In this article, we covered network access control (NAC), including its fundamental objectives, significance, and operation, as well as its enforcement and remediation strategies, key technologies and components, types, and the NAC use cases that are given below.
Network Access Control NAC
As a gatekeeper to the network, Network Access Control (NAC) controls access to sensitive resources and private networks. It is a crucial security concept and solution. Its main goal is to make sure that only individuals and devices that are authorised, authenticated, and compliant are allowed access, while banning or restricting those who are not.
Network Admission Control is another name for NAC.
Core Goals and Importance of NAC
With the rise of mobile devices (BYOD) and Internet of Things (IoT) devices, NAC offers a strong, proactive approach to network security.
The main objectives and advantages consist of:
Policy Enforcement
It makes sure that all devices follow predetermined security policies, such as having firewalls turned on, operating system patches installed, and antivirus software up to date.
Threat Prevention
NAC lowers the danger of malware, data breaches, and computer worm cross-contamination by preventing unauthorized or compromised devices from connecting to the network.
Containment and Incident Response
By identifying odd or suspicious activities, containment and incident response reduce hazards. It can also automatically quarantine or isolate devices to prevent malware from spreading laterally.
Complete Visibility
NAC offers a comprehensive, up-to-date list of all users and network-connected devices, including “shadow IT” and Internet of Things devices.
Compliance
By enforcing stringent security standards and offering comprehensive audit logs, it assists organisations in meeting regulatory requirements (such as HIPAA, PCI-DSS, and GDPR).
Zero Trust Foundation
The Zero Trust security architecture relies heavily on NAC, which continually verifies the identity and security posture of people and devices even after they are connected.
Also Read About What Is A Wireless LAN Controller WLC In Networking?
How does network access control work
NAC uses a methodical procedure that includes enforcement, policy application, and verification.
| Stage | Description | Key Focus |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Authentication (A) | Verifies the identity of the user (“Who is the user?”) or device attempting to connect. This involves checking credentials, certificates, or unique identifiers like the MAC address. | User Identity and Device Identity |
| 2. Posture Assessment | Checks the device’s health and compliance against organizational policies (e.g., presence of required software or patch revision levels). | Device Health and Compliance |
| 3. Authorization (A) & Enforcement | Determines the access level and privileges allowed (“What can the user do?”) based on their identity and posture. The system then applies the appropriate policy. | Access Level and Privilege |
Enforcement and Remediation Techniques
The NAC system decides access based on identification and posture and uses particular actions to enforce policies:
- Complete Access: Allowed to authorised and completely compliant devices.
- Users such as contractors or visitors are granted limited or restricted access, which usually entails assigning them to a separate network segment (such as a guest VLAN) that permits only internet access or restricted application use.
- Quarantine: To stop infection, devices that don’t pass the compliance check are put in a restricted network section called a “quarantine” VLAN. It is possible that the user will be taken to a captive site that offers remediation tools and instructions (solving the issue, such as installing updates).
- Denial: Devices that are not authorised or that do not comply are completely barred from the network.
In accordance with the Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP), NAC frequently uses Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to divide the network and guarantee that users only access resources pertinent to their job function.
Core Technologies and Components
For operation, NAC depends on a number of well-established technologies and parts:
AAA Framework
Systematic access security requires the Authentication, Authorisation, and Accounting (AAA) framework.
- Verifying a user’s identity is known as authentication.
- Determining which resources a user is permitted to access is known as authorisation.
- Accounting: Keeping track of user activities (time spent, resources accessed) in order to generate an audit trail.
Protocols and Servers
- 802.1X: Port-based access control for wired and wireless networks is defined by IEEE standard 802.1X. It is used to regulate access to Layer 2 switched ports and provides selective access based on authentication. Three primary roles are defined by the standard: the Authentication Server (AS), the Client/Suppliant (the end device), and the Authenticator (the network device, such as a switch or WLC).
- RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service): The Authentication Server (AS) frequently uses the RADIUS (Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service) protocol to verify the client’s identity in accordance with regulations.
- TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access Control Server Plus): Because it allows for granular command-level authorisation, TACACS+ (Terminal Access Controller Access Control Server Plus) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that is typically used for remote administrative access.
