We will explain the Internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP), its key features, advantages, scaling solutions, and how to configure iBGP in this blog.
What is iBGP?
One essential part of the Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) that is utilized especially for routing information exchange within a single Autonomous System (AS) is the Internal Border Gateway Protocol (iBGP).
iBGP functions internally to guarantee that routers within the same administrative domain reliably distribute the external routes they learn, whereas BGP is commonly referred to as an Exterior Gateway Protocol (EGP) for connecting various ASes (eBGP).
Important Features iBGP
Same Autonomous System (AS)
A BGP session involving two BGP peers in the same autonomous system is known as an iBGP session. Every iBGP peer needs to be a member of the same AS. The same AS number is used to configure them; for example, neighbour [address] remote-as [same AS number].
Transport and Connectivity
- Transport Protocol: TCP port 179 is used to establish iBGP peerings.
- Direct Connection: Direct connections between iBGP neighbours are not required. Several routers that are not using BGP can be used to divide them.
- IGP Requirement: An Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP), such as OSPF or EIGRP, must be operating within the AS in order for the iBGP neighbours to be able to communicate with one another, even though iBGP peers do not need to be directly connected.
Loop Prevention: The Split-Horizon Rule
The split-horizon rule is a stringent loop prevention guideline that governs how iBGP functions.
- Routes learnt from one iBGP peer to another will not be re-advertised by an iBGP speaker.
- This rule is required because, in contrast to eBGP, iBGP does not modify the AS number internally, so it is unable to use the AS_PATH parameter to prevent loops within the AS.
The Full Mesh Requirement
Every iBGP router in the AS normally needs to be set up as a neighbour to every other iBGP router because of the split-horizon rule. This topology is referred to as entire mesh.
- A full mesh in a network with N routers necessitates N(N-1)/2 peering sessions, which rapidly grow more complicated and unmanageable as N rises.
Next-Hop Handling (A Critical Intricacy)
When promoting a route, iBGP by default does not change the BGP NEXT_HOP property. The IP of the external BGP (eBGP) peer that first published the route is frequently the next-hop information, which doesn’t change.
- Reachability Issue: The receiving iBGP router will not add the route to its routing table if it does not have a way to get to the (external) next-hop address that is specified in the BGP update.
- Resolution: Usually, this is resolved by making sure the IGP, which operates inside the AS, notifies the next-hop address of reachability. To ensure reachability for the receiving peer, the sending router can also be set up to use the next-hop-self command, which changes the next hop address to its own address.
Also Read About Brouter Definition, How it Works, Features, Benefits, & Uses
Administrative Distance (AD)
The Administrative Distance (AD) of 200 that is set by default for iBGP routes is comparatively high. This indicates that they are typically less reliable than routes discovered by standard Interior Gateway Protocols (IGPs) like OSPF (AD 110) or eBGP (AD 20).
Advantages
iBGP performs a number of crucial tasks inside an AS:
- By carrying routes that are learnt externally across a transit AS, it enables networks to advertise a prefix from one autonomous system to another.
- It guarantees that all of the routers in the AS have the same external routing information.
- Because every router has a full view of the BGP data, it facilitates traffic engineering and policy control by enabling them to apply filters, route maps, and other policies, as well as make well-informed routing decisions.
Scaling Solutions
The primary scalability issue is the full-mesh requirement. There are two main ways to get around it:
Route Reflectors (RR): A Route Reflector is an iBGP router that is set up to loosen the full-mesh requirement by re-advertising iBGP-learned routes to its customers. Routes will be forwarded by a router set up as an RR between:
- Customers and other customers.
- Customers and non-customers (typical iBGP peers).
- clients as well as non-clients.
BGP Confederations: This technique splits a big AS into logically related smaller sub-ASes (using private AS numbers). Each sub-AS’s routers either use Route Reflectors or create a complete iBGP mesh, and the sub-ASes communicate with one another via inter-confederation eBGP, a unique type of eBGP. As a result, fewer iBGP peerings are needed on any one router.
