In this article, we learn about what IEEE 802.1X is, Key Components of 802.1X, how 802.1X authentication works, and benefits of 802.1X.
What is IEEE 802.1X
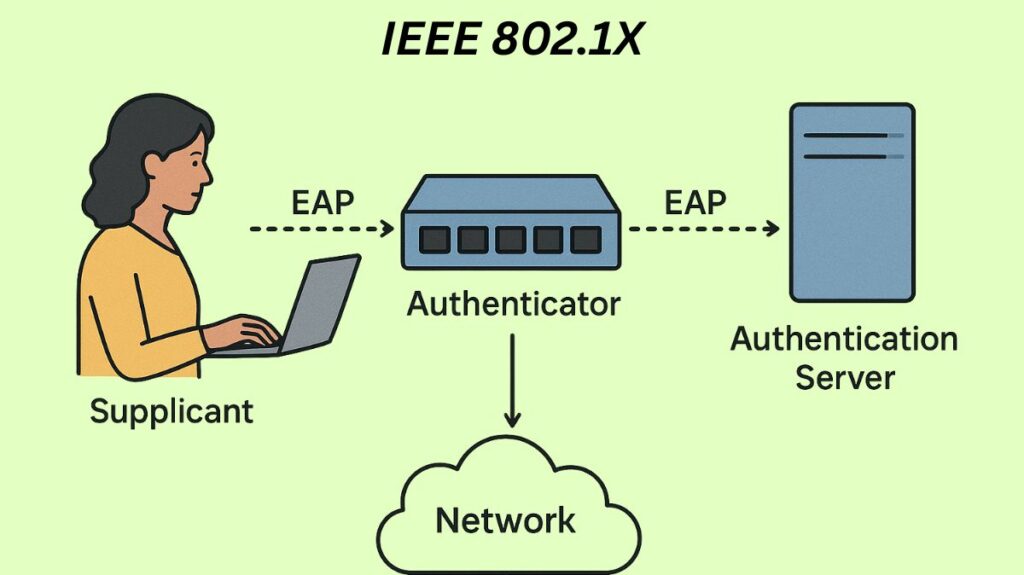
For both wired (LAN) and wireless (WLAN) networks, port-based access control and authentication (PNAC) is defined by the IEEE 802.1X standard, also referred to as IEEE 802.1X. By requiring user or device identification before allowing access to network media or services, 802.1X primarily aims to create identity-based networking. Access is restricted until a client authenticates properly when 802.1X is enabled.
In the OSI paradigm, 802.1X operates at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer). Through identification and policy enforcement, it allows administrators to govern access to enterprise resources consistently across wired and wireless networks.
You can also read What is Port Security and Benefits of Port Security
The Three Key Components of 802.1X
The 802.1X standard utilizes a three-party architecture to manage network access:
Supplicant (Client)
- This is the client device that requests to access the local area network or switch services, such as a workstation, laptop, or smartphone.
- Client software that complies with 802.1X must be used by the applicant.
- The program packages the user’s login information in an 802.1X-compliant manner.
Authenticator (Network Device)
- Based on the applicant’s authentication status, this device serves as the gatekeeper and regulates physical access to the network.
- Usually, a switch in a wired LAN or a wireless access point/Wireless LAN Controller (WLC) in a wireless LAN serves as the authenticator.
- By asking for identity information, confirming it with the authentication server, and then sending the answers back to the supplicant, it acts as a middleman or proxy.
Authentication Server (AS)
- The actual authentication of the applicant is carried out by this reliable equipment.
- To ascertain whether access is permitted, the AS verifies the client’s identity against a user database.
- Software that supports the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) and the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) protocols is often installed on the authentication server. It manages accounting, authorization, and authentication (AAA) tasks.
How 802.1X Authentication Works (Process Flow)
The authentication process involves several steps, facilitated by the Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP), which is the authentication framework used within 802.1X:
- Initial Connection: Access is requested by the supplicant device. In a wireless setting, the client usually associates with the Access Point (AP) using open authentication.
- EAP Exchange (Supplicant to Authenticator): The authenticator (switch/WLC) receives the supplicant’s credentials via 802.1X EAP.
- RADIUS Communication (Authenticator to AS): The centralized Authentication Server (RADIUS server) receives the authentication message from the authenticator. To be sent to the RADIUS server, the EAP message is enclosed in a UDP packet.
- Verification and Notification: Using its database and policies, the Authentication Server confirms the client’s identity. After that, it gives the authenticator an “accept” or “reject” message.
- Access Grant/Denial: Depending on the authentication status, the authenticator notifies the client of the response and manages physical network access.
You can also read Rule-Based Access Control RuBAC Advantages And Use Cases
Key Operational Contexts
Wired and Wireless Use Cases
The purpose of 802.1X is to protect both wireless and wired systems. Because it enables per-user authentication in place of shared keys, 802.1X authentication is essential to the WPA-Enterprise, WPA2-Enterprise, and WPA3-Enterprise security models in wireless networks.
Network Access Control (NAC)
Concepts of Network Access Control (NAC) are frequently combined with 802.1X. Before giving complete network access, the network can use this combined method to verify the supplicant’s security posture or health status (such as current antivirus software and patches). Policy enforcement has the authority to put a compromised or unpatched device into a quarantine Virtual Local Area Network, which would prevent it from connecting to the rest of the network.
Host Modes
An 802.1X port can be configured to support different modes for managing connected devices:
- Single-host mode: The port can authenticate only one supplicant. The port reverts to its unauthorized state if the supplicant departs or is replaced.
- Multihost mode: A single 802.1X-enabled port can have many hosts connected to it. In this manner, network access can be allowed to all associated supplicants with just one authorized user.
Authentication Methods and Security
Multiple EAP authentication techniques are supported by 802.1X. The EAP method that is selected has a significant impact on the security level.
Network administrators may utilize MAC Authentication Bypass (MAB) for devices that do not support 802.1X, including printers or cameras. In MAB, the device’s MAC address is used as the credential to authenticate with the RADIUS server.
In contrast to password-based techniques (such as PEAP-MSCHAPv2 or EAP-TTLS/PAP), the usage of digital certificates (EAP-TLS) is generally regarded as the most secure solution because it is based on asymmetrical cryptography and is impervious to over-the-air credential theft attempts.
Benefits of 802.1X
- Enhanced Security: By requiring distinct credentials or certificates for each device or user, it goes beyond simple shared passwords to stop unauthorized devices from accessing the network.
- Granular Access Control: It enables administrators to impose particular authorization rules (access policies) according to user roles, device types, or health conditions.
- Centralized Management: A central server (RADIUS) handles authentication, making management easier and provide a single location for logging (Accounting).
You can also read Advantages And Disadvantages Of RBAC & Types Of RBAC
