We discussed the following topics in this blog: SNMPv3 Operational Aspects, SNMPv3 Configuration, Key Security Features, SNMPv3 Architectural Models and Components, SNMPv3 Security Levels, Other SNMPv3 Enhancements, and Importance and Context.
What is snmpv3?
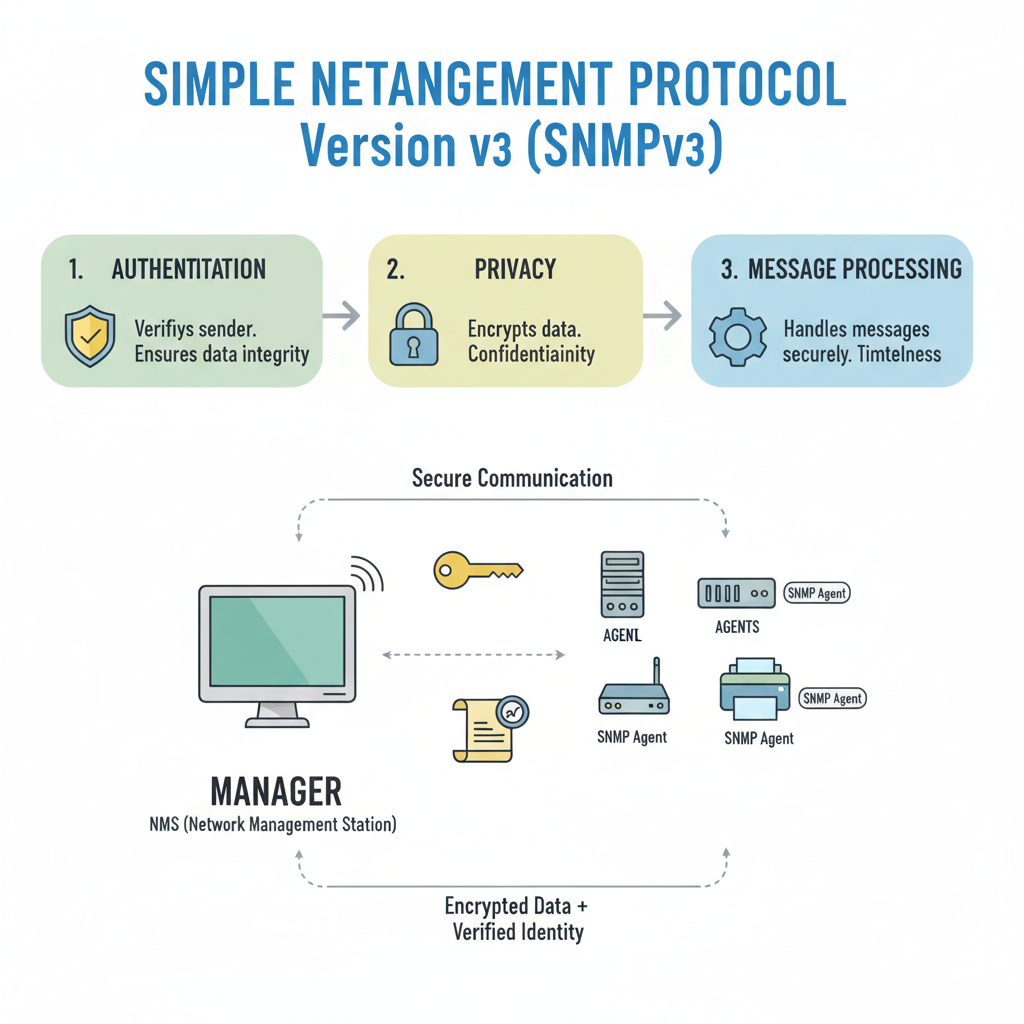
Today’s secure, standardised version of the Simple Network Management Protocol is called SNMPv3, or Simple Network Management Protocol version 3. It is an Internet Standard protocol that is used to monitor and control IP network devices such servers, printers, routers, and switches.
To fix the serious security flaws in its predecessors, SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c, namely clear-text community strings, SNMPv3 was created. By adding encryption, authentication, and cryptographic security features to all device interactions, it constitutes a significant advancement. At the greatest maturity level for an RFC, IETF declared SNMPv3 (specified by RFCs 3411–3418) to be a full Internet standard, rendering previous iterations obsolete.
