Network device management
The thorough process of monitoring, managing, and preserving the hardware and software elements of a computer network is known as network device management. In order to support an organization’s activities and user needs, it guarantees that the network infrastructure runs effectively, safely, and dependably.
How It Works
Tools, procedures, and protocols are all used in network device administration. Fundamentally, it uses monitoring devices to collect information on their performance and state. After then, this data is examined to find problems, enhance efficiency, and make plans for upcoming requirements. Important roles include:
Also Read About Network Device Monitoring: Control Plane & Protocol Insights
- Management systems monitor CPU, memory, interface status, bandwidth, and error rates using SNMP and ICMP. Telemetry and other modern technologies send high-resolution data in real time.
- Configuring, monitoring, and upgrading firewalls, switches, and routers is configuration management. Automation tools enforce consistency, push configurations, and allow speedy rollbacks if changes fail.
- By finding and fixing network faults, fault management decreases downtime. Logs and alarms show problems.
- To ensure network performance matches business needs and SLAs, performance management checks throughput, packet loss, and latency.
- Implementing, enforcing, monitoring risks, managing access, and conducting vulnerability assessments to safeguard the network from intruders is security management.
- New network devices are properly configured and integrated during provisioning.
- Manage and distribute firmware and software upgrades to patch vulnerabilities and provide new functionality to network devices.
History
As computer networks expanded, network device management became necessary.
Early Years (1980s): A fundamental standard for network device management was established by the Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP). Basic parameter monitoring, such as traffic and device status, was made possible.
1990s: As network monitoring systems advanced, they were able to provide more thorough traffic analysis and performance tracking. For easier administration, command-line interfaces (CLIs) were replaced by GUIs.
2000s onwards: After the 2000s, management tools adapted to larger, more distributed, and diversified environments as the internet and complex business networks gained prominence. Cisco’s NetFlow protocol enabled more complex analytics and automation by improving traffic pattern analysis. Cloud computing and the Internet of Things have raised need for flexible and scalable management solutions.
Why It Is Important
Network device administration must be efficient for many reasons.
- Early detection and resolution of issues ensures service and app availability.
- Improves Performance: Fixing bottlenecks and properly allocating resources speeds up networks.
- Threat detection, security concepts, and vulnerability regulation protect private data and systems.
- Automation and proactive problem-solving cut repair costs, resource use, and labour.
- company continuity: Maintains key company services during peak demand or unforeseen events.
- Facilitates Scalability and Planning: Provides network utilization data and expansion and technology adoption strategies.
Network Device Management Types
There are various ways to look at network device management:
By Function (FCAPS Model)
This framework is extensively used:
- Identifying, separating, and fixing network issues is known as fault management.
- Managing device configurations, including initial setup and continuous adjustments, is known as configuration management.
- Accounting Management: Monitoring the use of resources for capacity planning or billing.
- Performance management is the process of tracking and improving network performance indicators.
- Security management is the process of defending the network against threats and illegal access.
By Device Type
Frequently, management tools are categorized according to the kind of equipment they oversee:
- Router management includes setting up routing protocols, keeping an eye on traffic, and guaranteeing connectivity.
- Switch management includes traffic forwarding, port setup, and VLAN management.
- Firewall management includes setting up security rules, keeping an eye on traffic, and controlling access.
- SSIDs, security configurations, and client connectivity are all managed by wireless access point (WAP) management.
- Network device administration may overlap with controlling network interfaces and connections for servers and storage, even though these areas are frequently distinct.
By Protocol/Technology
- SNMP Management: Uses SNMP to poll device information.
- Analysis of network traffic flows for performance and security insights is the main goal of NetFlow/sFlow/IPFIX analysis.
- Direct device communication using command-line interfaces.
- GUI-based Management: Using third-party or vendor-provided GUIs.
- SDN Controllers: Software controls these devices.