Also Read About Cisco Dynamic Multipoint VPN DMVPN Phase 1 2 3 In Network
How to configure iBGP
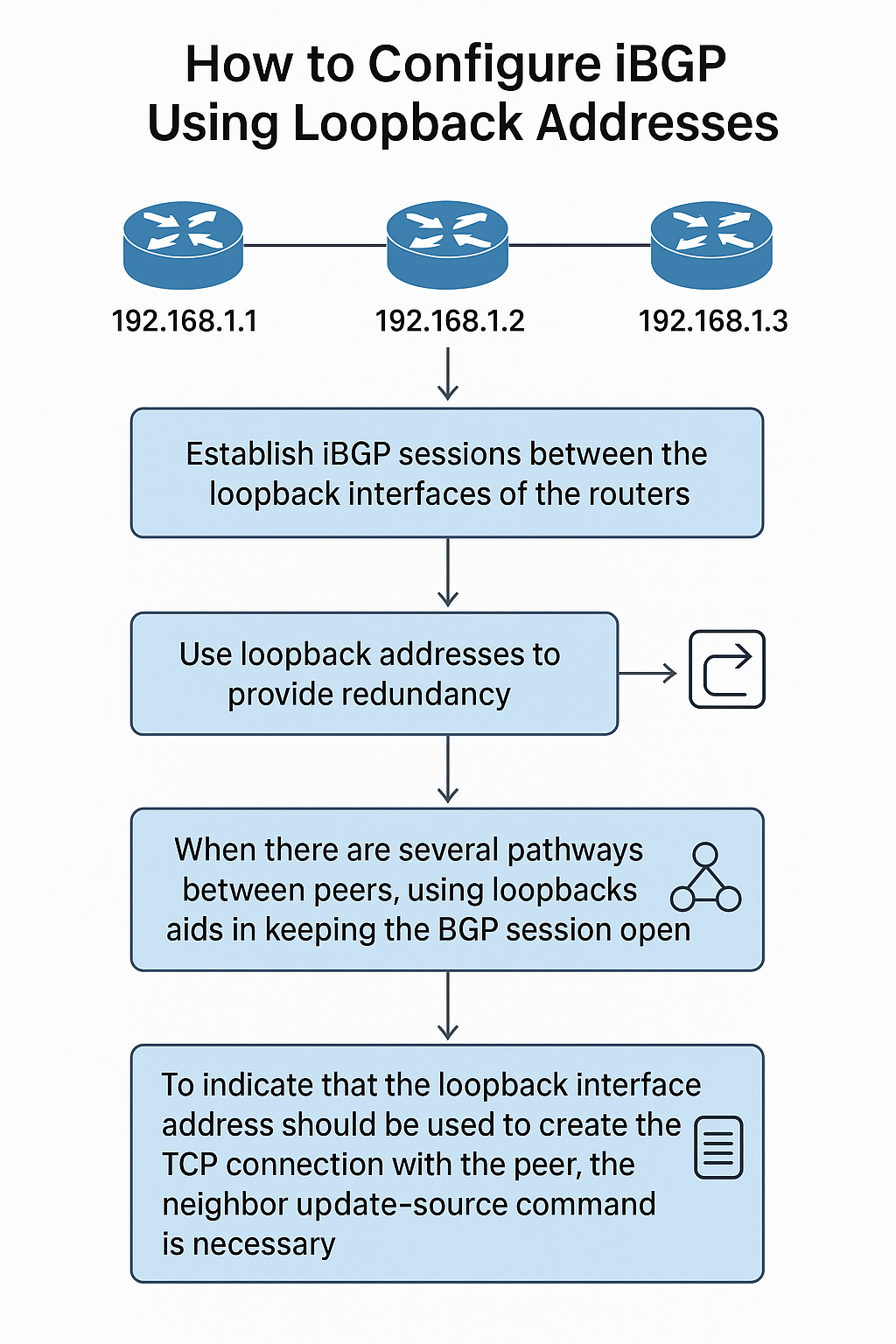
Using Loopback Addresses
Establishing iBGP sessions between the loopback interfaces of the routers is regarded as best practice.
- The BGP session could end if a physical interface failed.
- Unless the router malfunctions or the interface is specifically turned down, a loopback interface provides redundancy and will never go down.
- When there are several pathways between peers, using loopbacks aids in keeping the BGP session open.
- To indicate that the loopback interface address should be used to create the TCP connection with the peer, the neighbour update-source command is necessary.
Ensuring Reachability Across the AS
All intermediate routers in a transit AS (such as AS2 in the example topology given in the sources) must execute iBGP and learn the external routes in order for traffic to pass through that AS successfully. Because it lacks the necessary routing information, an intermediate router that does not run BGP will discard traffic intended for external networks. For this reason, all routers in transit or service provider networks usually run iBGP.
Also Read About Cisco Gateway load balancing protocol GLBP, How GLBP works
