What is cross chain interoperability?
The capacity of various blockchain networks to interact, exchange information, and carry out transactions with one another is known as cross-chain interoperability. By facilitating the movement of resources, information, and communications between different blockchain ecosystems, it makes the decentralized network more effective and integrated.
(Or)
Multiple blockchain networks can connect, exchange data, and transact through cross-chain interoperability. Blockchain networks have fragmented the decentralized web as autonomous entities. Cross-chain functionality facilitates blockchain ecosystem collaboration.
Also Read About Blockchain Digital Signatures: Immutable And Verifiable
Need Cross-Chain Capabilities
The blockchain landscape is fragmented as a result of the rise of multiple blockchain efforts, each with its own platforms and data collection techniques. Although distinct blockchain networks provide security and uniformity within their respective ecosystems, mass adoption and the completion of transactions across various networks are hampered by their incapacity to interact.
Thus, cross-chain solutions are essential for:
- Reducing Fragmentation: They stop distinct dApp instances from being isolated collections of smart contracts and link disparate on-chain settings.
- Free asset flow between networks boosts capital efficiency and liquidity, enabling growth and investment.
- Promoting Innovation: Blockchain networks enable more complicated and innovative decentralized app development.
- Enhancing User Experience: It gives users a more unified and integrated experience by doing away with the need for middlemen and intricate bridging techniques.
- Integrating current Web2 infrastructure with Web3 services requires bridging Web2 and Web3.
The Mechanisms and Operation of Cross-Chain Technology
Cross-chain solutions usually entail relaying the ensuing transaction to a destination blockchain after verifying the state of a source blockchain. To make this contact easier, a number of technologies and mechanisms have been created or suggested:
Cross-chain bridges
The exchange of tokens, assets, and data is made possible by “cross-chain bridges” across blockchain networks. Examples are Polygon Portal and Avalanche Bridge. Bridges usually mint or unlock tokens on the destination chain and lock or burn them on the source chain.
Atomic Swaps
Consumers can directly transfer cryptocurrency across blockchains without a middleman. Smart contracts, which guarantee simultaneous execution on both chains and prevent either side from breaking the agreement, are used to do this.
Sidechains
These are blockchain networks that operate in parallel and are bridged to the main network. Through a two-way peg, they can function with various consensus methods and attain a higher transaction throughput, allowing for quicker, possibly less secure transactions that are nevertheless protected by the security of the main blockchain. Ethereum’s Plasma and Bitcoin’s Liquid Network are two examples.
Relaychain
Polkadot’s architecture uses parachains, parallel chains that work with a “Relaychain”. The Relaychain manages security, consensus, and cross-chain interoperability, allowing parachains to share tasks and message each other.
Token transfers, smart contract execution, and data sharing across interconnected “zones” (blockchains) are all made possible by the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) Protocol, which is utilized in the Cosmos network.
Layer 2 Solutions
By outsourcing transaction processing off-chain and subsequently writing results back to the main chain, these solutions incorporate cross-chain ideas, albeit mostly for scalability. Among the examples are:
- State channels, such as Ethereum’s Raiden network and Bitcoin’s Lightning Network, enable off-chain interaction for numerous transactions while only reporting the final result to the main ledger.
- ZK-Rollups and Optimistic Rollups combine off-chain transactions into one main chain transaction.
Hyperledger Sawtooth
Hyperledger Sawtooth integrates with various blockchain technology. For example, its seth project makes it possible to implement smart contracts based on Ethereum Virtual Machines (EVMs) on Sawtooth.
Zones
Cosmos uses the Hub and Spoke Architecture paradigm, which links several “zones” (blockchains) to a central “hub” that controls trust and verifies transactions between zones, enabling scalable connectivity.
Notary Schemes
Although they include centralization, these schemes rely on reliable third parties (notaries) to allow transactions between blockchain networks, providing a workable option for interoperability in certain situations.
Oracles
These allow smart contracts to access real-world data by bridging the gap between off-chain and on-chain data sources. Chainlink and other decentralized oracle services guarantee the accuracy and dependability of this data.
Blockchain routers
These serve as go-betweens to create safe pathways for the exchange of data and value between various blockchain networks.
Cross chains interoperability benefits
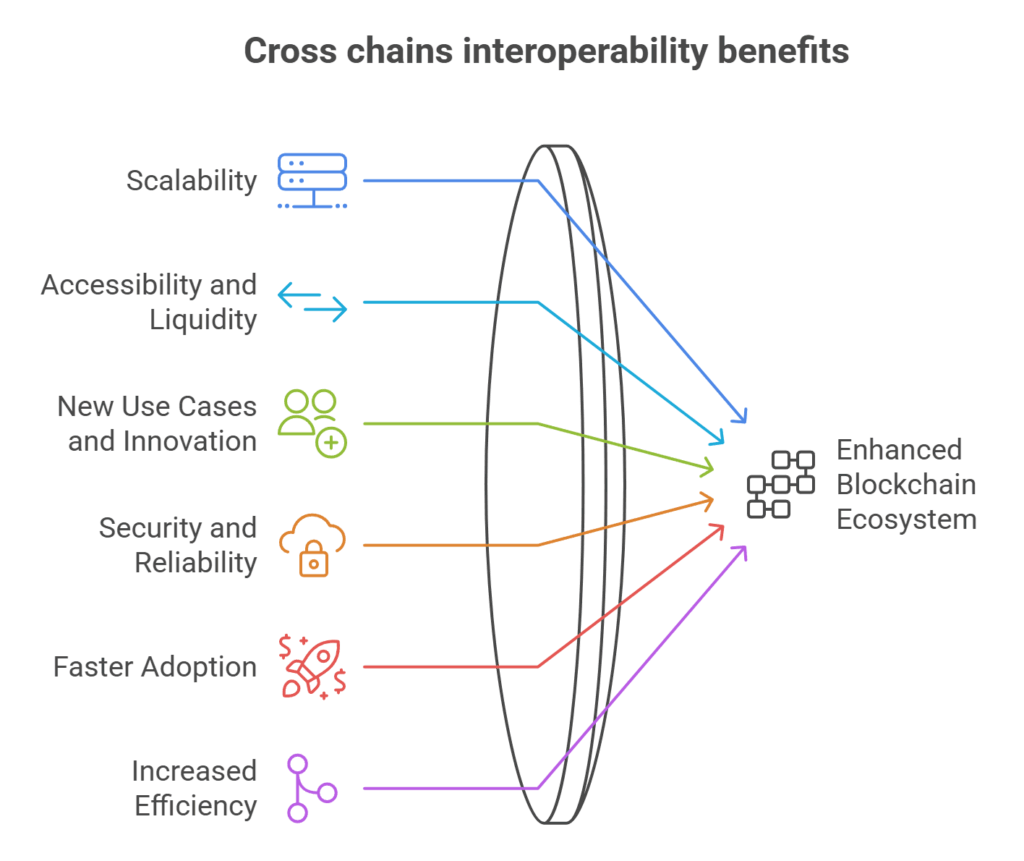
Interchain interoperability benefits blockchain ecosystem:
- Scalability: Interoperability spreads transactions across several chains, clearing network congestion and improving efficiency.
