In this post, we covered the following topics in detail: Next Generation Firewalls (NGFWs), their evolution and necessity, how they work, their features, advantages and disadvantages of Next Generation Firewalls, types, and how they differ from other security technologies.
Next generation firewall
An advanced network security tool that greatly surpasses the capabilities of conventional firewalls is called a Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW). It provides more thorough defense against contemporary cyberthreats by combining several security features into a single platform. Third-generation firewall technology includes NGFWs.
Evolution and Need for NGFWs
The necessity to defend against increasingly sophisticated threats that conventional firewalls were unable to manage led to the development of NGFWs. IP addresses, ports, and protocols are the main criteria used by traditional firewalls to filter traffic. This strategy was no longer adequate when applications started acting differently, frequently using non-standard ports or tunnelling through SSL, which made it challenging for legacy firewalls to detect and manage them.
By taking advantage of flaws in apps rather than networking components, contemporary threats including web-based malware, targeted attacks, and application-layer vulnerabilities frequently get past conventional firewalls. Additionally, traditional firewalls had a large blind spot because they couldn’t inspect encrypted communication. Because of this, there was an urgent need for increased visibility and more intelligent enforcement, which NGFWs were intended to supply.
Also Read About What Are Firewall Logs? Benefits And Importance Of Firewalls
How NGFWs Work
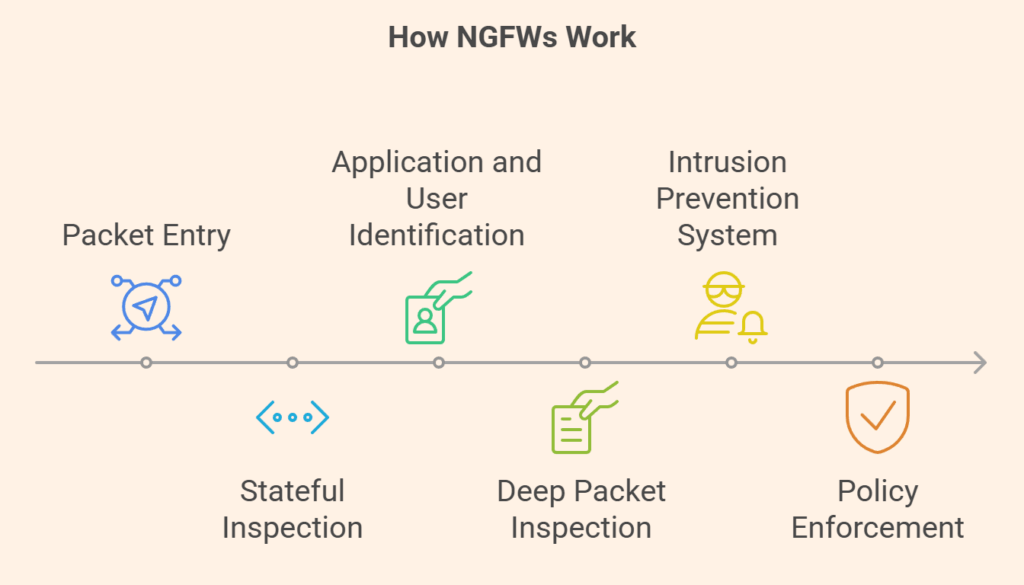
Creating a comprehensive picture of network traffic is how an NGFW operates. A data packet goes through a number of checks in a single pass after entering the firewall. The goal of this highly optimized method is to reduce latency.
- Stateful Inspection: To make sure the packet is a part of a legitimate, established connection, the firewall first conducts a stateful inspection.
- Identification of the Application and User: Next, it determines which application and user are connected to the traffic.
- Deep Packet Inspection (DPI): This method checks the payload for viruses or other harmful material. In order to identify known dangers, the traffic is also compared to a signature database.
- The integrated intrusion prevention system, or IPS/IDS, examines network traffic for any unusual patterns or actions that would point to a network intrusion.
- Policy Enforcement: Lastly, the firewall applies the predetermined security policy by permitting or prohibiting the traffic in light of all of this contextual data.
An NGFW can provide a far more robust and proactive defense than conventional firewalls by integrating these several layers of analysis.