Also Read About Components of MPLS, Multiprotocol Label Switching Advantages
Key Security Features
Strong security features offered by SNMPv3 guarantee tamper-proof communication and safe access. In sensitive, contemporary network contexts, these security measures are essential.
- Authentication: This feature makes sure that SNMP messages have message integrity (making sure the packet hasn’t been changed in transit) and come from a legitimate source (data origin authentication).
- A username and password are necessary for authentication, but they are never transmitted in plain text.
- It verifies the message’s identification and signs it using hashing techniques, namely HMAC-SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) or HMAC-MD5.
- Encryption (Privacy): This optional feature jumbles the payload of SNMPv3 packets, shielding information from illegal eavesdropping and snooping.
- Supported encryption methods include Triple DES (3DES), Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and Data Encryption Standard (DES) (often DES-56 in Cypher Block Chaining mode).
SNMPv3 Architectural Models and Components
The modular SNMPv3 architecture manages security and access control using particular models.
Security Models and Features
- The fundamental basis for message security is the User-based Security Model (USM). It provides privacy (encryption) features, manages users, and performs authentication (using keys produced from the Engine ID).
- By specifying which users or groups are permitted access to which particular items within the Management Information Base (MIB), the View-based Access Control Model (VACM) establishes access permissions.
Also Read About Applications Of MD5 Message Digest 5 Algorithm & Features
New Configuration Elements
Three essential new components were added to SNMPv3 to replace the inadequate community strings found in earlier iterations:
- SNMP View: A subset of the Management Information Base (MIB) that a user is allowed to view or access is defined by the SNMP View. Views are used to limit access to particular statistics, interfaces, or private data (such as device passwords).
- SNMP Group: An SNMP Group needs to be connected to an SNMP View. The Group provides the security level to be enabled during device interaction (e.g., priv) and defines the general type of access (e.g., read-only or read/write).
- SNMP User: An SNMP User is linked to an SNMP Group. The user’s username, password, and the particular encryption and authentication level (such as SHA and DES56) are specified during the configuration process, restricting their access and viewing based on the designated Group.
SNMPv3 Security
Administrators must choose a security level that determines the level of protection provided to the packets while configuring an SNMPv3 connection. Message integrity is essential to all three levels.
| Command Keyword | Security Level | Description | Protocols Used | Checks Message Integrity? | Performs Authentication? | Encrypts Messages? |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
noauth | noAuthNoPriv | No authentication and no encryption. (Not recommended) | Uses a username match for authentication. | Yes | No | No |
auth | authNoPriv | Authentication provided, but No Privacy (no encryption). | Authentication uses HMAC-MD5 or SHA. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
priv | authPriv | Authentication and Privacy (encryption) provided. (Highly Recommended) | Authentication uses HMAC-MD5 or SHA; Encryption uses DES, 3DES, or AES. | Yes | Yes | Yes |
Also Read About What is Encapsulating Security Payload and How ESP Works
Other SNMPv3 Enhancements
Inform Notifications: Introduced by SNMPv3, inform notifications function similarly to traps (asynchronous agent-to-manager notifications) but offer a confirmation mechanism. More communication dependability is provided by the SNMP manager’s requirement to confirm receipt of the Inform message.
Engine ID: Each SNMP entity is uniquely identified by SNMPv3’s Engine ID Identifier. The creation of distinct keys for message authentication and maintaining appropriate time synchronisation between entities depend on this ID.
Remote Configuration: SNMPv3 enables remote deletion, modification, configuration, and insertion of entries by allowing administrators to use SET commands for MIB objects to configure and alter the SNMP agent.
Transport Protocol: SNMPv3 allows delivery over both TCP and UDP, however SNMP messages normally use UDP (ports 161/162). Additionally, SNMPv3 can be safely transmitted via Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) or Transport Layer Security (TLS).
Operational Aspects
Transport Protocol
SNMPv3 employs both TCP and UDP, in contrast to SNMPv1, which mostly used UDP. UDP is commonly used in SNMP communications, such as Traps and Informs.
