Let us discuss about CISCO IOS, CISCO IOS Architecture, it’s functions, features and more.
CISCO IOS
The proprietary Cisco IOS (Internetworking Operating System) series of network operating systems was created by Cisco Systems. It is the operating system used by the majority of Catalyst switches and Cisco routers. Networked applications were first made possible by the programming that William Yeager created in 1986.
In essence, Cisco IOS serves as the “brain and control system” of Cisco networking equipment, enabling management, routing, security, configuration, and switching.
Core Functions and Features
Internetworking, routing, switching, and telephony are all integrated into Cisco IOS, a multipurpose operating system. Its primary duties and characteristics consist of:
Carrying Network Protocols and Functions: Using a variety of networking protocols and data link technologies, it allows devices to communicate by supporting a large number of network protocols and the functions that go along with them.
Routing and Switching: It gives switches the ability to effectively forward data frames based on MAC addresses and gives routers the logic they need to decide which path is appropriate for data packets. In IOS, packet forwarding (switching) and routing are two different processes.
Connecting High-Speed Traffic: It makes it easier for fast traffic to go between devices.
Adding Security: ACLs, firewalls, VPN support, and authentication, authorization, and encryption (SSH, VPN) are some of the elements that increase security by limiting access and preventing unauthorized network use. Cisco advises using the security model known as authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA).
Providing Scalability: It supports a broad range of devices, from tiny branch routers to enterprise core routers, and provides scalability for simple network expansion and redundancy.
Supplying Network Reliability: It guarantees dependable access to network resources, hence providing network reliability.
Device Management: It offers monitoring, debugging, logging, and configuration backup utilities.
You can also read Advantages Of VLSM Variable Length Subnet Masking, Purpose
CISCO IOS Architecture
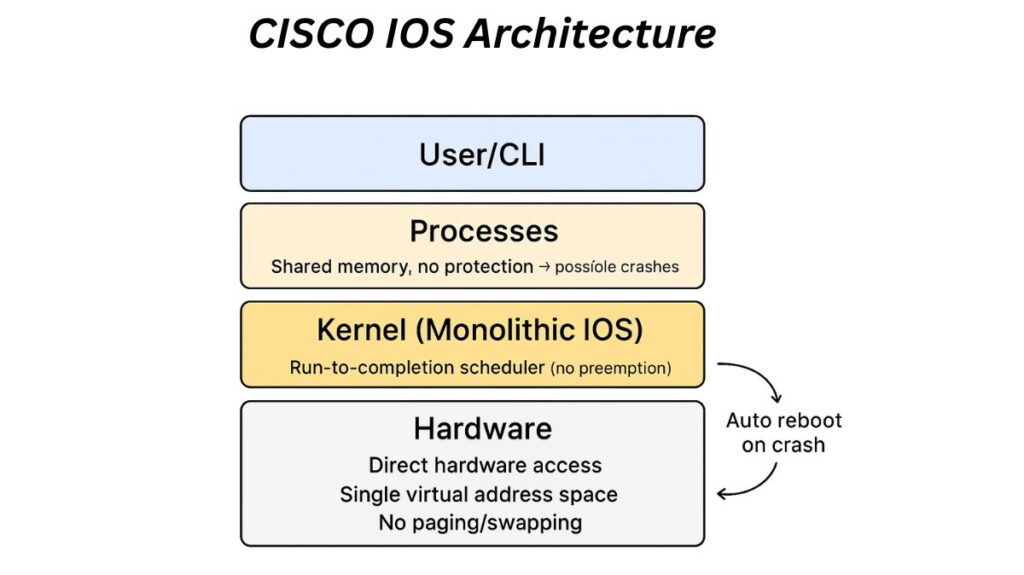
Given the restricted hardware capabilities of routers and switches in the 1980s, Cisco IOS was designed with a monolithic architecture.
- Direct hardware access is available to all processes to save CPU processing time.
- Processes can potentially write over each other’s data because there is no memory protection between them. This increases complexity and raises the possibility of data corruption or system crashes. The saved configuration is reloaded upon an automated reboot in the event of an iOS crash.
