The definition, how it work, functions and benefits of FTP servers, security FTP servers, FTP in Cisco IOS, TFTP vs FTP, and FTP servers vs file services are all discussed in this blog.
What is a ftp server?
A computer program or application known as a File Transfer Protocol (FTP) server is made to make it easier for files to be transferred between it and FTP clients across a network, usually the Internet or a local network. It serves as a central location where numerous users can store and access files.
An FTP server is essentially an online file cabinet that allows computers connected to a network to store, distribute, and view data.
Also Read About Advantages Of A File Server And How Do File Servers Works
How FTP Server Works?
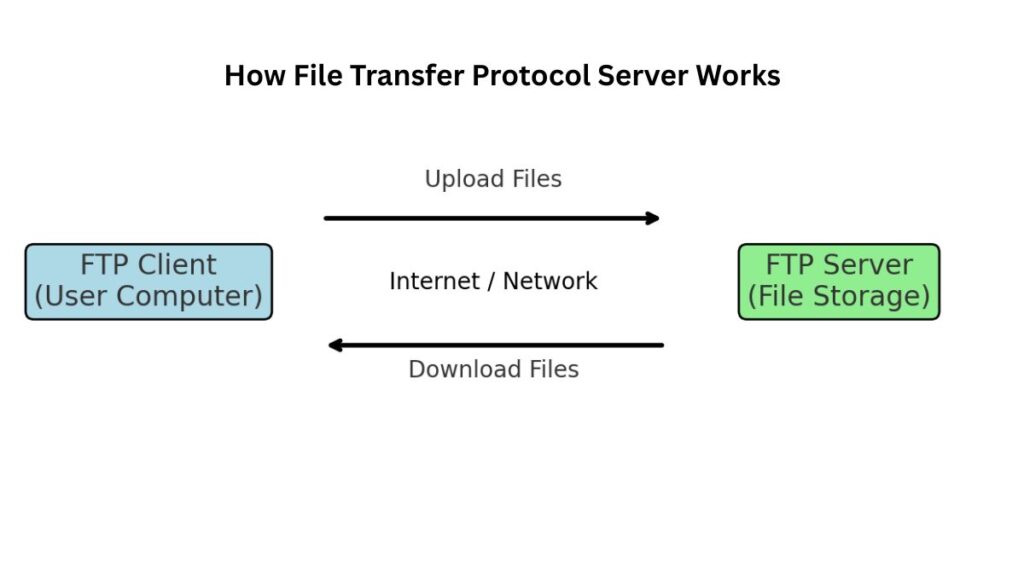
Easy Flow:
- Using an FTP client program (such as FileZilla, WinSCP, or the command line), a user establishes a connection to the FTP server.
- The client logs in anonymously or with a username and password.
- The user has the ability to download files from the server or upload files to it.
- The specified actions are carried out by the FTP server.
In detailed explanation
The client/server architecture is how FTP works. Using an application that supports the FTP protocol, a user connects to an FTP server on a distant host in the role of a client. The underlying language for carrying out internet commands, TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), makes this process easier.
- Establishment of Connection: The FTP client connects to the FTP server. While some servers allow anonymous access, most connections require the client to authenticate with a username and password.
- Dual Channels: One of FTP’s special features is that it uses two different kinds of connections to communicate during a session:
- Control Connection: This is the main connection, which by default uses port 21. It is in charge of receiving responses from the server and delivering commands from the client. An FTP session is started, maintained, and ended by it.
- Data Connection: This connection is only used for data transfers, including file downloads and uploads. In active mode, port 20 is usually used. Depending on the connection option, the number of data ports may change.
- Command Execution: After establishing a connection, the client can instruct the server to carry out actions. Important FTP commands include, for example:
- USER: Uses a username to verify a user.
- PASS: Uses a password to authenticate a user.
- LIST: List the contents of a directory.
- STOR: Keeps a file uploaded to the server. A file is retrieved (downloaded) from the server using RETR.
- CWD: Modifies the working directory that is currently in use.
- QUIT: Cuts off communication with the FTP server.
- Connection Modes: FTP can function in two ways for the data connection:
- Active Mode: The server actively connects to a port while the user (client) opens it and listens. Client-side firewalls can cause problems with this mode.
- Passive Mode: The user (client) connects to the server passively while it opens a port and listens passively. This mode is frequently used as a default safety measure, particularly in situations when a firewall prevents the client from receiving inbound connections.
