This blog discusses ICMP attacks, including what they are, how they works, ICMP attacks types, further ICMP exploits, and how to prevent them.
What is ICMP attack?
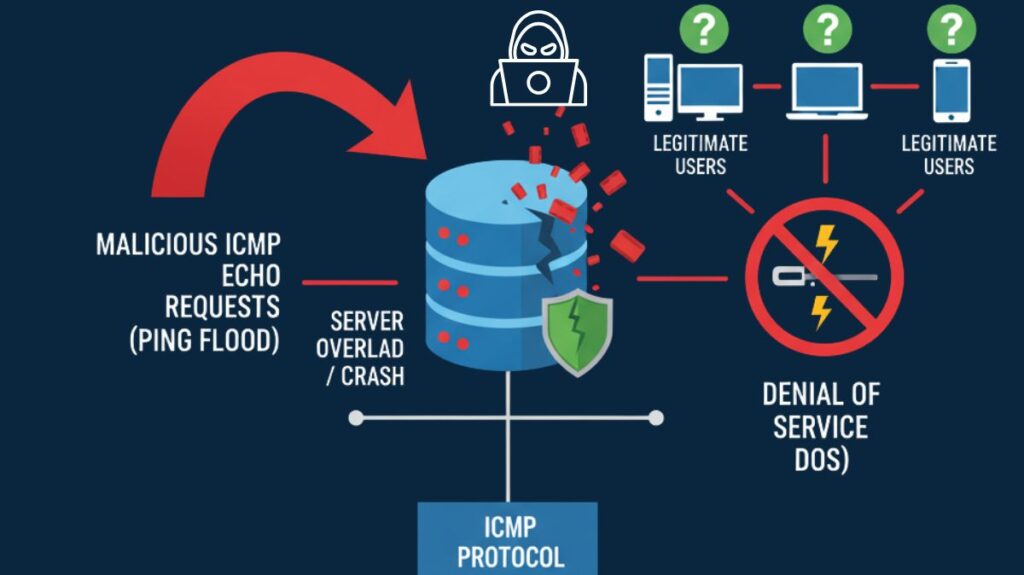
A type of denial-of-service (DoS) or distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks known as an ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) attack takes use of the ICMP protocol, which is mostly used for network fault reporting and diagnostics, including the tools ping and traceroute. Attackers misuse this protocol to evade security measures, conduct reconnaissance, or interfere with network functions.
In order to cause a denial of service, the basic objective of ICMP attack is to bombard a target with ICMP packets, overloading its CPU, memory, and bandwidth and prohibiting it from providing services to authorised users.
How ICMP Attacks Work?
Because ICMP is typically trusted for network troubleshooting, ICMP attacks typically operate by exhausting resources.
Target Identification: The target network or device is identified by the attacker. Attackers can use external programs to expose the target’s IP address (Blind ping), target a single computer on a local network (Targeted local exposed), or disrupt communications by using routers (Router leaked).
Traffic Generation: To create a huge flood of ICMP packets aimed at the target, the attacker employs a variety of strategies, frequently using botnets or specifically constructed packets.
Processing Overhead: The target rapidly uses up its computer resources and network bandwidth in an effort to process the large number of ICMP queries and produce responses, or echo-replies.
Denial of Service: When a target’s resources run out, it stops responding to valid requests, which causes service interruption.
Although contemporary botnet attacks frequently rely on a vast network of unspoof bots to overload capacity, attackers occasionally use spoofing (fabricated source IP addresses) to conceal their identity or reroute traffic.
