RJ61 Connector

The RJ61, or Registered Jack 61, is a kind of modular connector that is mostly utilized in applications related to telephones and telecommunications. Up to four distinct phone lines can be supported on a single twisted-pair cable, according to its architecture.
Physical Characteristics and Pin Configuration
With eight contacts and eight positions (8P8C), the RJ61 connector is physically somewhat similar to the RJ45 connector. They can literally fit into the same jack because they are the same size and shape.
The eight metal contacts are frequently gold-plated for dependable electrical conductivity and extended service life, and they are usually placed in two rows of four contacts.
The RJ61 is wired differently from the RJ45, despite their physical similarities; this distinctive pinout is the key difference. Pins 4 and 5 are used by the first phone line pair in an RJ61, followed by pins 3 and 6 for the second, 2 and 7 for the third and 1 and 8 for the fourth. The low-frequency analogue voice signals are intended to be used with this wiring.
You can also read DHCP Server Conflict, DHCPv4 Operation & DHCPv6 Operation
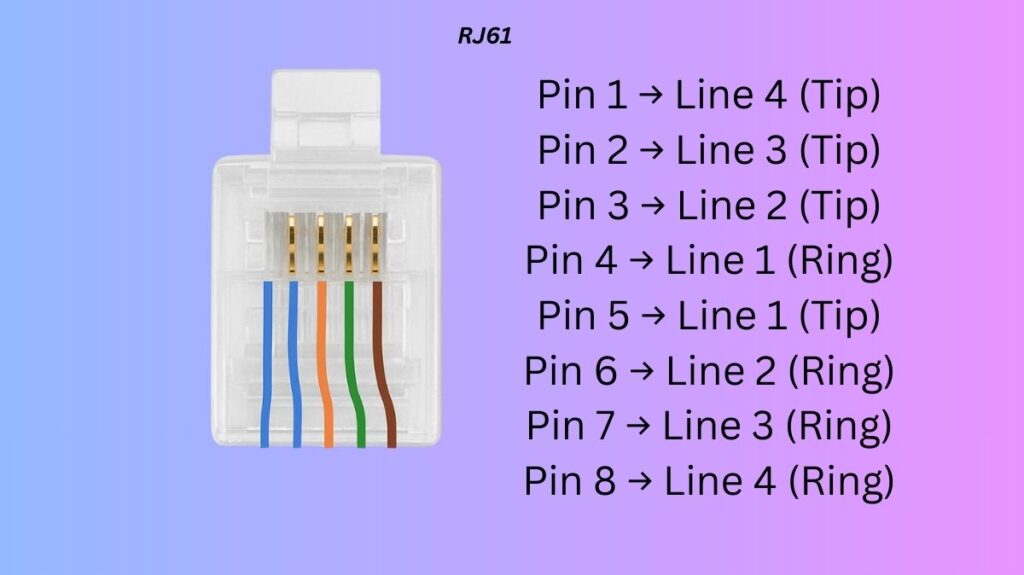
Pin Configuration (RJ61 – TIA/EIA-568A equivalent for 4 phone lines):
Pin 1 → Line 4 (Tip)
Pin 2 → Line 3 (Tip)
Pin 3 → Line 2 (Tip)
Pin 4 → Line 1 (Ring)
Pin 5 → Line 1 (Tip)
Pin 6 → Line 2 (Ring)
Pin 7 → Line 3 (Ring)
Pin 8 → Line 4 (Ring)
So, the connector supports four telephone pairs (lines 1–4).
Primary Applications:
The design of the RJ61 connector makes it perfect for certain telecom applications, especially where space is an issue or more than one phone line is required on a single cable:
Analogue Telephony: Frequently utilized for analogue phone connections in homes or businesses.
Multi-Line Telephone Systems: Business telephone systems like Key Telephone Systems (KTS) and Private Branch Exchange (PBX) systems sometimes have multi-line telephone systems, which make wiring easier by enabling up to four distinct phone lines over a single cable.
Telecommunications Panels: Multiple phone lines are distributed from a single cable to different endpoints within a building using telecommunications panels, also known as patch panels or telecommunications closets.
Modem and Fax Interfaces: In certain setups, it can act as an interface for fax machines and modems to join the phone network.
Proprietary or Custom Applications: Suitable for industrial applications requiring specialized connectivity or for particular custom communication systems.
Differences and Incompatibility with Ethernet (RJ45)
One important issue is that, even though RJ61 and RJ45 seem the same, they are not interchangeable.
Wiring Diagram: RJ61’s internal wiring is incompatible with Ethernet standards and was created for telephone systems, which use separate wire pairs to transfer analogue information. In order to minimize crosstalk and guarantee signal integrity for high-speed digital transmission, Ethernet (RJ45) cabling adheres to T568A or T568B standards, which require twisted pairs to be adjacent (e.g., pins 1 and 2, 3 and 6).
Suitability for Data: The pins for pairs 3 and 4 are too far apart for high signaling frequencies, making RJ61 unsuitable for use with high-speed data. If twisted-pair data patch cables are used with this pin separation, crosstalk between voice lines may result.
Network Performance: RJ61 cables are not designed with Ethernet performance in mind, and they might not satisfy the strict specifications set forth by Ethernet standards for signal quality, attenuation, and crosstalk. In an Ethernet setting, this may result in problems with signal quality and network performance.
Hardware Compatibility: Ethernet devices are made to work with Ethernet cables that are compatible with RJ45 connections. When RJ61 cable is used in an Ethernet context, compatibility problems may arise, which could lead to network device damage or improper operation.
Cabling: Although RJ61 employs twisted pair cables, high-speed data cannot be transmitted using the conventional 8-core “satin silver” flat cable that is frequently used with 4-line analogue telephones with RJ61 sockets. Pins are kept near for pairs 3 and 4 in twisted-pair data cabling (such as that used for RJ48, T568A, and T568B) to prevent these problems.
Historical Context:
The TIA/EIA-568 (now ANSI/TIA-568) protocols and structured cabling systems caused the RJ61 cabling model to become obsolete. In facilities, a single cabling standard for data and voice is now provided by the T568A and T568B standards.
To put it simply, RJ61 plugs resemble RJ45 plugs, but they are designed for multi-line telephone systems (up to four lines), not Ethernet networking.
You can also read Network Print Server, How It Works & Types Of Print Servers