- Because it has a run-to-completion scheduler, a process must make a kernel call before another process can execute; the kernel does not preempt an active process.
- The device’s physical memory is the only addressable memory since all of the physical memory is mapped into a single virtual address space without memory paging or swapping.
Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Accessing the Cisco IOS Command-Line Interface (CLI)
Cisco equipment can be remotely or directly accessed to configure them using the CLI. We refer to access to the IOS command line as an EXEC session.
Direct Connection Methods:
- Console Terminal: For initial configuration, this is the most popular approach. A computer running terminal communications software (such as Tera Term or HyperTerminal) and an RJ-45-to-RJ-45 rollover cable are needed to connect directly to the device’s console port. Additionally, some devices could have a mini-USB cable that connects to a mini-USB console port. Although smaller switches, such as the Cisco 3560 or 2960, may have it on the front, the console port is usually an RJ45, 8-pin modular connector that is located at the back of the device.
Remote Access Methods:
The CLI can be accessed remotely using Telnet. The device must be setup with an IP address and a Telnet password in order to establish a Telnet connection.
- Telnet: An encryption-based, more secure substitute for Telnet.
- SSH (Secure Shell): Web browser management is available for Cisco devices, including Wireless LAN Controllers (WLCs). TLS is used by HTTPS for encryption.
- HTTP/HTTPS (WebUI): CLI access is categorized by Cisco IOS into various modes, each of which has its own set of commands. To display the current mode, the command prompt modifies.
You can also read What is SLAAC IPv6(Stateless IPv6 Address Autoconfiguration)
CLI EXEC Sessions and Modes
This is the first mode that appears after logging in, denoted by a prompt that ends in > (e.g., Router> or Switch>). It gives you restricted access to standard monitoring and troubleshooting commands, such as ping and display. Changes to the configuration cannot be made in this mode.
User EXEC Mode: Accessed by entering “enable,” which is indicated by a prompt that ends in “#” (e.g., Router# or Switch#), when in User EXEC mode. All device commands, including setup and management, are fully accessible. This mode is the sole way to perform commands like reload, which reboots the device.
Privileged EXEC Mode (Enable Mode): Configured terminal command to enter from Privileged EXEC mode. It is possible to modify global parameters in this mode. Next, Cisco IOS has a number of subconfiguration modes, including line configuration mode (e.g., Router(config-line)#) and interface configuration mode (e.g., Router(config-if)#).An administrator is guided through fundamental configurations using the Setup Mode, a first configuration dialogue. If a router boots without an NVRAM startup-config file, it begins automatically. Typing setup will also allow you to access it from privileged mode. In general, it is not advised for seasoned users.
Sub-Configuration Modes (e.g., Router(config-if)#, Router(config-line)#): Accessed from Global Configuration mode to configure specific components like interfaces or lines.
Navigation and Editing, use commands like exit (to move back one level) or end (or Ctrl+Z to go back to Privileged EXEC mode). The 10 most recent commands are automatically stored in the Command History, and context-sensitive help is available through the Help Facility (?). The majority of iOS builds also come with a Tcl interpreter for scripting.ices.
Setup Mode:
- An administrator is prompted with questions about fundamental configurations in this initial configuration dialogue.
- It is initiated automatically in the event that a router boots up without an NVRAM
startup-configfile. - Type
setupto access it in privileged mode. Experienced networking professionals who prefer CLI configuration mode are often advised against using it.
You can also read IPv6 Migration Explained: Transition From IPv4 To IPv6
CLI Navigation and Editing
Several features are available in Cisco IOS to make using CLI easier:
Help Facility: The question mark (?) provides context-sensitive help. Typing?provides a list of every command that is available in the current mode.has a command’s parameters listed, and com?gives a list of commands that begin with “com.”
Command History: Cisco IOS lets users go back and forth, select, and modify commands by default by storing the ten most recently entered commands in a history buffer.
Editing Shortcuts (Hot Keys): These are accessible for using the CLI to navigate and edit commands.
Configuration and Memory Management
Different types of memory are used by Cisco IOS devices to hold the operating system and configuration commands.
Running Configuration (running-config): Keeps the active configuration commands in Random Access Memory (RAM). These modifications are dynamic and, unless they are saved, are lost upon reboot or power outage.
