Wireless Wide Area Network WWAN
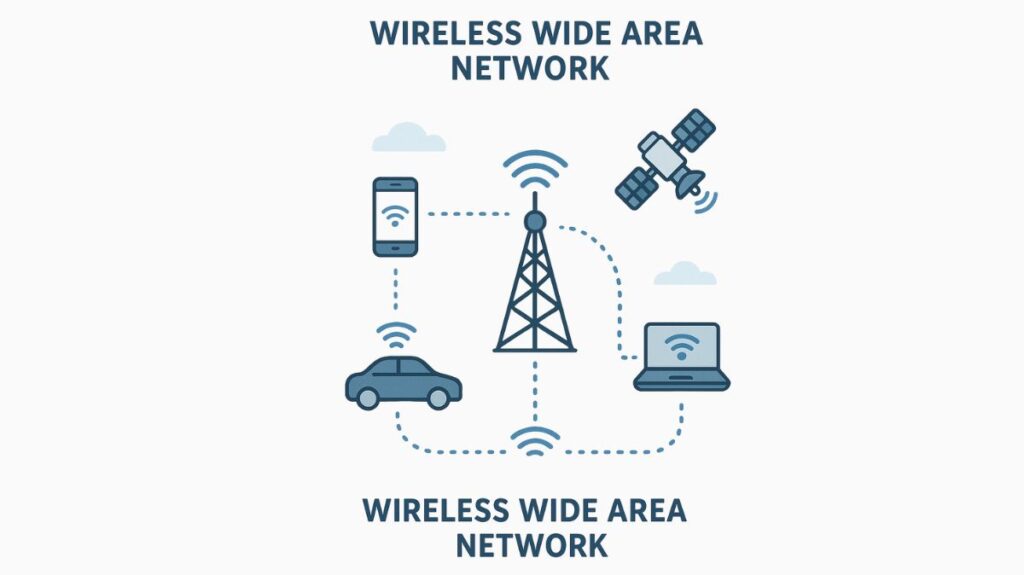
A Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) is a kind of wireless network that uses cellular technology and often spans a very broad geographic area. A Wide Area Network (WAN) serves as the foundation for WWAN.
Users can use the network without a physical cable connection. It’s the ability to send data via wireless signals over great distances, including cities, countries, regions, and even the entire world.
You can also read Wireless Metropolitan Area Networks, Applications & Benefits
Core Technology and Function
Mobile telephony cellular network technologies are the foundation for WWAN capability. These technologies enable wide-area device connections to networks, including the internet.
Important WWAN technologies consist of:
- 2G/3G Networks: Early WWAN development phases include 2G and 3G networks, which mainly offer SMS, voice calls, and basic mobile internet browsing.
- 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution): High-definition video playback and big file downloads are made possible by 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution), a leading WWAN technology that dramatically enhanced bandwidth rates (up to hundreds of Mbps).
- 5G Networks: With far faster transmission speeds (theoretical peaks of several Gbps), lower latency, and better connection density, this next-generation standard offers the quickest and most dependable WWAN technology to date.
- Satellite Links/Communication: These technologies, which may include VSAT (Very Small Aperture Terminal), are used to provide connectivity, particularly in places where cable and DSL are not available.
- GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) and CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access): These were the two main cellular transmission technologies used in earlier systems (2G and 3G).
WWANs rely on public cellular networks to provide internet broadband connectivity for companies. They can also serve as a useful backup for primary wired internet connections, taking over right away in the event that a fiber link goes down.
Key Components
A WWAN requires the following devices and infrastructure:
- Mobile Terminals/User Equipment (UE): Devices with integrated wireless WAN access features, such as laptops, tablets, smartphones, mobile routers, and Internet of Things devices. The necessary wireless communication modules (such as 4G or 5G modules) are present in these devices.
- Base Station (BTS)/Cellular Network: Cellular networks and base stations (BTSs) are crucial pieces of infrastructure that enable data transmission by sending and receiving wireless signals to and from mobile devices.
- SIM Card: A SIM card is a tiny chip that holds identity data specific to the person, such as IMSI. The network operator can ascertain whether a user is authorized to access WWAN services by using the SIM card to authenticate the user.
- Modem/Router: Devices that link computers to wireless networks so that data can be transferred and received are known as modems and routers.
You can also read What Is WPA Shared Key? Advantages of Shared key In Network
Comparison with Other Network Types
WWAN is distinguished from other network types primarily by its range and the technology it uses:
| Network Type | Full Name | Typical Coverage Area | Primary Technology |
|---|---|---|---|
| WAN | Wide Area Network | Large geographic area (city, country, globe) | Primarily wired communication lines |
| WWAN | Wireless Wide Area Network | Broad areas (cities, regions, countries, worldwide) | Cellular (4G LTE, 5G) |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network | Local area (e.g., home, office, campus, up to 100 meters) | Wi-Fi (IEEE 802.11) |
| WPAN | Wireless Personal Area Network | Very short range (e.g., within a single room, up to 10 meters) | Bluetooth, NFC |
Unlike WLAN and WPAN, which cover smaller, confined areas, WWAN’s wider coverage makes it suitable for larger geographical areas.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- High mobility and flexibility: WWAN is perfect for people who travel or work remotely since it allows users to access the network from anywhere at any time, as long as they are within its service area.
- Broad coverage: WWAN can offer wireless coverage throughout regions, cities, villages, and even the entire world.
- Convenient deployment: Compared to traditional wired options, deployment is comparatively quick and easy since wireless technology eliminates the need for extensive wired communication links.
- Cost-effectiveness: WWAN often requires less equipment and maintenance than wired networks, making it potentially more affordable than deploying physical cables, particularly in remote areas.
Disadvantages
- Signal affected by the environment: Unstable networks can result from environmental influences such as inclement weather, shifting topography, or obstructions in buildings (such as a basement or lift).
- Limited network capacity: Multiple people accessing a network at once can cause congestion and slower speeds in places with high user density, such as big retail malls.
- Higher data transmission cost: WWAN frequently has a higher cost of data transmission than wired networks, especially when sending big volumes of data (such as streaming HD video).
- Security concerns: Although WWANs usually use authentication and encryption techniques, they might still be susceptible to security threats, just like other wireless technologies.
You can also read What Is A WPA2 PSK Key? And How Does WPA2 PSK Work?
