Layer 2 Switches

According to the OSI model, a Layer 2 Switches is a network device that functions at the Data Link layer, or Layer 2. Data frame forwarding between devices connected to the same local area network (LAN) is its main duty. A Layer 2 Switches learns which device is connected to which port so that packets are sent only to the intended destination, decreasing traffic, in contrast to a hub that overloads the network with data packets.
How does Layer 2 Switch Work
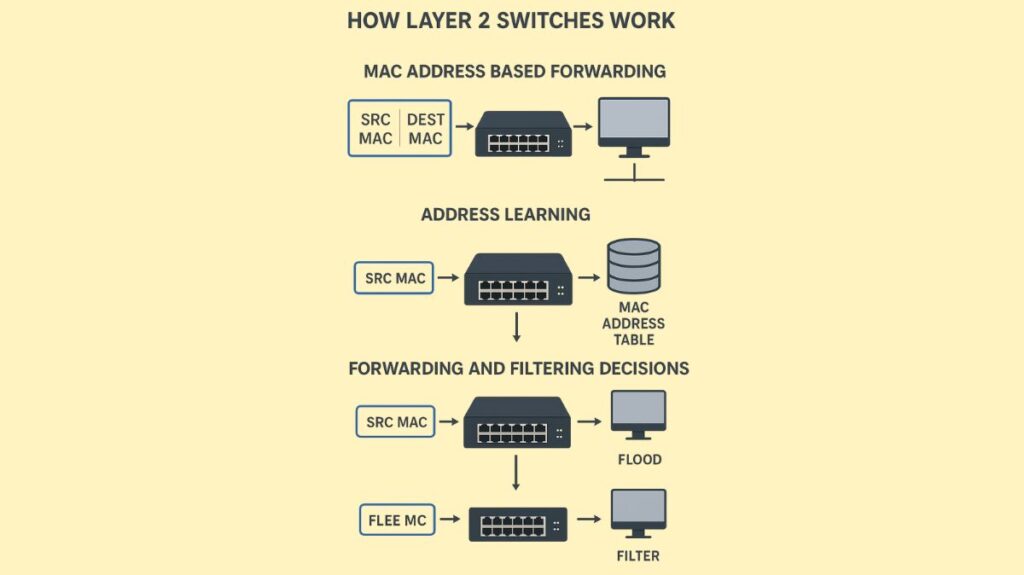
MAC Address Based Forwarding: Information packets or frames are directed by Layer 2 switches using MAC addresses (Media Access Control addresses). Both the source and the destination MAC addresses are present in every data frame.
Address Learning: The switch stores the source MAC address of the incoming frame, together with the port number it originated from, in its MAC address database (also called a CAM table or filter table) when a data frame reaches a switch port. The switch “learns” the location of devices in this way. The switch may first flood the network, much like a hub, to fill its MAC address table if a MAC address is unknown.
Forward/Filter Decisions: Upon receiving a frame intended for a particular MAC address, the switch looks for the address in its MAC address table.
- In order to ensure smooth traffic flow and reduce collisions, the switch only transfers the frame to the appropriate output port if the destination MAC address is detected.
- The switch will send the frame out to all ports except the one it received it from in order to “flood” it if the destination MAC address cannot be detected, which indicates that the device has not yet communicated or that its entry has expired. The MAC address of the destination device will be discovered and entered into the table as soon as it responds.
- Frames on the correct segment will not be advanced if the source and destination are on the same port. This is known as frame filtering.
You can also read Advantages And Disadvantages Of IPv4 & IPv4 Packet Structure
Layer 2 Switch Features
MAC Address Table: Necessary to determine the connected device’s MAC address and port number, allowing for proper frame direction.
VLAN Support: Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs), which generate smaller broadcast domains and enable network segmentation at this layer, are supported by a large number of Layer 2 switches.
Collision Domain Segmentation: By allocating specific network segments or distinct collision zones for every port (microsegmentation), Layer 2 switches reduce collisions and enhance network performance. Comparing this to older technology like hubs, there is a noticeable improvement.
Broadcast Domains: Broadcast domains are not divided by Layer 2 switches by default; instead, any device linked to a Layer 2 switch is in the same broadcast domain. Nonetheless, as previously stated, VLANs can be utilized to establish more compact broadcast domains at Layer 2.
Hardware-Based Switching: When compared to traditional software-based bridges, modern Layer 2 switches are more faster and offer lower latency thanks to the widespread usage of Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) for high-speed frame forwarding.
Full-Duplex Communication: Because of their full-duplex communication capabilities, devices can send and receive data at the same time.
Loop Avoidance: In redundant network topologies, Layer 2 switches employ protocols such as Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) and Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) to identify and stop loops by putting some connections in sleep mode.
You can also read Advantages and Disadvantages of Ethernet, Wi-Fi VS Ethernet
Advantages of Layer 2 Switch
Fast Forwarding/Low Latency: Hardware-based switching and the elimination of the need to examine higher-layer data allow them to forward frames rapidly.
Efficient: More effective than hubs as they don’t transmit extraneous content.
Improved Network Performance: Through collision domain segmentation, network performance can be improved and congestion can be decreased.
Cost-Effective: Generally economical in LAN settings.
No Data Modification: They are faster because they only alter the frame encapsulation, not the data packet.
Disadvantages of Layer 2 Switches
No Inter-Network Routing: A router or Layer 3 switch is needed to forward traffic between networks or subnets, which they are unable to do.
Limited to MAC Addressing: They solely use MAC addresses; they don’t do IP routing.
Broadcast Storm Vulnerability: Should they be improperly maintained (for example, without VLANs), they might be susceptible to broadcast storms.
Scalability: They are not well suited for very big, scalable networks that need to distinguish across networks instead of just hosts since they do not automatically divide broadcast domains.
You can also read Advantages Of Network Address Translation NAT And Types
Operational Aspects and Management
Memory Buffering: Frames are momentarily stored by switches in a memory buffer that all ports can share.
Forwarding Methods: They can employ a variety of forwarding techniques, such as store-and-forward switching (greater latency, conducts CRC for data integrity), cut-through switching (low latency, no error checking), and fragment-free mode (cut-through variant with some error checking).
Management Features: Command-Line Interface (CLI) configuration options are available on managed Layer 2 switches. EtherChannel (bundling links for enhanced bandwidth and redundancy), administrative state, port security (limiting MAC addresses per port), speed and duplex tuning, and more are features. Access port management is also frequently accomplished with STP capabilities like PortFast and BPDU Guard.
Security: They can be a component of security tactics like DHCP snooping, 802.1X authentication, and remote management over SSH or Telnet.
Role in Modern Networks
- In multi-tier campus LAN systems, Layer 2 switches often lie at the access layer, connecting end devices to the network.
- By forwarding frames according to destination MAC addresses, Layer 2 switches in Software-Defined Networking (SDN) contribute to the data plane.
- They can connect to servers (leaf switches) and have high-bandwidth uplinks to spine switches in data centre designs, forming a spine-leaf architecture.
In a LAN, a Layer 2 switch serves as an intelligent traffic controller that routes data according to MAC addresses to provide quick and effective communication between devices connected to the same network.
You can also read What Is DNAT Destination Network Address Translation? Uses