Startup Configuration (startup-config): Stores the initial configuration used when the device reloads Cisco IOS. It resides in NVRAM (Nonvolatile RAM). To save changes, copy running-config startup-config (or copy run start) is used. To erase startup-config, commands like erase startup-config or write erase (for older IOS versions) are used.
Flash Memory: By default, it keeps the Cisco IOS image (the operating system file). Upgrading iOS pictures involves copying new files to flash memory. Show flash and dir flash are commands that are used to view contents.
ROM (Read-Only Memory): Includes the bootstrap application, a mini-IOS (RXBOOT or bootloader), and POST (power-on self-test). In addition to system diagnostics and recovery, it is utilized for router startup and maintenance. The mini-IOS (RXBOOT) is a tiny operating system in ROM that has the ability to load a complete Cisco IOS into flash memory and launch an interface.
Boot Sequence
A Cisco equipment goes through a number of actions when it first boots up:
Power-On Self-Test (POST): To check hardware components, the device runs diagnostics from ROM and conducts a POST.
Bootstrap Loader: By default, flash memory is used by the ROM’s bootstrap to find and load the Cisco IOS software. Which IOS image is loaded at router bootup is managed by the configuration register. By setting the configuration register to 0x2102, the router is instructed to load the configuration from NVRAM and the IOS from flash.
Configuration File: The IOS software then searches the NVRAM for the startup-config configuration file, which is legitimate. The router may look for a configuration file on a TFTP server or switch to setup mode if startup-config is not found.
You can also read CISCO Switch Configuration: A Safe and Effective Setup Guide
Versioning and Trains
Versions of Cisco IOS often take the format a.b(c.d)e.
- The numerals for main and minor versions are
a.b. Cstands for the release number inside a “train.” A “train” is a means of distributing Cisco software to particular platforms and functionalities.d(interim build number) ande(software release train identifier, e.g.,Tfor Technology,Efor Enterprise,Sfor Service Provider) provide further detail.- Mainline (the most stable), T (new features, less stable), S (Service Provider), E (Enterprise), B (broadband), and X (Special Release) were among the “trains” into which releases has historically been divided.
- A single M/T train has existed since Cisco IOS release 15. Extended maintenance releases (
Mreleases) include bug fixes for 44 months, whereas ordinary maintenance releases (T releases) include bug fixes for 18 months.
Basic Navigation Commands
?→ Help menu (lists available commands).enable→ Enter Privileged EXEC mode.configure terminal→ Enter Global Configuration mode.show running-config→ View current configuration.copy running-config startup-config→ Save configuration.exit→ Move back one mode.logout→ Exit session.
Security and Vulnerabilities
- ‘Type 7’ ciphertext, which is easily decoded, is the default weak encryption for passwords entered into the CLI. “Shoulder-surfing” is avoided, although it is not secure. “Type 5” passwords, or those that have the
secret enabled, are more secure since they employ salted MD5 hashes. - After an IOS vulnerability was revealed at the 2005 Black Hat Briefings conference, Cisco was sued and a patch was released.
Related and Successor Technologies
Not every Cisco networking product is iOS compatible. Other network operating systems have been created by Cisco:
Cisco IOS XE: An updated version of iOS built on the Linux architecture, intended to provide better uptime and maintenance without the need for reboots. It still uses the well-known CLI from the original iOS.
Cisco IOS XR: For high-availability devices like the Cisco CRS-1, a brand-new operating system with preemptive scheduling, memory protection, and modularity was created. It started out using QNX before moving to Linux.
Cisco NX-OS: Cisco Nexus Ethernet and MDS Fibre Channel switches run an operating system based on Linux in data centre settings.
Cisco IOS File System (IFS)
One of the features of Cisco IOS devices is the Cisco IOS Integrated File System (IFS). On a Cisco device, users can create, browse, and work with folders and files using this system. It supports a number of file systems, such as system memory (running configuration), NVRAM, network file systems (TFTP, FTP, and RCP), and flash memory. Configuration files and iOS images can be moved between components or developers using the copy command.
You can also read Understanding Switching Logic: The Brain Of A Network Switch