Features of next generation firewall
NGFWs operate at higher layers of the OSI model, including the application layer (Layer 7), and offer a layered security strategy that offers deep, contextual visibility into network traffic. Important characteristics that set NGFWs apart are:
Application Awareness and Control (AVC)
The ability of NGFWs to recognize and manage traffic according to the particular application being used, irrespective of the port or protocol it uses, is known as Application Awareness and Control (AVC). This makes it possible to implement detailed regulations, like allowing a web conferencing application that has been approved by the company but prohibiting an unauthorized one that uses the same port.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI)
An NGFW’s intelligence relies heavily on this. DPI enables the firewall to examine a packet’s actual data payload in addition to its header data (Layers 3 and 4). This feature aids in identifying risks concealed in what appear to be authentic traffic, such as malicious code and hidden spyware.
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS)
NGFWs incorporate an IPS, which keeps a close eye on network traffic to look for known threats and malicious activities. The IPS can instantly stop communications if it detects an attack signature (such as malware or buffer overflow). Zero-day assaults can be stopped inline by modern NGFWs.
Identity and User-Based Policies
NGFWs may establish and implement security policies based on specific users or user groups rather than just IP addresses. This makes it possible to precisely control access, guaranteeing that only approved users can access particular resources.
Integrated Threat Intelligence
Global networks of security providers can supply real-time threat intelligence feeds to NGFWs. This enables the firewall to proactively protect by ensuring it is continuously updated with the most recent information on malicious IP addresses, zero-day attacks, and emerging threats.
SSL/TLS Decryption and Inspection
Since the majority of internet communication is encrypted, NGFWs are able to decrypt, examine, and re-encrypt SSL/TLS traffic in order to uncover risks that would otherwise go undetected.
Advanced Malware Detection
By employing strategies like sandboxing and machine learning, they are able to identify and stop advanced malware, including zero-day threats.
URL filtering
NGFWs can use this function to look at URLs in web requests, classify them, and then filter or rate-limit traffic according to pre-established guidelines.
Single-Pass Architecture
This type of NGFW is more efficient than reprocessing traffic repeatedly since it processes each packet only once and applies all necessary security features in a single flow.
Other Modern Features
Additional contemporary features include support for Layer 2 switching and Layer 3 routing, DNS security, Next-Generation Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), IoT security, and mitigation of credential theft and abuse. Additionally, they facilitate third-party integration using REST APIs and Quality of Service (QoS) rules.
Also Read About What Is A Layer 3 Switch? And Advantages Of Layer 3 Switch
Advantages of next generation firewall
NGFWs offer organizations a number of advantages:
- Enhanced Security: By examining traffic at several levels and identifying complex threats, they provide a more thorough security posture.
- Better Visibility and Control: They enable policies based on business context by offering deeper visibility into apps, people, and material.
- Simplified Infrastructure and Management: They eliminate the need for separate tools, simplify administration, and reduce complexity by combining several security features (firewall, IPS, antivirus, URL filtering, and CASB) into a single platform.
- Quicker Threat Detection and Reaction: They prioritize warnings for prompt response, identifying threats in seconds and a breach within hours or minutes.
- Security Without Performance Sacrifice: Even with full security services activated and heavy traffic volumes, efficient design, such as single-pass processing, maintains low latency.
- Cost-Effective: By eliminating the need for several security devices and streamlining management, NGFWs can prove to be more economical in the long term, even though the initial investment may be costlier.
- Support for Zero Trust Security Models: By confirming people, devices, and apps before allowing access, they aid in the enforcement of Zero Trust principles.
