MD5 Message Digest 5 Algorithm
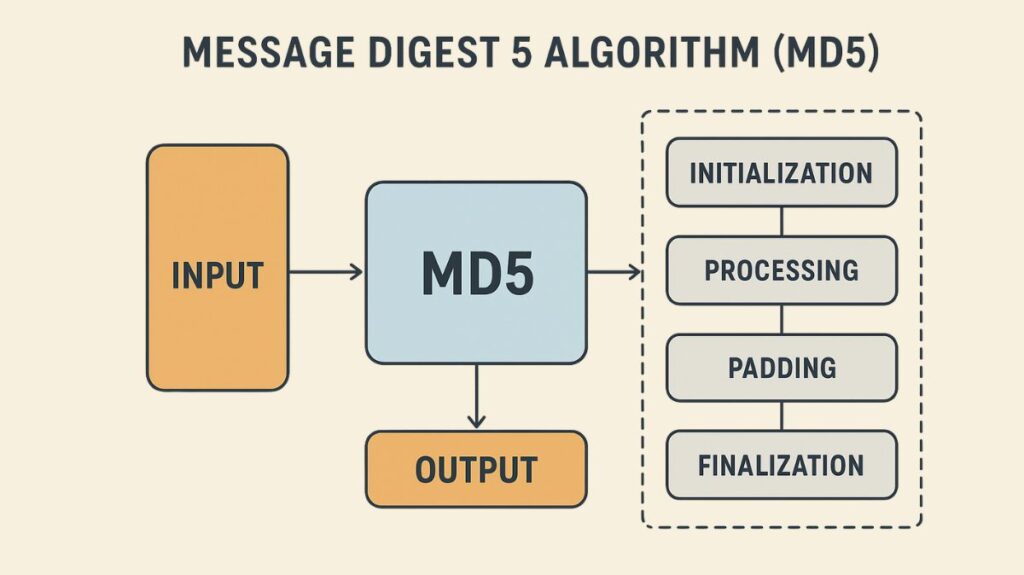
The Message Digest 5 algorithm, or MD5, is a particular mathematical technique designed to be used in a variety of security protocols. It belongs to the class of hash algorithms.
An example of a cryptographic hash function is MD5. It is a one-way function or unidirectional process that generates a fixed-size output from a variable-sized input (data or message). The digest, message digest, or just hash are some names for this output.
Also Read About What is eBGP External Border Gateway Protocol and Use Cases
Example:
Input: "Hello"
MD5: 8b1a9953c4611296a827abf8c47804d7
Input: "hello"
MD5: 5d41402abc4b2a76b9719d911017c592→ Take note of how the hash is totally changed by a minor change in case.
Important Features and Security Situations
Hash Output Size: A 128-bit digest is produced by MD5.
Computational Difficulty: The MD5 formula is designed to make it computationally challenging to calculate the original clear-text input, even in cases where the hash result is known. This is predicated on the fact that every clear-text input yields a distinct hash value.
Evolution and Vulnerability: For almost 30 years, the MD5 algorithm has been in use. As computer performance has increased and the algorithm has been studied, MD5 has become less difficult to crack. In the 2010s, Cisco addressed these issues by introducing better hashing solutions utilising SHA-256 (Type 8/PBKDF2 and Type 9/Scrypt).
Also Read About What is SHA -1(Secure Hash Algorithm 1), how does SHA 1 work
Applications of MD5
- Password Storage on Cisco Devices (IOS)
To improve device security, Cisco routers and switches frequently employ MD5 to store an encoded password value in the configuration instead of the clear-text password.
enable secretCommand: IOS generates a hash for the enable secret password by default using MD5. This appears as encryption type 5 in the operating configuration.
- Authentication Process: IOS performs the MD5 hashing function on user input when a user enters a password to enter enable mode. The stored hash value (the “secret”) is then compared to this freshly computed hash. Access is allowed if the hashes match.
username secretCommand: When using the username name secret password command, the default algorithm is MD5 (Type 5).
- IOS Code Integrity Verification
Cisco checks the integrity of IOS code files using MD5:
- Procedure: Cisco determines and posts the MD5 hash value for a file on its download website when it creates a new IOS image.
- Verification: The router’s verify /md5 command can be executed by a user. It verifies that the file has not been altered (data integrity) if the locally recalculated hash matches the published MD5 hash.
- Protocol Authentication and Integrity Checks
Several protocols use MD5 to guarantee data integrity and authentication:
- Using a 128-bit shared secret key, MD5 is one of the two popular hash message authentication code (HMAC) methods mentioned. By incorporating a secret key into its computation, HMAC ensures data integrity and authenticity and stops an adversary from recalculating the right hash in the case that the packet is altered. The resulting hash value is appended to the original message when R1 hashes using MD5; R2 does the same hash operation and compares the outcomes to ensure data integrity.
- During routine connection checks, the Challenge Handshake Authentication Protocol (CHAP) employs MD5 as a one-way hash function. In response to a challenge, the remote device uses MD5 to calculate a value and transmits it back; the local router verifies that the link is still in contact with the same host by comparing the hash value.
- MD5 is a hashing method used in IPsec (Internet Protocol Security) technology to ensure integrity. A one-way hash, such as MD5, is used by the Authentication Header (AH) protocol to authenticate packets.
- Strong authentication with MD5 or SHA is supported by SNMPv3 (Simple Network Management Protocol version 3).
- Open Shortest Path First version 2 (OSPFv2): Code 2 in the 16-bit Authentication mechanism field indicates that OSPFv2 supports MD5 as an authentication mechanism.
- Hot Standby Router Protocol (HSRP): By creating an MD5 digest for the HSRP section of the multicast packet, MD5 authentication provides higher security than plain text authentication for HSRP. A key chain or a key string can be used to directly or indirectly configure the MD5 hash key. If the hash of the arriving packet differs from the MD5-generated hash, HSRP packets are refused.
Also Read About What Is OSPF Open Shortest Path First? Advantages Of OSPF