- Network Access Server (NAS): A network access server (NAS) is a device that acts as an access control point and frequently doubles as a virtual private network (VPN), enabling distant workers to safely connect to the company network.
NAC Solutions and Advanced Features
Advanced solutions like Cisco’s Identity Services Engine (ISE) can incorporate NAC capability. Contemporary solutions frequently include:
- Context Awareness: Context awareness is the ability to grant access based on a variety of factors, such as the user’s identity, the device being used, and the workstation’s security state (context).
- Group-Based Access: Software-Defined Access (SDA) from Cisco is an example of a group-based access solution. It streamlines security by setting policies based on user groups using Scalable Group Tags (SGTs) instead of individual IP addresses.
Types of NAC
NAC solutions can be divided into groups according on the timing of policy enforcement:
| Type | Timing | Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-admission NAC | Policy is enforced before access is granted. | End-stations are inspected prior to being allowed onto the network, preventing clients with out-of-date security from talking to sensitive servers. |
| Post-admission NAC | Policy is enforced after the device is connected. | It continuously monitors and enforces rules based on user actions, restricting lateral movement within the network, sometimes requiring re-authentication for different areas. |
Other variations in design include:
- Agent vs. Agentless: Some solutions use scanning and network inventory methods remotely (agentless), while others require software (an agent) to be installed on the end device in order to report characteristics.
- Out-of-band vs. Inline: While inline solutions function as internal firewalls and may offer more sophisticated enforcement capabilities, out-of-band systems make use of pre-existing infrastructure.
NAC Use Cases
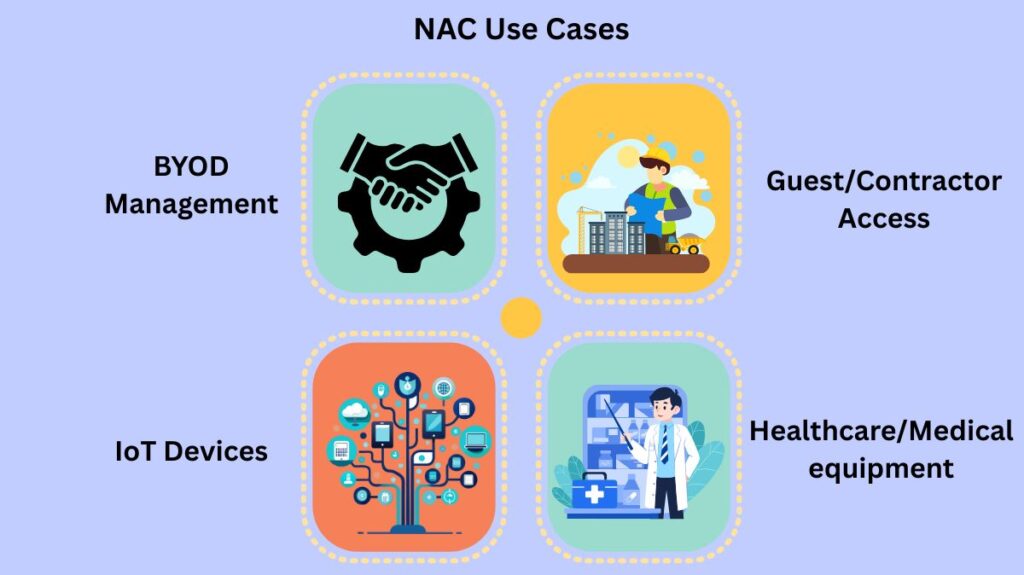
For the management of several contemporary networking infrastructures and device kinds, NAC is essential:
- BYOD Management: Ensuring that personal staff devices adhere to company security requirements prior to network access is known as BYOD management.
- IoT Devices: Expanding the attack surface by applying access policies and established profiling methods to safeguard devices such as cameras, sensors, and medical equipment.
- Guest/Contractor Access: Ensuring non-employees are securely onboarded while limiting their access to only the resources they require.
- Healthcare/Medical equipment: Enforcing stringent access controls on specialized medical equipment to protect medical information and identifying devices entering a convergent network.
Also Read About What Is A Network Security Threat? History, And How It Works