Advantages of Network Device Management
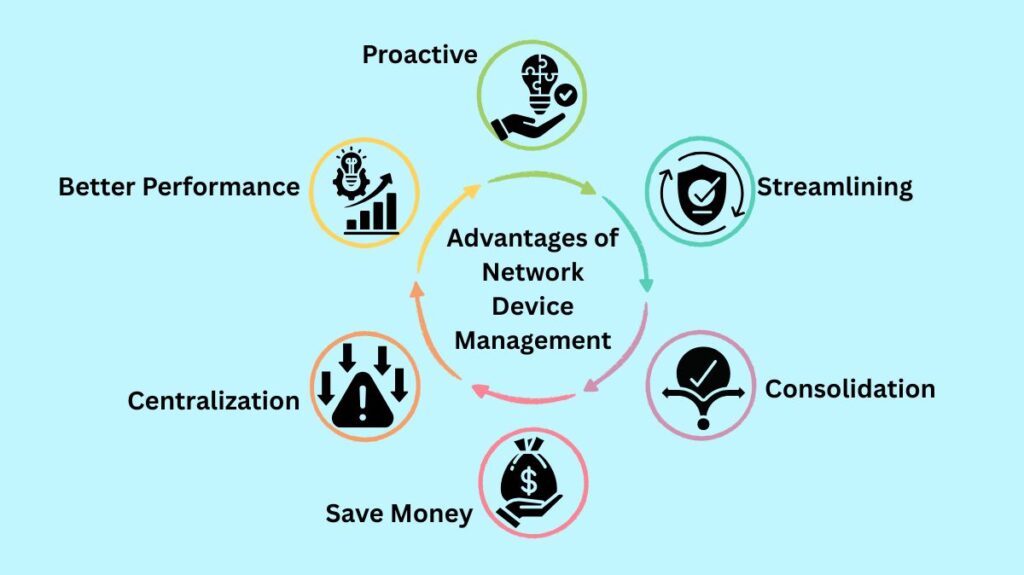
- Proactive: Proactive monitoring and problem-solving increase network availability.
- Better Performance: Fixing bottlenecks ensures the fastest and most efficient network.
- Centralization: Centralized threat detection and control reduce risks.
- Save Money: Efficiency and automation decrease manual intervention and costly outages.
- Consolidation: Unified network visibility and control enable faster reactions and improved decision-making.
- Streamlining: Consistent setups and audit records simplify regulatory compliance.
Also Read About Network Device Maintenance Applications And How It Works
Disadvantages
- Complexity: Implementing and managing complex systems requires knowledge and skills.
- Cost: Top management tools and skilled workers are expensive.
- Alert Fatigue: Poorly constructed systems may cause excessive alarms, making it hard to see problems.
- Proprietary management tools may limit vendor flexibility.
- Management System Security Risks: Attackers may target the management system if it is not properly secured.
Applications
Network device management is used in a number of contexts:
- Enterprise networks: overseeing data centres, LANs, and WANs to guarantee corporate operations.
- Service Providers: Managing extensive networks to offer clients services.
- Managing network infrastructure in both on-premises data centres and cloud platforms is known as cloud and hybrid environments.
- Overseeing the security and connection of an increasing number of Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
- SOCs, or security operations centres, keep an eye on network device behaviour to spot security risks.
- Verifying that network configurations and operations adhere to rules and industry standards is known as compliance auditing.
- Capacity planning is the process of forecasting future resource requirements using performance data.
Cisco Specifics
As a top supplier of networking hardware, Cisco provides a variety of tools and approaches for managing network devices.
- Cisco DNA Centre: An intent-based networking platform that offers Cisco networks centralized automation, management, and assurance. It makes monitoring, configuration, and device onboarding easier.
- A previous iteration of Cisco’s network management solution, Cisco Prime Infrastructure provides extensive tools for both wired and wireless networks.
- Cisco Security Device Manager (SDM) simplifies security feature monitoring and configuration on Cisco IOS routers via the web.
- Cisco equipment can be monitored via third-party SNMP, NetFlow, and sFlow technologies.
- CDP: Cisco devices expose their capabilities and neighbours for network mapping and troubleshooting.
- SolarWinds, ManageEngine OpManager, PRTG, and Datadog facilitate Cisco multi-vendor administration.
Also Read About Advantages, Disadvantages Of Routers & How Do Routers Work
