What is Wireless Personal Area Network?
A Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN), also referred to as just WPAN, is a kind of wireless network intended to link devices over a relatively short distance, usually within a person’s own workspace. In essence, WPAN is a Personal Area Network (PAN) in which wireless media is used by the connected devices.
WPANs are essential for facilitating easy and convenient wireless communication inside localized contexts and between personal devices. They are frequently made to offer affordable and power-efficient solutions for a variety of gadgets.
Also Read About WPA Wi Fi Protected Access Definition And Features of WPA
Important Features and Range
WPANs are differentiated by a number of essential characteristics:
Range
WPANs have a limited or extremely limited operational range. The range is usually within roughly 10 meters (33 ft). Devices in close proximity are meant to be served by this restricted range. Bluetooth and other short-range protocols are typically ineffective at distances longer than 5 to 10 meters.
Infrastructure & Setup
There is little to no infrastructure setup required for a WPAN connection. WPANs don’t need a lot of network infrastructure to work, in contrast to Wireless Local Area Networks (WLAN). They include a straightforward setup procedure and easy connectivity. The idea of “plugging in” is crucial; when two WPAN-enabled devices are close to one another, they communicate as though they were connected by a wire.
Cost and Power
WPAN technologies have a low power consumption and are made to be energy-efficient. They also offer affordable solutions.
Connectivity
WPANs are person-centric, which means that each user and their devices are at the centre of the network. They usually make it possible for devices to communicate with one another peer-to-peer, exchanging data directly without the use of a middle-tier infrastructure. WPANs provide flexibility and portability.
Also Read About Wireless Local Area Network WLAN Creation and Components
Standards and Technologies
The IEEE 802.15 working group is responsible for standardising WPANs. WPANs employ a number of standardised technologies, including:
| Technology | IEEE Standard | Primary Use Case | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bluetooth | 802.15.1 | Connecting peripherals (headsets, keyboards, mice) and file transfer. | Most popular WPAN technology. Medium data rate, robust for general personal use. Operates in the 2.4 GHz ISM band. |
| Zigbee | 802.15.4 | Low-power applications, smart home, and IoT devices. | Very low data rate, extremely energy efficient, supports mesh networking. |
| Infrared (IrDA) | N/A | Older technology, used in remote controls. | Requires line-of-sight communication. |
| Near Field Communication (NFC) | N/A | Very short-range communication (a few centimeters) for contactless payments or device pairing. | Shortest range communication. |
| Wireless USB | N/A | High-rate, short-distance data transfer. | Higher data rates than traditional Bluetooth. |
| Ultra-Wideband (UWB) | N/A | High-speed data transfer over short distances; precise location tracking. |
Also Read About What Is VLAN Tagging Cisco? An Introduction To IEEE 802.1Q
IEEE Classification
The IEEE divides WPAN into three different groups according to data throughput:
- The IEEE 802.15.3 standard defines high-rate WPAN (HR-WPAN), which has a data throughput of more than 20 Mbps.
- The IEEE 802.15.1 standard defines medium-rate WPAN (MR-WPAN), which has a 1 Mbps data speed.
- The IEEE 802.15.4 standard defines low-rate WPAN (LR-WPAN), which has a data throughput of less than 0.25 Mbps.
Applications and Topology
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is one of the many uses for WPAN technologies:
- Devices & Peripherals: Linking wireless headsets, printers, keyboards, mouse, and hands-free gadgets to a computer.
- Data and Multimedia: File sharing between phones or laptops, synchronising data between personal devices (e.g., smartphone and smartwatch), and short-range networking for multimedia applications.
- Sensors, lighting controls, security systems, thermostats, and other smart home appliances are examples of smart environments.
- Additional Uses: Contactless payments and industrial sensor applications.
Star Topology, Mesh Topology, and Cluster Tree Topology are among the supported WPAN network connectivity configurations (network topologies). Devices can relay data using mesh networking, which is made possible by technologies like Zigbee and expands the coverage area.
