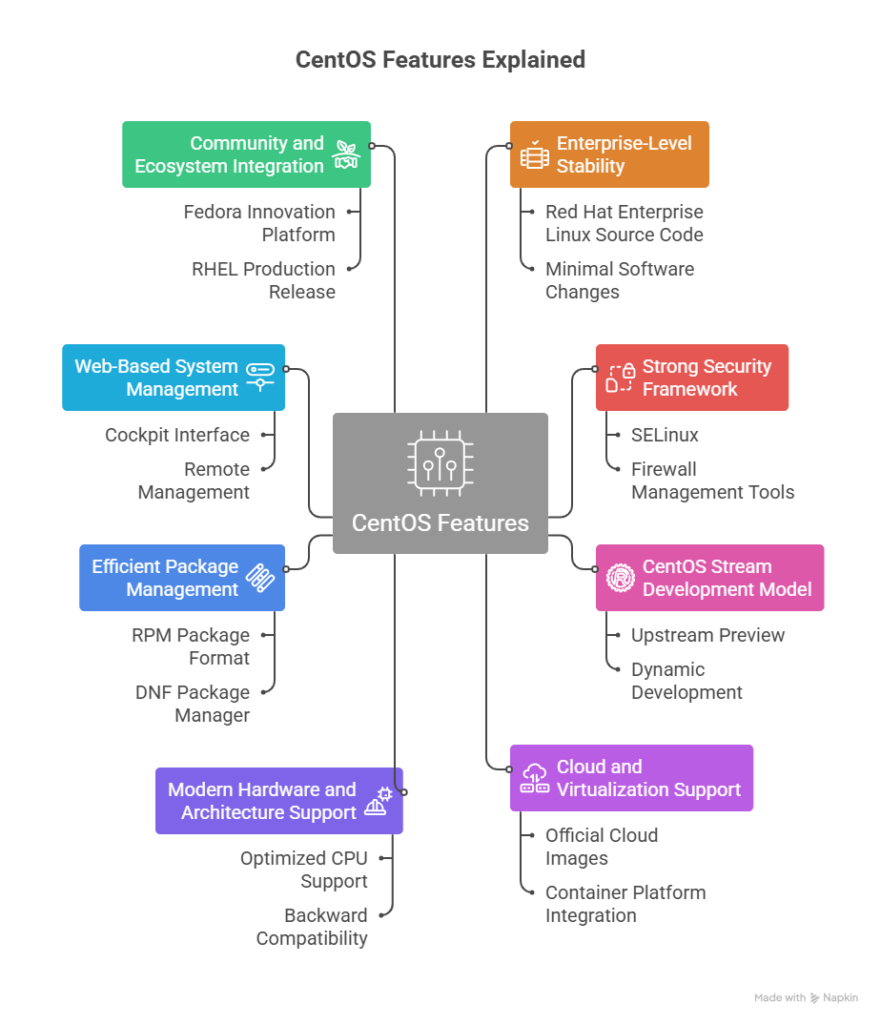
CentOS Features
Also Read About What Is CentOS Operating System? CentOS Pros And Cons
CentOS Installation (2026)
This is how to install CentOS Stream, the primary version:
- Get CentOS Stream 9 or 10 ISO at CentOS.org.
- BalenaEtcher or Rufus create bootable USBs.
- Boot: Start your machine via USB after resuming.
Anaconda installer:
- Network: Enable Ethernet and WiFi before updating.
- Software: Select “Minimal Install” for a lightweight server or “Server with GUI” for desktop.
- Select sudo and set a strong root password.
- Reboot: Unplug the USB and sign in to your newly installed computer.
How did everyone else fare? (The Survivors)
- When people discuss “CentOS” these days, they frequently refer to its spiritual offspring. Look at the following if you want the stable, ten-year support of the original CentOS:
- The original CentOS inventor founded Rocky Linux.
- AlmaLinux is a community-owned initiative that now collaborates with the scientific communities at Fermilab and CERN.
CentOS Stream vs Rocky / AlmaLinux
| Feature | CentOS Stream | Rocky / AlmaLinux |
| Model | Upstream (Ahead of RHEL) | Downstream (Mirror of RHEL) |
| Stability | Moderate (Good for Dev) | High (Good for Production) |
| Updates | Continuous / Weekly | Periodic / Minor Releases |
| Best For | Testing & Development | Servers & Web Hosting |
Also Read About Ubuntu Operating System: History, Features And Advantages
Who is currently using it?
- DevOps engineers are developing “Cloud Native” applications using CentOS Stream and testing them against upcoming RHEL features.
- Scientific Computing: CentOS was formerly a center for large research institutes like CERN, and many still use it for non-critical testing nodes.
- The “Special Interest Groups” (SIGs) that develop hyperscale cloud and automobile tools are powered by the “Under-the-Hood” operating system.
CentOS latest version
You can find CentOS Stream 10 as the “latest” CentOS version.
Version Status: January 2026
The kernel’s upstream development branch, “Stream” versions, is the CentOS Project’s focus.
| Version | Status | Release Date | End of Life (EOL) |
| CentOS Stream 10 | Latest / Active | 2024/2025 | ~2030 |
| CentOS Stream 9 | Active | Dec 2021 | May 2027 |
| CentOS Linux 7 | Dead | July 2014 | June 30, 2024 |
| CentOS Linux 8 | Dead | Sept 2019 | Dec 31, 2021 |
CentOS Stream 10
- Linux 6.12 is the kernel.