MIB Views
A subset of the Management Information Base (MIB) is defined by the MIB views concept, which is introduced in SNMPv3. This enables an administrator to restrict particular SNMP managers’ access to particular MIB sections. Unless configured otherwise using write v1default, an SNMPv3 group has read-only behaviour by default, with a read MIB view of v1default (which comprises the majority of the MIB) and no write view.
Messages
The typical SNMP message types Get, Set, and unsolicited notifications, such as Trap and Inform messages are supported by SNMPv3.
- Similar to trap messages, inform messages alert the Network Management Station (NMS) to an occurrence; however, informs also include reliability, necessitating an SNMP Response message from the NMS to confirm receipt.
- GetBulk:SNMPv2 introduced this operation, which SNMPv3 supports. It minimises the number of GET requests by enabling a host to retrieve a significant amount of data at once.
Also Read About Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol and DHCP DORA Process
SNMPv3 configuration
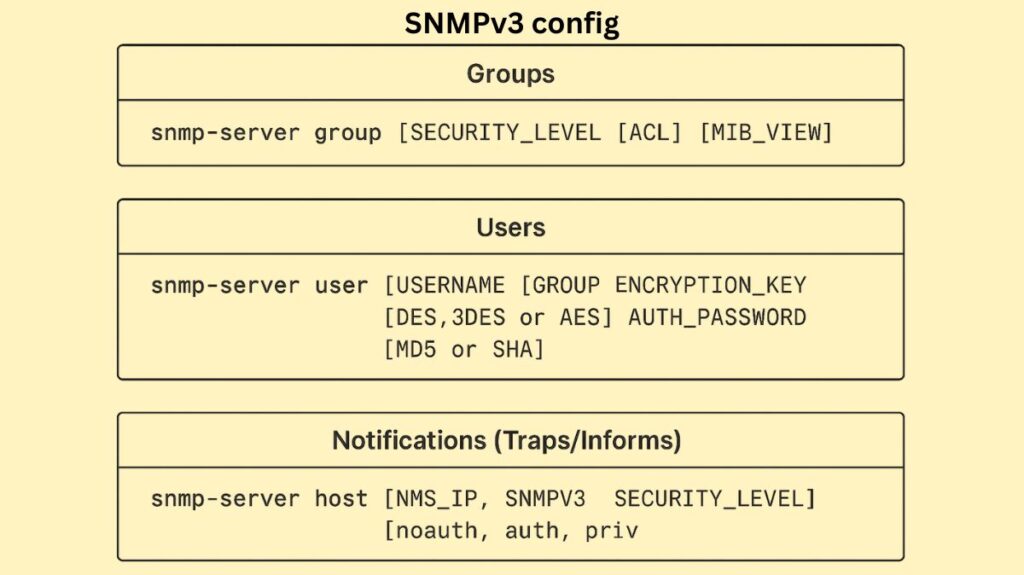
The commands used in SNMPv3 configuration are very different from those used in SNMPv1/v2c since groups and users are used in place of communities.
Groups: Groups of users with the same security settings, such as the security level (noauth, auth, or priv) and access controls (ACLs or MIB views), can be defined using the snmp-server group command.
Users: The snmp-server user command links users to a specified SNMP group by defining the username, the encryption key (using DES, 3DES, or AES), and the authentication password (using MD5 or SHA).
Notifications (Traps/Informs): The snmp-server host command provides the NMS IP address, SNMPv3 version, security level, and related username in order to transmit notifications.
Importance and Context
An SNMP manager (NMS) and SNMP agents (controlled devices such as switches and routers) can communicate using a standardised message format thanks to the application layer protocol known as SNMP. Network administration tasks such as querying, performance and status monitoring (e.g., CPU utilization), statistics compilation, and occasionally device reconfiguration are all done with SNMP.
SNMPv1 and SNMPv2c are seen as security threats since they employ community strings, or clear-text passwords. Because of its improved security features, SNMPv3 is advised when SNMP capability is needed on a network.
The usage of SNMPv3 is especially mentioned as a measure for security on the administration plane, which is in charge of protocols used by administrators (such as SSH and SNMP), frequently in conjunction with Secure Shell (SSH) and Authentication, Authorisation, and Accounting (AAA).
