This article covered the following topics: definition of DAC, core principles, advantages and disadvantages of discretionary access control are discussed, along with how it works, examples of its use, and discretionary access control vs mandatory access control.
What is a discretionary access control?
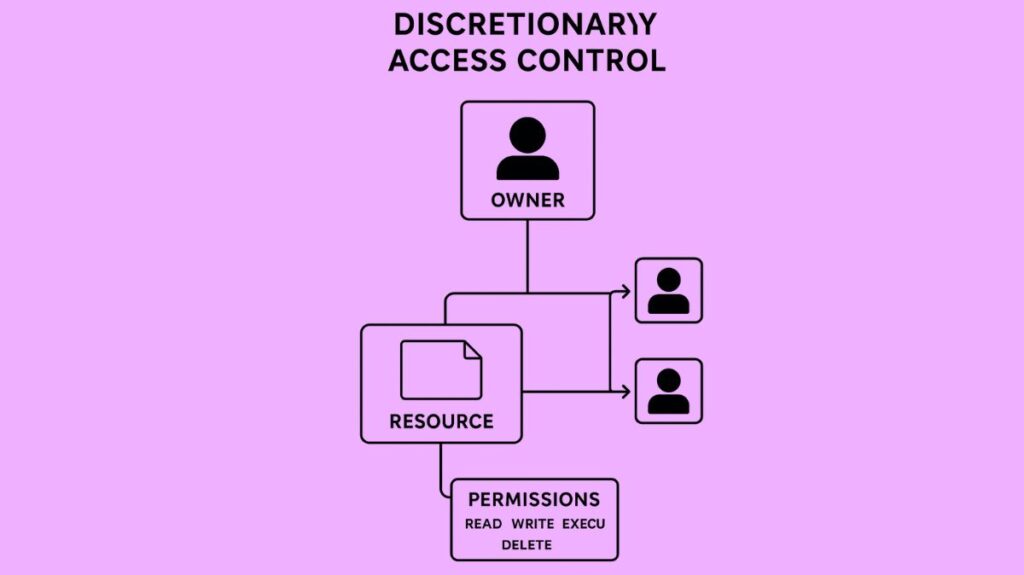
The owner of an object has the power to allow or deny access to it in accordance with their own judgement under the Discretionary Access Control (DAC) access control concept. With the help of tools like Access Control Lists (ACLs) and permission bits present in Unix, Linux, and Windows, this model is adaptable and enables user-driven sharing and delegation. For high-security situations, DAC is less secure than other models due to its dependence on user discretion, which might raise the danger of misuse or security breaches, even while it provides user-friendliness and agility for data management.
The word “discretionary” describes how the owner or creator of the resource retains complete control over access.
Also Read About User Security Awareness: Tips For Protecting Your Authority
Core Principles
Ownership
A certain user is recognized as the resource’s owner and has the power to control its access restrictions.
User Discretion
The defining feature is user discretion, which allows the owner to decide who has access rights and to grant, revoke, or change those permissions whenever they see fit without requiring permission from a central security administrator.
Transferability of Privileges
TCSEC claims that because a subject with a particular access privilege is usually able to transfer that right possibly indirectly to any other subject, the controls are discretionary. With this ability, a person who has been given access can do things like:
- Transferring the resource or information to different objects or subjects.
- Granting other subjects their privileges.
- Modifying the security features of objects or system components.
- Selecting security features for freshly made items.
- Altering the access control regulations.
