- Devp2p: The specific networking protocol for Ethereum. Through a low-level communication layer, it enables nodes to connect and exchange information over a decentralized network. It provides tools for controlling connections between nodes (such as ping and pong messages) and a peer discovery technique that makes use of a distributed hash table. Devp2p is the foundation for more intricate protocols, such as Whisper.
In order to send and receive messages between various blockchain networks, there are also inter-blockchain communication protocols. This creates difficulties in making sure that various software and logic can understand messages.
In the end, P2P messaging is made possible by decentralized communication protocols acting as algorithms. Both the adoption of Web3 technology and the trustless functioning of blockchain networks depend on them. Despite their difficulties, they have the power to revolutionize communication by facilitating exchanges free from middlemen’s interference.