- Accessibility and Liquidity: Assets flow easily between networks, increasing trade.
New Use Cases and Innovation: Complex dApps can use many blockchain networks. - Removal of centralized exchanges and middlemen improves transaction security and reduces counterparty risk.
- Secure and Dependable Operations: CCIP protocols use risk management networks to ensure transaction integrity.
- When cross-chain interactions are secure and straightforward, blockchain technology can be adopted faster across industries.
- Increased Efficiency: It streamlines operations by enabling data exchange and interoperable transactions, reducing unnecessary effort, and optimizing resources.
- Improvements in connectivity make data exchange and communication easy, increasing blockchain ecosystem cooperation and synergy.
Also Read About Blockchain Digital Signatures: Immutable And Verifiable
Cross-chain interoperability drawbacks
Cross-chain interoperability has despite its drawbacks:
- Security: Given that bridge breaches have resulted in the loss of over $2 billion, it is critical to ensure the security of cross-chain transactions. Funds may be at risk due to communications systems’ inadequate security.
- Standardization: Interactions between various blockchain protocols may become more difficult if they are not standardized.
- Complexity: Cross-chain transactions can be intricate, necessitating thorough evaluation of petrol prices, security, and other aspects.
- Blockchain networks may struggle to balance trust model and security protocol variations while maintaining security and decentralization.
- Inconsistent governance structures and consensus methods may make data immutability difficult in interoperable blockchain-based systems.
- Blockchain networks need strong interoperability standards and solutions to decentralize and safeguard data.
- Legal and regulatory compliance hampers blockchain interoperability, especially for cross-border transactions and data exchange. Industry, legislators, and regulators must establish clear frameworks and standards to minimize regulatory ambiguities, compliance requirements, and jurisdictional issues that limit interoperable solutions.
- Finality: To avoid reversed transactions, source chain money must be accessible on the destination chain.
Cross-chain applications
Chainlink’s CCIP is a popular cross-chain solution. This open-source, blockchain-neutral standard secures token transfers and arbitrary messages between chains. CCIP aims to connect blockchain networks with a single interface to enable complicated cross-chain applications and interactions.
CCIP’s salient characteristics and security improvements include:
Defense-in-depth Security
Chainlink oracle networks, a tried-and-true standard that has secured tens of billions of dollars and enabled over $18 trillion in onchain transaction value, power CCIP, which is constructed with battle-tested security.
Risk management network
An autonomous network of nodes that continuously analyses, identifies, and reduces risks to guarantee dependable and secure operations is known as a risk management network.
Cross-Chain Tokens (CCTs)
With self-serve deployment features, complete control and ownership, improved programmability, and zero-slippage transfers, CCIP enables developers to implement cross-chain-native assets. An easy-to-use interface for managing CCTs is offered by the CCIP Token Manager.
Flexibility and Developer Control
Token developers maintain complete control over their pools, contracts, and unique implementation logic, including rate limitations.
Programmable Token Transfers
Upon arrival, users can do operations like swapping or staking by sending tokens and use instructions to a receiving smart contract on a separate blockchain.
Arbitrary Messaging
By sending arbitrary data (encoded as bytes) between smart contracts on various blockchains, developers can construct cross-chain native applications.
Robust Development
Prominent authorities in computer security and cryptography are assisting in the development of CCIP.
Who Gains from Interoperability cross Chains?
Several parties benefit from chain interoperability:
- Consumers gain asset flexibility and control from cross-chain interoperability. They can use decentralized apps, diversify their holdings, and swiftly shift tokens between blockchain networks.
- Developers: Cross-chain interoperability allows developers build native dApps for several smart contracts and blockchains.
- Streamlining asset transfers and data exchanges enhances supply chain management, facilitates cross-border payments, optimizes operations, reduces expenditures, and improves market access.
- Ecosystem: Interoperability strengthens blockchain. Promoting network and project cooperation boosts industry innovation and acceptance.
Future cross-chain compatibility
Blockchain technology needs cross-chain interoperability to strengthen and combine decentralized networks. Polkadot and Cosmos facilitate communication. To fully utilize blockchain technology and promote broader usage, ongoing efforts to resolve issues and develop interoperable solutions are crucial.