How DAC Works
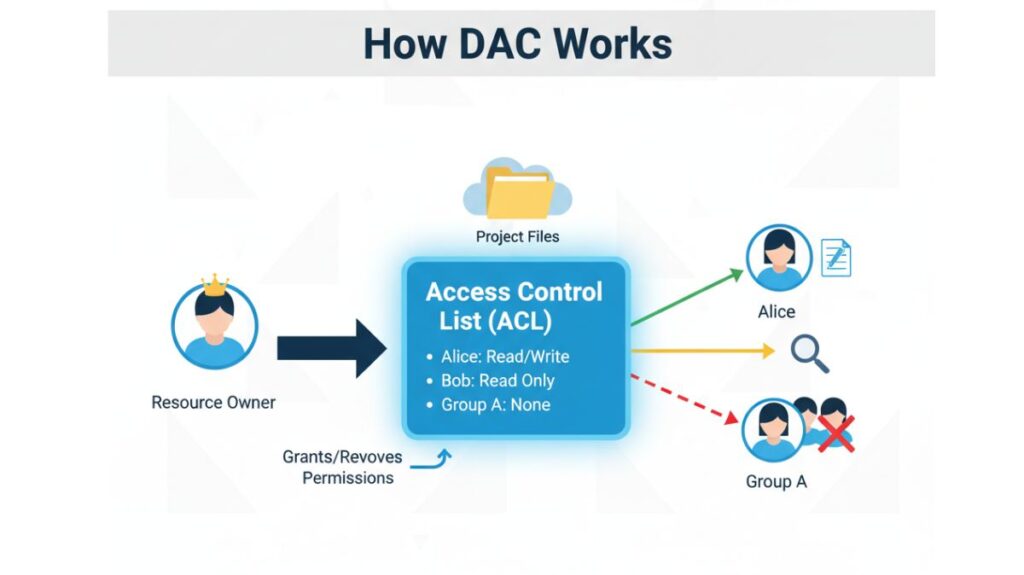
DAC depends on the resource’s (object) rights and the user’s (subject) identity.
Ownership
- A resource (such as a file, folder, or database table) is owned by the person who created it.
- All other subjects’ access rights must be specified by the owner, who has complete control.
Access Rules
One of two main approaches is usually used to enforce access decisions:
Access Control Lists (ACLs): The most popular approach is to use Access Control Lists (ACLs). The object (the file or folder) has a list called the ACL connected to it. A user or group and the rights they have been given are specified in each entry in the list (e.g., Alice: Read/Write, Bob: Read Only, Group A: None).
Capacity Systems: This less popular technique links a subject to a token or “capability” that allows them to access an item. For instance, a hidden URL for an unlisted file or a private key for a bitcoin wallet.
User Discretion
The ability of the owner to give, withdraw, or alter access rights at any moment without requiring consent from a security administrator or central authority is what distinguishes DAC.
DAC depends on the resource’s (object) rights and the user’s (subject) identity. Usually, certain procedures are used to enforce access decisions:
Access Control Lists (ACLs)
The most popular approach is to use Access Control Lists (ACLs). A list that is affixed to the object (the file or folder) is called an ACL. A user or group and the precise permissions they have been given are listed in each item (e.g., Alice: Read/Write).
Permission Bits
Operating systems like Windows, Linux, and Unix make considerable use of permission bits. For instance, the Unix file mode represents Read, Write, and Execute permissions using three bits for each of the User, Group, and Others categories.
Oapacity Systems
This less popular technique links a subject to a token or “capability” that allows them to access an item, like a private key or a secret URL. Because capability systems enable people to transfer their access, they are also referred to as offering discretionary controls.
Typically, rights like Read, Write, Execute, Delete, or Modify are used to define permissions.
Also Read About How To Prevent Password Attacks, Advantages & Disadvantages
DAC in Practice and Examples
In the majority of general-purpose computing environments, the default setting is DAC, the most popular access control paradigm.
Systems in the real world that use DAC include:
- Operating systems (Unix/Linux, Windows): Systems of operation: Popular operating systems like Windows, Unix, and Linux use the DAC model to control file and directory access through the use of permission bits and ACLs.
- Cloud Collaboration Tools: The owner controls who has “Viewer,” “Commenter,” or “Editor” rights when sharing a document on platforms like Google Drive or Microsoft SharePoint.
- Databases: Users can give other users particular rights on tables or schemas.
- Smartphone Permissions: You have the option to accept or reject an app’s request for access to your contacts, camera, or location.