Advantages and Disadvantages
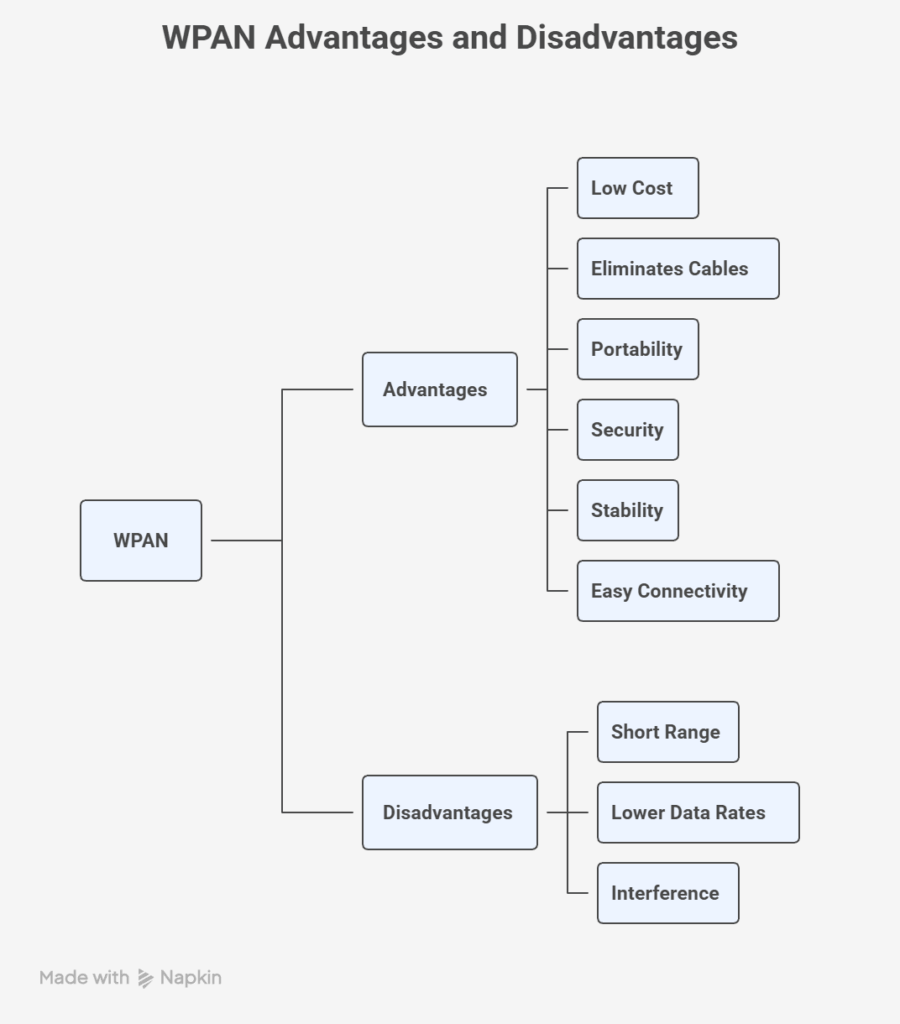
WPANs have a number of advantages and disadvantages.
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Low cost and inexpensive solutions. | Short range. |
| Eliminates cables. | Lower data rates and transfer speed compared to other networks. |
| Portability and flexibility. | Possible interference from other wireless signals operating on the same frequency band. |
| Security, stability, and easy connectivity. |
Also Read About What Is A WPA2 PSK Key? And How Does WPA2 PSK Work?
WPAN in Relation to Other Networks
In terms of infrastructure and scalability, a Wireless Personal Area Network (WPAN) differs from other network types:
WPAN vs. PAN: WPAN is a PAN in wireless form. Electronic devices within a user’s local vicinity (a few centimetres to a few meters) are connected by a PAN. PAN connections can be wireless (such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, Zigbee, and IrDA) or cable (such as USB and FireWire).
WLAN vs. WPAN: Of the wireless networks (WLAN, WMAN, and WWAN), WPANs have the shortest coverage distances. WPANs have a very narrow range, typically lower data speeds, and require little to no infrastructure, in contrast to WLANs, which span a whole building or residence and require an access point or router.
WPAN vs. BAN: Medical sensors that are positioned on or close to the human body to monitor biomedical functions (such as a wireless pacemaker) are commonly referred to as Body Area Networks (BANs). Although WPAN technology may be used by BANs, biological sensors are not often included in WPANs.
