In this blog, we discussed what a reflection attack is, its advantages, its operation, and how to prevent reflection attacks.
What is reflection attack?
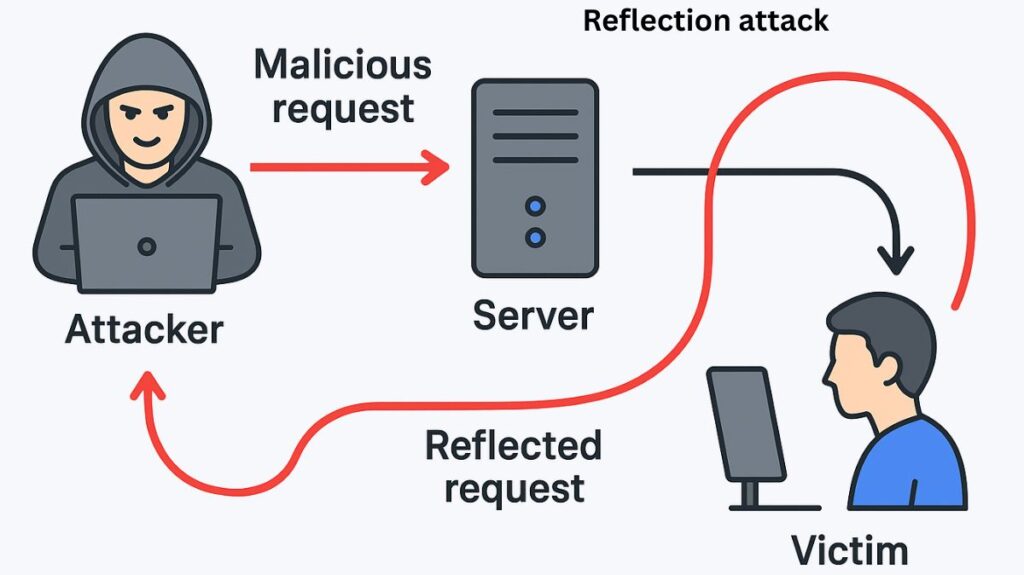
One kind of Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attacks is called a reflection attack, which uses a third-party server, referred to as a “reflector,” to overload a target victim with traffic. To put it simply, the attacker makes the intended victim see the attack traffic “reflected” off of trustworthy servers.
Because it frequently makes use of trustworthy protocols and servers, it can be hard to tell the malicious traffic from the typical intended victim, making this attack complex to defend against.
Because it frequently makes use of trustworthy protocols and servers, it can be hard to detect malicious traffic from legal network traffic, making this attack complex to protect against.
Also Read About Difference Between DoS Vs DDoS Attack, Types & Advantages
How a Reflection Attack Works (DDoS Context)
The Attacker, the Reflector, and the Victim are the three primary parties involved in the attack. The procedure makes use of IP spoofing, usually taking use of services that will reply to requests from anybody, like those that use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Spoofing: In order to make packets appear to come from the target (the victim), the attacker (the malicious actor) forges the source IP address.
Request to Reflector: Several genuine, openly accessible servers, referred to as Reflectors, receive these spoof requests from the attacker. Reflector servers are frequently weak servers that are set up to answer queries and operate services like DNS, NTP, or CLDAP.
The Reflection (Deluge): The Reflector server evaluates the request and replies to the forged source IP address (the Victim), assuming the request came from the Victim’s IP address.
Overwhelm: When a victim receives a lot of unsolicited responses, their network connection may become overloaded, making it difficult for them to access the Internet or other network resources.
The Benefits of Reflection Attacks
Reflection attacks are successful and challenging to prevent for a number of main reasons:
Anonymity: By employing a fake IP address, the attacker conceals their genuine identity. It will be challenging to determine the attacker’s actual origin because the victim’s server logs will only display traffic from the authentic reflector servers.
Obscuring the Attack: The attack traffic is composed of replies from authentic servers, which makes it difficult for network security systems to tell it apart from real traffic.
Distributed Nature: The attacks uses a large number of reflector servers, which disperses the traffic source and makes blocking it more difficult.
Also Read About NTP Server Configuration And How Does NTP Server Work?
How to prevent reflection attack
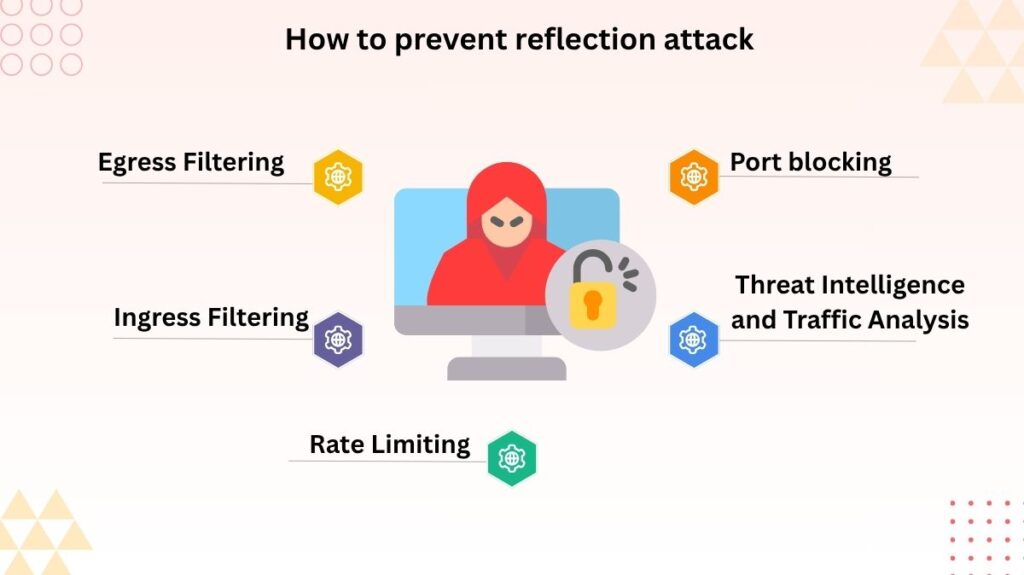
A multi-layered strategy is needed to mitigate reflection attacks:
Egress Filtering: To stop IP spoofing from their network, network service providers might employ egress filtering. They can prevent an attacker from exploiting their network to initiate a spoofing attack by verifying that outgoing packets have a legitimate source IP from within the network.
Ingress Filtering: In a similar manner, network managers can examine arriving packets using ingress filtering. A packet may be dropped if it originates from an external network but purports to be from an internal IP.
Rate Limiting: To keep a deluge of traffic from overtaxing the network, network devices can be set up to limit the quantity of requests they will accept from a single source or to a particular destination.
Port blocking: An attacker’s potential reflector count can be decreased by blocking unnecessary UDP ports. For necessary services like DNS, this isn’t always a choice.
Threat Intelligence and Traffic Analysis: Real-time attack detection and blocking can be facilitated by tools that examine traffic patterns and using threat intelligence to find known malicious IP addresses or attack signatures.
Also Read About Cisco ARP Spoofing Attack Prevention And Detection Guide