Also Read About Source Network Address Translation SNAT, how does snat work
ICMP Attacks Types
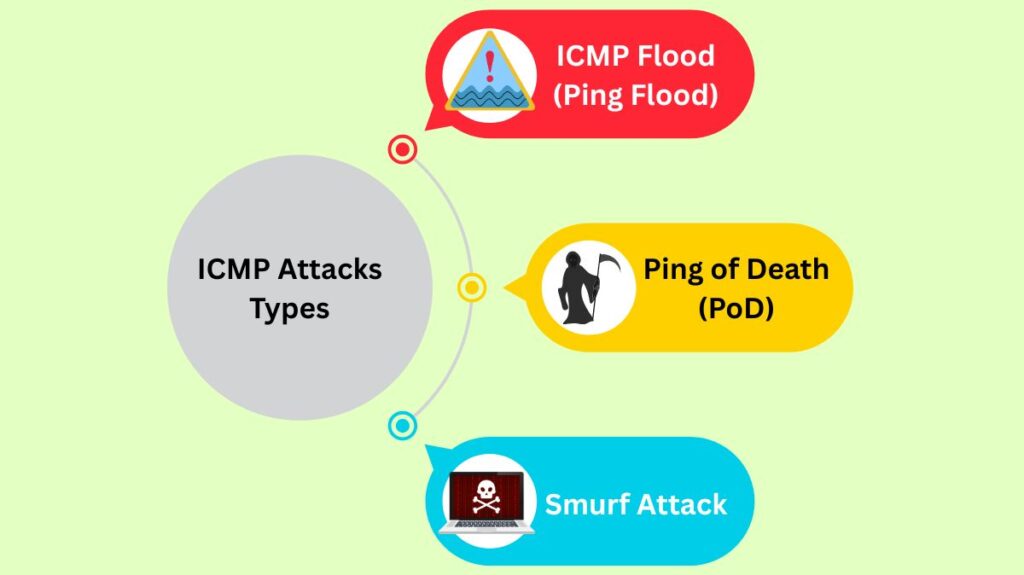
The goal of the most prevalent ICMP attacks is to overload the target’s capacity:
| Attack Type | Mechanism | Effect | Context |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICMP Flood (Ping Flood) | An attacker sends a massive volume of ICMP echo-request (ping) packets to the target. The target is forced to process each request and send an echo-reply, exhausting its resources. | Slows down or crashes the system. When launched from multiple compromised systems, it becomes a DDoS attack. | This is a volumetric attack; the damage is proportional to the number of requests made. It overwhelms both incoming and outgoing network channels. |
| Ping of Death (PoD) | The attacker sends a malformed or oversized ICMP packet, larger than 65,535 bytes. The packet is fragmented en route. | When the target attempts to reassemble the oversized packet, a buffer overflow occurs, leading to a system crash, freeze, or reboot. | This is a legacy/historic attack that exploited older systems (e.g., Windows 95/NT, Linux, Unix). Most modern systems have built-in protections against it. |
| Smurf Attack | This is an amplification attack. The attacker spoofs the victim’s IP address in an ICMP echo-request and sends it to a network’s broadcast address. | All devices on that network receive the request and reply to the victim’s spoofed IP, flooding the victim with a deluge of unwanted traffic. | This attack was widely used in the 1990s but is less common today because modern network configurations typically prevent IP broadcasting. |
Additional ICMP Exploits
Additionally, ICMP can be used for more specific objectives:
- Man-in-the-Middle attacks can be employed by exploiting ICMP Redirect packets to change the victim’s routing table and reroute traffic via a hostile server.
- Because ICMP is frequently allowed for diagnostic purposes, attackers use ICMP tunnelling to get around firewalls by encapsulating malicious traffic inside ICMP packets.
- Large ICMP packets are divided into smaller ones in an ICMP fragmentation attack, which forces the targeted system to expend too much energy on reassembly and may cause instability.
ICMP attack prevention
A multi-layered network security strategy is necessary to stop ICMP attacks:
- Firewall Rules and Filtering: Set up your firewall to either filter or prevent external ICMP traffic. Rate restriction is another technique you may use to restrict how many ICMP echo requests a system can handle in a second.
- Rate Limiting: Put rules in place to restrict how many ICMP packets or echo requests a system may handle in a second. Another solution is to restrict the maximum size of ping queries that can be sent.
- Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): To keep an eye on network traffic for unusual trends, like an abrupt increase in ICMP traffic. Administrators can be warned about possible threats or have attacks automatically blocked by these methods.
- Network Monitoring: To create a baseline, routinely check network traffic; anomalies, like an unusually high volume of ICMP packets, may indicate an attack.
- Disabling ICMP: To stop all ICMP-based attacks on non-critical systems, ICMP capabilities must be fully disabled. But this also makes it impossible to use diagnostic tools like traceroute and ping, which makes network troubleshooting more difficult.
- Patching and Updates: Patching the Ping of Death and other older vulnerabilities is made easier by applying regular updates.
- DDoS Mitigation Services: Bigger companies use expert services to filter malicious traffic before it enters the network, reducing the volume of attacks.
- Ingress/Egress Filtering: Use ingress/egress filtering to stop fake IP packets from getting into or out of the network.
- Preventing Smurf Attacks: Set up routers to turn off directed broadcast requests.
Also Read About SMS Phishing Tutorial: SMS Phishing Detection And Defense