Disadvantages of next generation firewalls
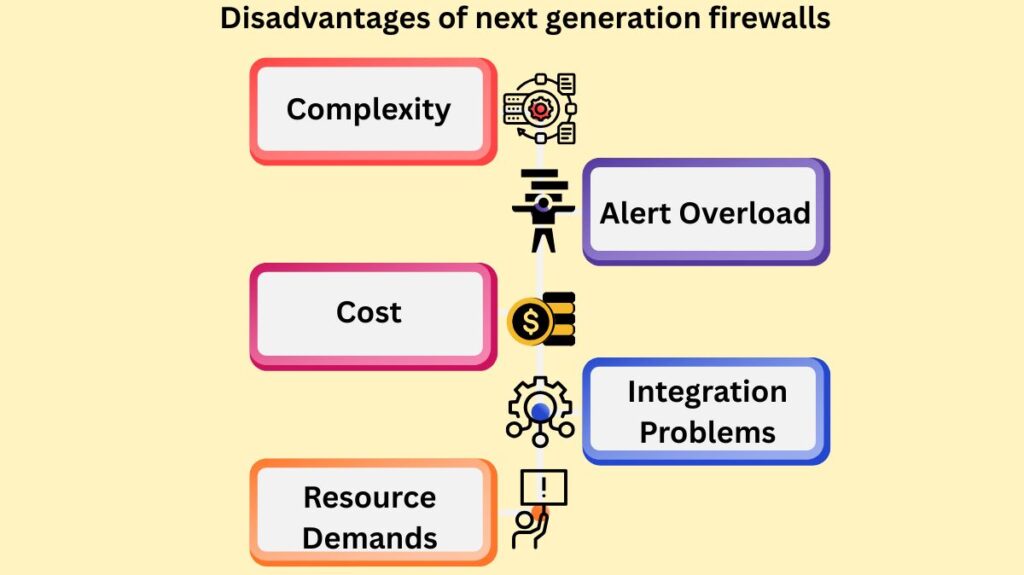
Notwithstanding their benefits, NGFWs have certain disadvantages:
- Complexity: They can be challenging to install and manage, necessitating the use of extra knowledge and abilities from security professionals.
- Cost: Compared to traditional firewalls, NGFWs are typically more costly to purchase and maintain.
- Resource Demands: If overwhelmed, their increased processing power requirements could impact network speed.
- Alert Overload: They may cause a lot of false positives and other alerts, which puts more strain on security administrators.
- Integration Problems: Despite being built for integration, threat intelligence feeds require frequent updates, and interoperability problems with other security solutions may still occur.
Types of NGFWs
To accommodate diverse contexts, NGFWs can be implemented in a variety of ways:
Hardware-based NGFW
All users connected to the internal network are immediately covered by these physical devices, which examine all incoming data.
Software-based NGFW
These require installation on every device but allow flexibility by operating as programs on servers or endpoints.
Cloud-based NGFW (Firewall-as-a-Service – FWaaS)
Similar to software firewalls, cloud-based NGFW (Firewall-as-a-Service, or FWaaS) is installed in off-premise data centers and is either maintained by the business or a service provider. A key element of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) networking models is FWaaS.
Cisco’s NGFW Products
Cisco’s current firewall products are mostly marketed under the Firepower and Cisco Adaptive Security Appliance (ASA) product lines. Sourcefire was purchased by Cisco in 2013, and many of its cutting-edge security software capabilities were incorporated into their NGFW and NGIPS products, which are now primarily referred to as Cisco Firepower firewalls. True NGFW devices are those that use Firepower Threat Defense (FTD). There are also virtual versions, including Firepower Threat Defense Virtual and ASAv.
NGFW vs Other Security Technologies
NGFW vs. Traditional Firewall
The main differences are that NGFWs integrate intrusion prevention and threat intelligence, inspect application-level traffic, and perform deep packet inspection beyond basic port and protocol analysis. Stateful inspection and simple packet filtering are the only features available on traditional firewalls.
NGFW vs. Unified Threat Management (UTM)
Although both integrate several security tasks, NGFWs provide more in-depth integration, cross-function context sharing, and fine-grained visibility into people, apps, and content. For smaller settings, UTMs usually bundle essential functions, emphasizing ease of use above personalization. NGFWs are a part of a broader system that is integrated with UTMs.
NGFW vs. Web Application Firewall (WAF)
WAFs are designed to defend against vulnerabilities such as injection attacks in certain web applications at the application layer (Layer 7), especially HTTP-based traffic. Although they also function at Layer 7, NGFWs offer more comprehensive network-layer protection and visibility throughout the OSI stack, including user mapping, general access control, and encrypted traffic inspection for the whole network.
NGFWs are essentially a major advancement in firewall technology, offering a more reliable, clever, and effective method of network protection in the complicated threat environment of today.
Also Read About Source Network Address Translation SNAT, how does snat work