Key Functions and Benefits of FTP Servers
FTP servers provide a number of features and important advantages, especially for companies that handle massive amounts of data:
- File Uploading and Downloading: Users have the ability to upload files from their PC to the server and download files that are kept on the server.
- Remote File Management: Facilitates operations such as file relocation, deletion, and renaming on the server.
- Managing Big Files: Because FTP servers can manage big files, businesses may easily share enormous volumes of data that might be too big for email.
- Better Workflows: They make file-sharing easier by permitting planned transfers, minimizing the time required to locate files, and facilitating the transfer of massive volumes of data all at once.
- Control and Access Management: FTP servers offer sophisticated access controls that let administrators choose who has the ability to edit, publish, download, and distribute files according to particular permissions.
- Data Recovery and Backup: By providing regular and automated backups at several places, an effective FTP server can guarantee that organisational files and data are not lost or corrupted, allowing for easy restoration when needed.
- Automation and Scripting: FTP servers provide a wide range of automation capabilities, enabling users to write scripts for automated data interchange between servers, batch uploads, file synchronization, scheduled backups, and specialized file retrieval.
Also Read About IPv4 Address Exhaustion: Simple Guide To IP Address Shortage
Security FTP server
All files, passwords, and usernames are transferred in clear text using the original FTP protocol, RFC 959 (1985). It is vulnerable to interception and contains security issues. More secure protocols are widely used to overcome these vulnerabilities:
FTP Secure
This protocol adds SSL or TLS encryption to FTP, making it more secure. FTPS authentication uses a public key certificate, password, and user ID like HTTPS.
- Implicit FTPS: Always encrypts command and data channels means SSL encryption from the start. Businesses that must comply with federal rules should use port 990 for secure connectivity.
- Explicit FTPS: Client requests security directly from the server. If security is not specified, the server may reject the connection or allow unsecure mode. Only the command channel can be protected with port 21.
SSH File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
SFTP is an SSH subsystem for secure file transmission. SFTP encrypts directory listings, user authentication, and file transfers using secure SSH connections. Using only port 22 simplifies firewall installations. To protect files in transit, SFTP and FTPS ensure end-to-end encryption.
FTP in Cisco IOS
- Cisco IOS supports FTP for router file transfers, including OS images.
- The copy ftp flash command copies an IOS image from an FTP server to a router’s flash memory.
- Cisco IOS
copycommands can provide URIs. This URI can include the protocol, username, password, FTP server IP address, and filename in one line (ftp://username:password@ip_address/filename). - To provide default FTP credentials, use global configuration commands like
ip ftp username <name>andip ftp password <pass>. - Routers can boot from FTP servers.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs) can manage FTP traffic on routers by blocking TCP ports 20 and 21 for specific source/destination subnets.
TFTP vs FTP

FTP is more feature-rich and reliable than TFTP (Trivial File Transfer Protocol):
Reliability
Because it uses TCP, FTP is reliable and connection-oriented. TFTP uses UDP, making it unpredictable and connectionless, however it has a checksum for error checking after transfer.
Features
FTP supports listing directory contents, creating, deleting, and browsing directories. TFTP is for file transfers, not directory browsing or administration.
Authentication
FTP sends them in plain text without FTPS but permits usernames and passwords. Any client can connect to an operable TFTP server because it lacks authentication.
Ports
FTP uses TCP ports 20 and 21, while TFTP uses UDP port 69.
Also Read About DNS Servers, DNS Resource Record’s CNAME, MX, and More
FTP Servers vs File Services
When considering data management systems, File Services and FTP servers must be distinguished.
- FTP servers: FTP servers are unsurpassed at managing huge files and transferring them securely and quickly. FTP servers are perfect for file sharing and collaboration because they enable uploading, downloading, and managing data remotely straightforward. FTP servers also use SFTP and FTPS encryption methods to protect your sensitive data.
- File Services: In contrast, file services offer more features than merely file transfer. With sophisticated capabilities like version control, file synchronisation, access controls, and collaboration tools, they provide a centralized file storage solution. You may configure rights for various users or groups, organise your file hierarchy, and monitor file changes over time with File Services. Because of this, File Services offers a more complete solution for handling and arranging massive volumes of data inside a company.
The size of an organization, the volume of data, and the level of management and protection needed all influence which option is best.