Discretionary Access Control Vs Mandatory Access Control
| Feature | Discretionary Access Control (DAC) | Mandatory Access Control (MAC) |
| Control Authority | Resource Owner defines access permissions for their resources. | Central Authority (system/security policy) defines all access rules. |
| Access Decision | Based on user identity and permissions set by the owner. | Based on security labels/classifications (subject clearance vs. object sensitivity). |
| User Discretion | High: Owners can grant/revoke access at their discretion. | None: Users cannot override or modify system-defined access rules. |
| Flexibility | High, easy for users to share and collaborate. | Low, rigid and strictly enforced. |
| Security Assurance | Lower, prone to misconfigurations and insider threats. | Highest, as rules are system-enforced and cannot be bypassed. |
| Administration | Distributed; owners manage their own resource permissions. | Centralized; security administrators manage all security labels and policies. |
| Primary Goal | User autonomy and flexible resource sharing. | Data confidentiality and integrity; strict policy enforcement. |
| Typical Use Cases | General operating systems (Windows, Linux), cloud storage, collaboration tools. | Government/military (classified data), high-security industrial systems, some financial/healthcare systems. |
| Risk Profile | Risk of accidental data exposure, misconfigurations, insider misuse. | Risk of over-restriction, complexity in initial setup, but strong protection against unauthorized access. |
Also Read About What Is Mitigation In Network Security? Techniques And Risks
Advantages of discretionary access control
- User-Friendly: The system is easy to use since it gives users the ability to control their own data and access.
- Flexibility: It offers dynamic access control, which is advantageous for user-driven sharing and teamwork.
- Granularity: Fine-grained control is made possible by owners’ ability to assign particular permissions to both individuals and groups.
Disadvantages of discretionary access control
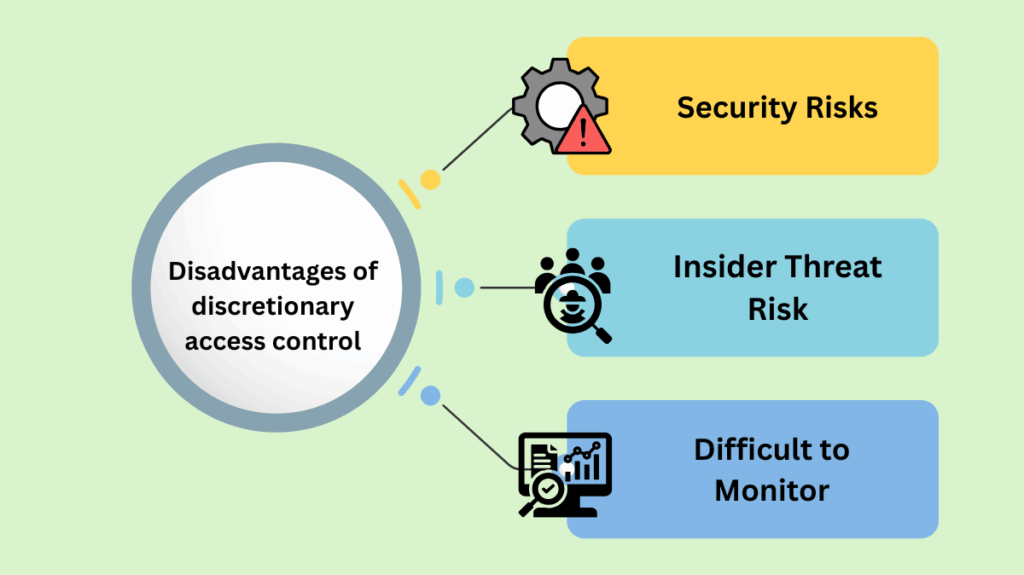
- Security Risks: Sensitive information may be accidentally or purposefully misused if the owner’s judgement is relied upon.
- Insider Threat Risk: Unauthorised users may be granted access by a malicious or negligent owner, resulting in security flaws.
- Difficult to Monitor: Monitoring and enforcing organization-wide security policies can be difficult due to the decentralized nature of access management.
In conclusion, because DAC mostly depends on the resource owner’s discretion to decide who has access, it is thought to be less secure than MAC despite being more adaptable and user-friendly.
Also Raed About Network Device Monitoring: Control Plane & Protocol Insights