- 3.12 Python
- Developing RHEL 10 is the priority.
- IBM Power, IBM Z, ARM64, and x86_64 (v3) are supported.
Why “CentOS Linux 9” Doesn’t Exist
Red Hat modified the roadmap in 2020. They switched from creating a “rebuild” (CentOS Linux) to a “preview” (CentOS Stream).
- Old CentOS: Copy it after RHEL is released. Extremely stable for manufacturing.
- CentOS Stream: Create features prior to RHEL deployment. (Slightly more “rolling” than the previous version, better for developers).
Best Alternatives for Production (Free)
The majority of customers have switched to these distributions if they prefer the previous “stable” experience of CentOS, a 1:1 binary compatible clone of RHEL:
- Rocky Linux: The original CentOS founder created Rocky Linux. At the moment, it is the most often used straight substitute for business servers.
- AlmaLinux: It uses RHEL binaries and is community-owned.
- Oracle Linux: Free RHEL-compatible Oracle Linux has a “Break-Fix” kernel option.
Summary for your download:
- Maintaining the CentOS name? Download CentOS Stream 10.
- Get Rocky Linux 9 or AlmaLinux 9 for a 100% stable web server.
| Feature | CentOS Stream 10 | CentOS Stream 9 |
| Status | Latest / Mainstream | Maintenance / Secondary |
| Base RHEL Version | RHEL 10 | RHEL 9 |
| Display Server | Wayland (X11 removed) | Wayland (X11 optional) |
| Package Manager | DNF 5 (Faster) | DNF 4 |
| Support Ends | 2030 | 2027 |
CentOS vs Ubuntu
Server administrators used to frequently argue over between CentOS and Ubuntu, but as of 2026, things have drastically altered. The comparison is now actually between Ubuntu LTS and CentOS Stream (or its successors), as the original CentOS Linux has reached its End of Life (EOL).
State of the Union” in 2026
- Officially Dead/End-of-Life: CentOS Linux (7, 8). Without additional support from a third party, running these in production right now poses a serious security risk.
- Current version: CentOS Stream. It receives features before Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) does, making it “upstream” of RHEL. Because it is a rolling release, steady production servers will find it less predictable.
- Ubuntu LTS (Long-Term Support): With a reliable 5- to 12-year support cycle, Ubuntu LTS is currently the industry leader for cloud and web servers.
Ecosystem & Package Management
- The APT package manager is used by Ubuntu. It is well-known for having enormous repositories and “PPAs” (Personal Package Archives), which make it very simple to locate and install practically any program.
- DNF is used by CentOS Stream. EPEL is needed. Although large, the selection is frequently more conservative and carefully chosen than Ubuntu’s.
Security (SELinux vs. AppArmor)
- AppArmor is the default on Ubuntu. It is typically thought to be more “forgiving” of novices and simpler to configure.
- SELinux is used by CentOS. This is a strong security module at the kernel level that is both much more complicated and much more granular. Troubleshooting when it blocks a service frequently calls for a high level of experience.
Community and Support
- The world’s largest community is found on Ubuntu. If you encounter a problem, the answer is most likely available on Stack Overflow or a forum.
- RHEL documentation is frequently required for CentOS users. The community has become divided since the switch to “Stream,” with many people switching to substitutes like Rocky Linux or AlmaLinux, which function similarly to the “old,” reliable CentOS.
| Feature | Ubuntu (LTS) | CentOS Stream |
| Base Architecture | Debian | RHEL (Red Hat) |
| Package Manager | apt (using .deb) | dnf / yum (using .rpm) |
| Release Style | Predictable (Fixed every 2 years) | Rolling (Continuous updates) |
| Stability | Very High (LTS versions) | Moderate (Upstream/Development) |
| Software Versions | Generally newer | Middle-ground (Ahead of RHEL) |
| Learning Curve | Beginner-friendly | Intermediate / Admin-focused |
| Best For | Cloud, DevOps, Developers | RHEL Development, Testing |
Centos vs ubuntu which is better?
Choose Ubuntu LTS if:
- You seek a “it just works” experience or are a novice.
- You use Kubernetes and Docker for cloud-native apps.
- You need the latest PHP, Node.js, or Python without problems.
- A system that won’t need major updates and gets security fixes for five years is ideal.
Choose CentOS Stream if:
- As a developer, you specialize in creating software for the Red Hat environment.
- Before additions are added to RHEL, you want to see and test them.
- You like dnf and know Red Hat/Fedora well.
If you want the “Old CentOS” a stable, free RHEL clone Rocky Linux or AlmaLinux are better than CentOS Stream.
CentOS Linux vs Red Hat Enterprise Linux
| Feature | CentOS Linux (Legacy) | CentOS Stream (Current) | Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) |
| Status | Dead (EOL) | Active / Development | Active / Production |
| Cost | Free | Free | Paid (Free for developers) |
| Stability | High (Frozen code) | Moderate (Rolling updates) | Maximum (Battle-tested) |
| Updates | None (Security risk) | Continuous (Feature-first) | Predictable (Stability-first) |
| Support | Community forums only | Community + Red Hat | 24/7 Professional Support |
| Usage | Migrating away | Dev/Test for RHEL | Mission-critical Production |
Also Read About What Is Linux Kernel? Why It Is Important And Its Components
